J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2018 Nov;61(6):716-722. 10.3340/jkns.2017.0275.
Contribution of Lateral Interbody Fusion in Staged Correction of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA. Vedat.Deviren@ucsf.edu
- KMID: 2428113
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0275
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
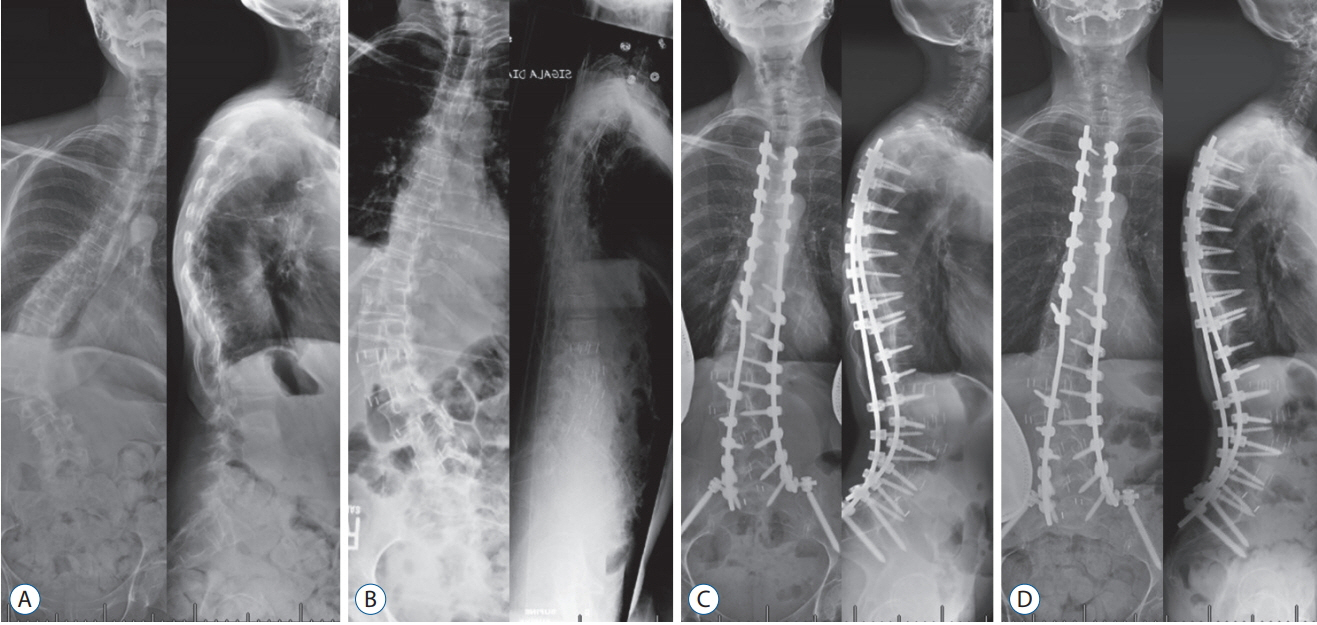
Lateral interbody fusion (LIF) is attractive as a less invasive technique to address anterior spinal pathology in the treatment of adult spinal deformity. Its own uses and benefits in treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis are undefined. To investigate the radiographic and clinical outcomes of LIF, and staged LIF and posterior spinal fusion (PSF) for the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis patients, we analyzed radiographic and clinical outcomes of adult degenerative scoliosis patients who underwent LIF and posterior spinal fusion.
METHODS
Forty consecutive adult degenerative scoliosis patients who underwent LIF followed by staged PSF at a single institution were retrospectively reviewed. Long-standing 36" anterior-posterior and lateral radiographs were taken preoperatively, at inter-stage, 3 months, 1 year, and 2 years after surgery were reviewed. Outcomes were assessed through the visual analogue scale (VAS), 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36), and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI).
RESULTS
Forty patients with a mean age of 66.3 (range, 49-79) met inclusion criteria. A mean of 3.8 levels (range, 2-5) were fused using LIF, while a mean of 9.0 levels (range, 3-16) were fused during the posterior approach. The mean time between stages was 1.4 days (range, 1-6). The mean follow-up was 19.6 months. Lumbar lordosis was significantly restored from 36.4º preoperatively up to 48.9º (71.4% of total correction) after LIF and 53.9º after PSF. Lumbar coronal Cobb was prominently improved from 38.6º preoperatively to 24.1º (55.8% of total correction) after LIF, 12.6º after PSF respectively. The mean pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis mismatch was markedly improved from 22.2º preoperatively to 8.1º (86.5% of total correction) after LIF, 5.9º after PSF. Correction of coronal imbalance and sagittal vertebral axis did not reach significance. The rate of perioperative complication was 37.5%. Five patients underwent revision surgery due to wound infection. No major perioperative medical complications occurred. At last follow-up, there were significant improvements in VAS, SF-36 Physical Component Summary and ODI scores.
CONCLUSION
LIF provides significant corrections in the coronal and sagittal plane in the patients with adult degenerative scoliosis. However, LIF combined with staged PSF provides more excellent radiographic and clinical outcomes, with reduced perioperative risk in the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Acosta FL, Liu J, Slimack N, Moller D, Fessler R, Koski T. Changes in coronal and sagittal plane alignment following minimally invasive direct lateral interbody fusion for the treatment of degenerative lumbar disease in adults: a radiographic study. J Neurosurg Spine. 15:92–96. 2011.
Article2. Aharinejad S, Bertagnoli R, Wicke K, Firbas W, Schneider B. Morphometric analysis of vertebrae and intervertebral discs as a basis of disc replacement. Am J Anat. 189:69–76. 1990.
Article3. Amin BY, Mummaneni PV, Ibrahim T, Zouzias A, Uribe J. Four-level minimally invasive lateral interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus. 35(2 Suppl):Video 10. 2013.
Article4. Anand N, Baron EM, Khandehroo B, Kahwaty S. Long-term 2- to 5-year clinical and functional outcomes of minimally invasive surgery for adult scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:1566–1575. 2013.
Article5. Anand N, Baron EM, Khandehroo B. Is circumferential minimally invasive surgery effective in the treatment of moderate adult idiopathic scoliosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 472:1762–1768. 2014.
Article6. Baghdadi YM, Larson AN, Dekutoski MB, Cui Q, Sebastian AS, Armitage BM, et al. Sagittal balance and spinopelvic parameters after lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative scoliosis: a case-control study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:E166–E173. 2014.7. Benner B, Ehni G. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 4:548–552. 1979.
Article8. Berjano P, Lamartina C. Far lateral approaches (XLIF) in adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J 22 Suppl. 2:S242–S253. 2013.
Article9. Berven SH, Deviren V, Smith JA, Hu SH, Bradford DS. Management of fixed sagittal plane deformity: outcome of combined anterior and posterior surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 28:1710–1715. discussion 1716. 2003.
Article10. Birknes JK, White AP, Albert TJ, Shaffrey CI, Harrop JS. Adult degenerative scoliosis: a review. Neurosurgery. 63(3 Suppl):94–103. 2008.11. Caputo AM, Michael KW, Chapman TM, Jennings JM, Hubbard EW, Isaacs RE, et al. Extreme lateral interbody fusion for the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis. J Clin Neurosci. 20:1558–1563. 2013.
Article12. Castro C, Oliveira L, Amaral R, Marchi L, Pimenta L. Is the lateral transpsoas approach feasible for the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 472:1776–1783. 2013.
Article13. Dakwar E, Cardona RF, Smith DA, Uribe JS. Early outcomes and safety of the minimally invasive, lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach for adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus. 28:E8. 2010.
Article14. Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Coonrad RW. Degenerative adult onset scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 13:241–245. 1988.
Article15. Isaacs RE, Hyde J, Goodrich JA, Rodgers WB, Phillips FM. A prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter evaluation of extreme lateral interbody fusion for the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis: perioperative outcomes and complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35(26 Suppl):S322–S330. 2010.16. Johnson RD, Valore A, Villaminar A, Comisso M, Balsano M. Pelvic parameters of sagittal balance in extreme lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disc disease. J Clin Neurosci. 20:576–581. 2013.
Article17. Khajavi K, Shen AY. Two-year radiographic and clinical outcomes of a minimally invasive, lateral, transpsoas approach for anterior lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 23:1215–1223. 2014.
Article18. Lippman CR, Spence CA, Youssef AS, Cahill DW. Correction of adult scoliosis via a posterior-only approach. Neurosurg Focus. 14:e5. 2003.
Article19. Lonner BS, Murthy SK, Boachie-Adjei O. Single-staged double anterior and posterior spinal reconstruction for rigid adult spinal deformity: a report of four cases. Spine J. 5:104–108. 2005.
Article20. Mundis GM, Akbarnia BA, Phillips FM. Adult deformity correction through minimally invasive lateral approach techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35(26 Suppl):S312–S321. 2010.
Article21. Oskouian RJ Jr, Shaffrey CI. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 17:299–315. vii. 2006.
Article22. Ozgur BM, Aryan HE, Pimenta L, Taylor WR. Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF): a novel surgical technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 6:435–443. 2006.
Article23. Phillips FM, Isaacs RE, Rodgers WB, Khajavi K, Tohmeh AG, Deviren V, et al. Adult degenerative scoliosis treated with XLIF: clinical and radiographical results of a prospective multicenter study with 24-month follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:1853–1861. 2013.24. Rhee JM, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K, Edwards C, et al. Staged posterior surgery for severe adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 28:2116–2121. 2003.
Article25. Shufflebarger HL, Grimm JO, Bui V, Thomson JD. Anterior and posterior spinal fusion. staged versus same-day surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 16:930–933. 1991.
Article26. Silva FE, Lenke LG. Adult degenerative scoliosis: evaluation and management. Neurosurg Focus. 28:E1. 2010.
Article27. Tempel ZJ, Gandhoke GS, Bonfield CM, Okonkwo DO, Kanter AS. Radiographic and clinical outcomes following combined lateral lumbar interbody fusion and posterior segmental stabilization in patients with adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus. 36:E11. 2014.
Article28. Tormenti MJ, Maserati MB, Bonfield CM, Okonkwo DO, Kanter AS. Complications and radiographic correction in adult scoliosis following combined transpsoas extreme lateral interbody fusion and posterior pedicle screw instrumentation. Neurosurg Focus. 28:E7. 2010.
Article29. Yadla S, Maltenfort MG, Ratliff JK, Harrop JS. Adult scoliosis surgery outcomes: a systematic review. Neurosurg Focus. 28:E3. 2010.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications
- Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Multilevel Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Associated with Degenerative Scoliosis
- Deformity Correction with Interbody Fusion Using Lateral versus Posterior Approach in Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: A Systematic Review and Observational Meta-analysis
- Surgical Treatment of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis