J Korean Fract Soc.
2018 Oct;31(4):159-164. 10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.159.
Atypical Femoral Fractures: What Do We Know about Them?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. slphlw@naver.com
- KMID: 2422898
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.159
Abstract
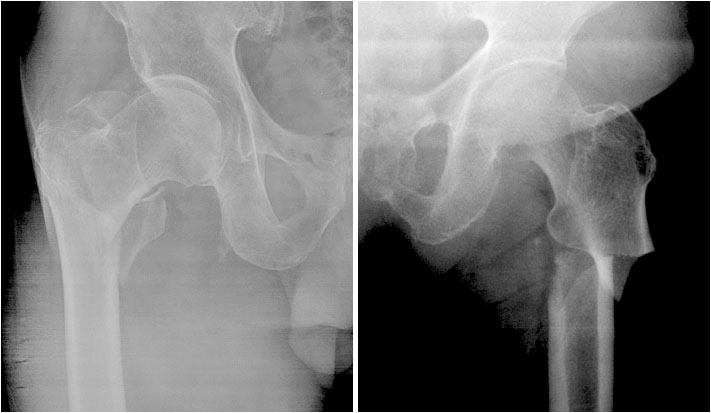
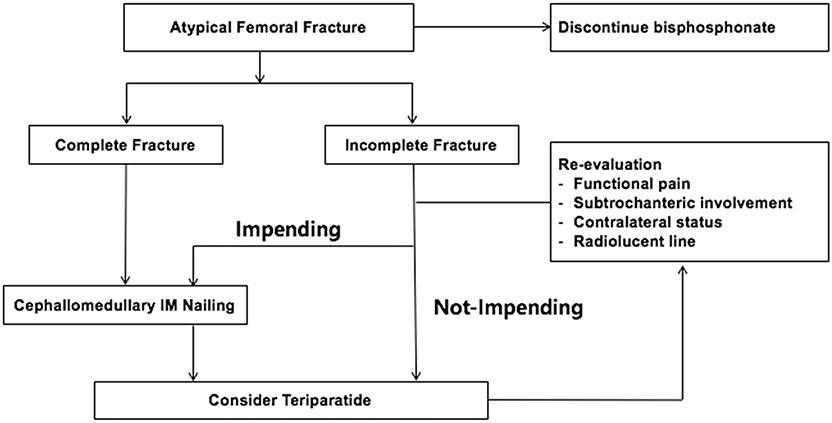
- Recently, atypical femoral fractures (AFFs) have been found in patients who were prescribed bisphosphonate to prevent osteoporotic fractures. Although the occurrence of AFF is rare, there are some concerns, such as a higher risk of delayed or non-union of AFF. This paper reviews the treatment of AFF and suggests some considerations during surgery.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Odvina CV, Zerwekh JE, Rao DS, Maalouf N, Gottschalk FA, Pak CY. Severely suppressed bone turnover: a potential complication of alendronate therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:1294–1301.
Article2. Shane E, Burr D, Ebeling PR, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25:2267–2294.
Article3. Park-Wyllie LY, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN, et al. Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA. 2011; 305:783–789.
Article4. Abrahamsen B, Einhorn TA. Beyond a reasonable doubt? Bisphosphonates and atypical femur fractures. Bone. 2012; 50:1196–1200.
Article5. Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Eastell R. Cumulative alendronate dose and the long-term absolute risk of subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femur fractures: a register-based national cohort analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:5258–5265.
Article6. Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2014; 29:1–23.
Article7. Im GI, Jeong SH. Pathogenesis, management and prevention of atypical femoral fractures. J Bone Metab. 2015; 22:1–8.
Article8. Kwek EB, Goh SK, Koh JS, Png MA, Howe TS. An emerging pattern of subtrochanteric stress fractures: a long-term complication of alendronate therapy? Injury. 2008; 39:224–231.
Article9. Goh SK, Yang KY, Koh JS, et al. Subtrochanteric insufficiency fractures in patients on alendronate therapy: a caution. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89:349–353.10. Schilcher J, Aspenberg P. Incidence of stress fractures of the femoral shaft in women treated with bisphosphonate. Acta Orthop. 2009; 80:413–415.
Article11. Koh JH, Myong JP, Jung SM, et al. Atypical femoral fracture in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with bisphosphonates: a nested case-control study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68:77–82.
Article12. Sato H, Kondo N, Wada Y, et al. The cumulative incidence of and risk factors for latent beaking in patients with autoimmune diseases taking long-term glucocorticoids and bisphosphonates. Osteoporos Int. 2016; 27:1217–1225.
Article13. Lenart BA, Neviaser AS, Lyman S, et al. Association of low-energy femoral fractures with prolonged bisphosphonate use: a case control study. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20:1353–1362.
Article14. Lee YK, Ha YC, Park C, Yoo JJ, Shin CS, Koo KH. Bisphosphonate use and increased incidence of subtrochanteric fracture in South Korea: results from the national claim registry. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24:707–711.
Article15. Vestergaard P, Schwartz F, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L. Risk of femoral shaft and subtrochanteric fractures among users of bisphosphonates and raloxifene. Osteoporos Int. 2011; 22:993–1001.
Article16. Wang Z, Ward MM, Chan L, Bhattacharyya T. Adherence to oral bisphosphonates and the risk of subtrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures among female medicare beneficiaries. Osteoporos Int. 2014; 25:2109–2116.
Article17. Wang Z, Bhattacharyya T. Trends in incidence of subtrochanteric fragility fractures and bisphosphonate use among the US elderly, 1996–2007. J Bone Miner Res. 2011; 26:553–560.
Article18. Abrahamsen B, Eiken P, Eastell R. Subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femur fractures in patients treated with alendronate: a register-based national cohort study. J Bone Miner Res. 2009; 24:1095–1102.
Article19. Swiontkowski MF. Oral bisphosphonates and risk of subtrochanteric or diaphyseal femur fractures in a population-based cohort. v. 2012. Yearbook of Orthopedics. New York: Elsevier Health Science;2012. p. 45–48.20. Rose PS. Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. v. 2012. Yearbook of Orthopedics. New York: Elsevier Health Science;2012. p. 355–357.21. Meier RP, Perneger TV, Stern R, Rizzoli R, Peter RE. Increasing occurrence of atypical femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use. Arch Intern Med. 2012; 172:930–936.
Article22. Schilcher J, Michaëlsson K, Aspenberg P. Bisphosphonate use and atypical fractures of the femoral shaft. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1728–1737.
Article23. Dell RM, Adams AL, Greene DF, et al. Incidence of atypical nontraumatic diaphyseal fractures of the femur. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27:2544–2550.
Article24. Clarke BL. Bisphosphonates and fractures of the subtrochanteric or diaphyseal femur. v. 2011. Yearbook of Endocrinology. New York: Elsevier Health Science;2011. p. 197–199.25. Beaudouin-Bazire C, Dalmas N, Bourgeois J, et al. Real frequency of ordinary and atypical sub-trochanteric and diaphyseal fractures in France based on X-rays and medical file analysis. Joint Bone Spine. 2013; 80:201–205.
Article26. LeBlanc ES, Rosales AG, Black DM, et al. Evaluating atypical features of femur fractures: how change in radiological criteria influenced incidence and demography of atypical femur fractures in a community setting. J Bone Miner Res. 2017; 32:2304–2314.
Article27. Ha YC, Cho MR, Park KH, Kim SY, Koo KH. Is surgery necessary for femoral insufficiency fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:3393–3398.
Article28. Neviaser AS, Lane JM, Lenart BA, Edobor-Osula F, Lorich DG. Low-energy femoral shaft fractures associated with alendronate use. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22:346–350.
Article29. Prasarn ML, Ahn J, Helfet DL, Lane JM, Lorich DG. Bisphosphonate-associated femur fractures have high complication rates with operative fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:2295–2301.
Article30. Weil YA, Rivkin G, Safran O, Liebergall M, Foldes AJ. The outcome of surgically treated femur fractures associated with long-term bisphosphonate use. J Trauma. 2011; 71:186–190.
Article31. Lim HS, Kim CK, Park YS, Moon YW, Lim SJ, Kim SM. Factors associated with increased healing time in complete femoral fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016; 98:1978–1987.
Article32. Lee KJ, Yoo JJ, Oh KJ, et al. Surgical outcome of intramedullary nailing in patients with complete atypical femoral fracture: a multicenter retrospective study. Injury. 2017; 48:941–945.
Article33. Tosounidis TH, Lampropoulou-Adamidou K, Kanakaris NK. Intramedullary nailing of sequential bilateral atypical subtrochanteric fractures and the management of distal femoral intraoperative fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2015; [epub]. DOI: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000370.
Article34. Kim JW, Kim H, Oh CW, et al. Surgical outcomes of intramedullary nailing for diaphyseal atypical femur fractures: is it safe to modify a nail entry in bowed femur? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017; 137:1515–1522.
Article35. Park YC, Song HK, Zheng XL, Yang KH. Intramedullary nailing for atypical femoral fracture with excessive anterolateral bowing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017; 99:726–735.
Article36. Molvik H, Khan W. Bisphosphonates and their influence on fracture healing: a systematic review. Osteoporos Int. 2015; 26:1251–1260.
Article37. Yue B, Ng A, Tang H, Joseph S, Richardson M. Delayed healing of lower limb fractures with bisphosphonate therapy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2015; 97:333–338.
Article38. Bogdan Y, Tornetta P 3rd, Einhorn TA, et al. Healing time and complications in operatively treated atypical femur fractures associated with bisphosphonate use: a multicenter retrospective cohort. J Orthop Trauma. 2016; 30:177–181.
Article39. Min BW, Koo KH, Park YS, et al. Scoring system for identifying impending complete fractures in incomplete atypical femoral fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:545–550.
Article40. Lee YK, Ha YC, Kang BJ, Chang JS, Koo KH. Predicting need for fixation of atypical femoral fracture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:2742–2745.
Article41. Unnanuntana A, Saleh A, Mensah KA, Kleimeyer JP, Lane JM. Atypical femoral fractures: what do we know about them?: AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95:e81–13.42. Murphy CM, Schindeler A, Cantrill LC, Mikulec K, Peacock L, Little DG. PTH(1-34) treatment increases bisphosphonate turnover in fracture repair in rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2015; 30:1022–1029.
Article43. Lee YK, Ha YC, Koo KH. Teriparatide, a nonsurgical solution for femoral nonunion? A report of three cases. Osteoporos Int. 2012; 23:2897–2900.
Article44. Pietrogrande L, Raimondo E. Teriparatide in the treatment of non-unions: scientific and clinical evidences. Injury. 2013; 44:Suppl 1. S54–S57.
Article45. Watts NB, Aggers D, McCarthy EF, et al. Responses to treatment with teriparatide in patients with atypical femur fractures previously treated with bisphosphonates. J Bone Miner Res. 2017; 32:1027–1033.
Article46. Chiang CY, Zebaze RM, Ghasem-Zadeh A, Iuliano-Burns S, Hardidge A, Seeman E. Teriparatide improves bone quality and healing of atypical femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate therapy. Bone. 2013; 52:360–365.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Atypical Femoral Fractures
- Surgical Treatment of the Atypical Femoral Fracture: Overcoming Femoral Bowing
- Periprosthetic Atypical Femoral Fracture-like Fracture after Hip Arthroplasty: A Report of Three Cases
- Surgical Outcomes of Atypical Femoral Fracture
- Medical Treatment of Atypical Femoral Fracture