Hip Pelvis.
2015 Sep;27(3):187-191. 10.5371/hp.2015.27.3.187.
Periprosthetic Atypical Femoral Fracture-like Fracture after Hip Arthroplasty: A Report of Three Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. min@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2069150
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.3.187
Abstract
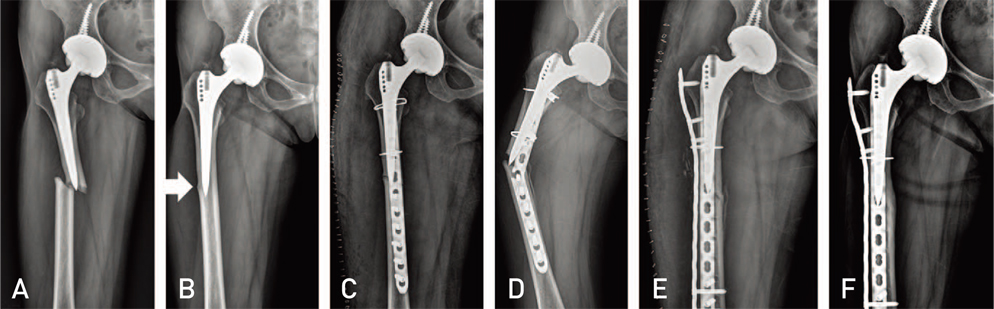
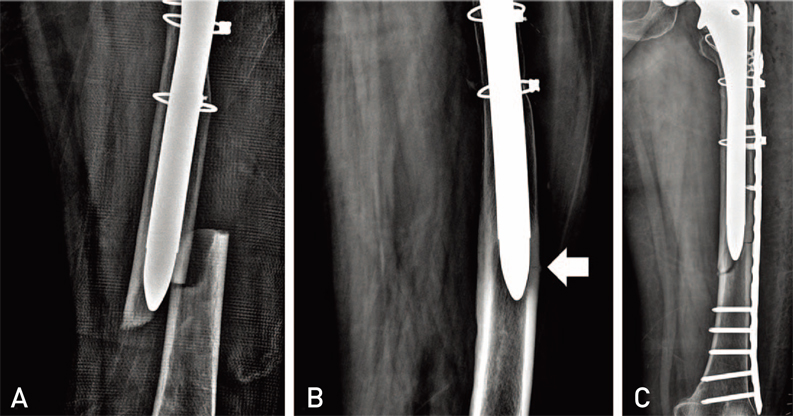
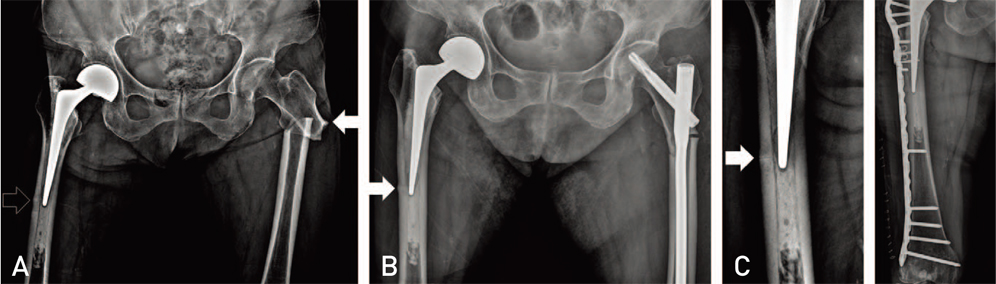
- Atypical femoral fractures are stress or insufficient fractures induced by low energy trauma or no trauma and have specific X-ray findings. Although the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research has excluded periprosthetic fractures from the definition of an atypical femoral fracture in 2013, this is still a matter of controversy because some authors report periprosthetic fractures showing specific features of atypical fractures around a well-fixed femoral stem. We report 3 cases of periprosthetic femur fractures that had specific radiographic features of atypical femoral fractures in patients with a history of prolonged bisphosphonate use; we also review relevant literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2014; 29:1–23.
Article2. Niikura T, Lee SY, Sakai Y, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M. Rare non-traumatic periprosthetic femoral fracture with features of an atypical femoral fracture: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2015; 9:103.
Article3. Curtin BM, Fehring TK. Bisphosphonate fractures as a cause of painful total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2011; 34:e939–e944.
Article4. Cross MB, Nam D, van der Meulen MC, Bostrom MP. A rare case of a bisphosphonate-induced peri-prosthetic femoral fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94:994–997.
Article5. Duncan CP, Masri BA. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect. 1995; 44:293–304.6. Ha YC, Cho MR, Park KH, Kim SY, Koo KH. Is surgery necessary for femoral insufficiency fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:3393–3398.
Article7. Prasarn ML, Ahn J, Helfet DL, Lane JM, Lorich DG. Bisphosphonate-associated femur fractures have high complication rates with operative fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:2295–2301.
Article8. Hanssen AD. Revision total hip arthroplasty: the painful hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:Suppl 5. 22.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Periprosthetic Femur Fracture due to Unrecognized Surgical Instrument Left in the Medullary Canal : A case report
- Lateral Insufficiency Fracture of the Femur caused by Osteopenia & Varus angulation after Hip Arthroplasty: Case Report
- Repeated Periprosthethic Femoral Fracture in a Below Knee Amputee with Ipsilateral Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty