J Endocr Surg.
2018 Sep;18(3):205-209. 10.16956/jes.2018.18.3.205.
Nonrecurrent Laryngeal Nerve Identification and Preservation during Transoral Robotic Thyroidectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. chojh0404@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2420778
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16956/jes.2018.18.3.205
Abstract
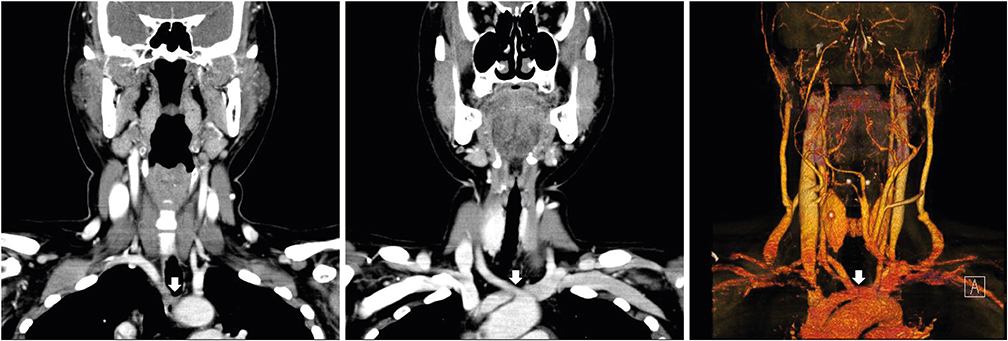
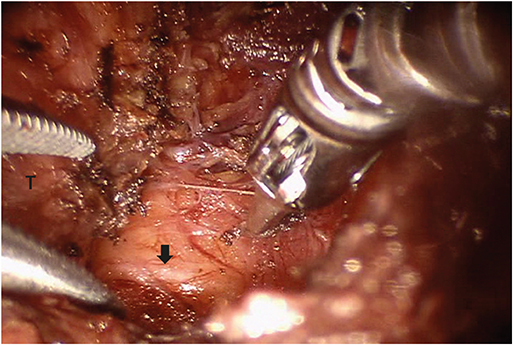
- The nonrecurrent laryngeal nerve (NRLN), a rare, anatomic variation of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, is associated with increased injury risk during thyroid surgery. Here, we report a 44-year-old female presenting with right NRLN, receiving transoral robotic thyroidectomy with intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM). Ultrasonogram of the patient's thyroid gland revealed a solitary nodule, with fine-needle aspiration cytology, indicating papillary carcinoma. Preoperative computed tomography scan revealed an aberrant right subclavian artery arising from the distal aortic arch, suggesting right NRLN. During transoral robotic hemi-thyroidectomy, IONM identified a NRLN emanating from the right vagus nerve and entering the larynx. The post-operative period was uneventful, and laryngoscopic examination demonstrated normal vocal cord movement with no changes observed in patient voice. This is the first report of transoral robotic thyroidectomy in a patient with NRLN. During transoral thyroidectomy, the right NRLN was easily identified and its integrity was preserved utilizing IONM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Timmermann W, Hamelmann WH, Thomusch O, Sekulla C, Grond S, Neumann HJ, et al. Effectiveness and results of intraoperative neuromonitoring in thyroid surgery. Statement of the interdisciplinary study group on intraoperative neuromonitoring of thyroid surgery. Chirurg. 2004; 75:916–922.
Article2. Barczyński M, Konturek A, Stopa M, Honowska A, Nowak W. Randomized controlled trial of visualization versus neuromonitoring of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. World J Surg. 2012; 36:1340–1347.
Article3. Lee HY, Richmon JD, Walvekar RR, Holsinger C, Kim HY. Robotic transoral periosteal thyroidectomy (TOPOT): experience in two cadavers. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2015; 25:139–142.
Article4. Benhidjeb T, Wilhelm T, Harlaar J, Kleinrensink GJ, Schneider TA, Stark M. Natural orifice surgery on thyroid gland: totally transoral video-assisted thyroidectomy (TOVAT): report of first experimental results of a new surgical method. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:1119–1120.
Article5. Anuwong A. Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy vestibular approach: a series of the first 60 human cases. World J Surg. 2016; 40:491–497.
Article6. Lee HY, You JY, Woo SU, Son GS, Lee JB, Bae JW, et al. Transoral periosteal thyroidectomy: cadaver to human. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:898–904.
Article7. Avisse C, Marcus C, Delattre JF, Marcus C, Cailliez-Tomasi JP, Palot JP, et al. Right nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerve and arteria lusoria: the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of an anatomic anomaly. Review of 17 cases. Surg Radiol Anat. 1998; 20:227–232.
Article8. Defechereux T, Albert V, Alexandre J, Bonnet P, Hamoir E, Meurisse M. The inferior non recurrent laryngeal nerve: a major surgical risk during thyroidectomy. Acta Chir Belg. 2000; 100:62–67.9. Attmann T, Brandt M, Müller-Hülsbeck S, Cremer J. Two-stage surgical and endovascular treatment of an aneurysmal aberrant right subclavian (Lusoria) artery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005; 27:1125–1127.
Article10. Toniato A, Mazzarotto R, Piotto A, Bernante P, Pagetta C, Pelizzo MR. Identification of the nonrecurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery: 20-year experience. World J Surg. 2004; 28:659–661.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concurrent Ipsilateral Recurrent and Nonrecurrent Laryngeal Nerve During Thyroidectomy: A Case Report
- A Case of Nonrecurrent Inferior Laryngeal Nerve
- Intraoperative Neuromonitoring during Thyroid Surgery
- Nonrecurrent Laryngeal Nerve
- Robotic Transoral Thyroidectomy: Right Thyroidectomy and Ipsilateral Central Neck Dissection with da Vinci Si Surgical System