J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Aug;63(2):161-165.
Synchronous Ectopic Pancreases in the Cardia and Antrum of the Stomach: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Korea. jkm7290@empal.com
- 3Department of Surgery, Hallym University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Korea.
Abstract
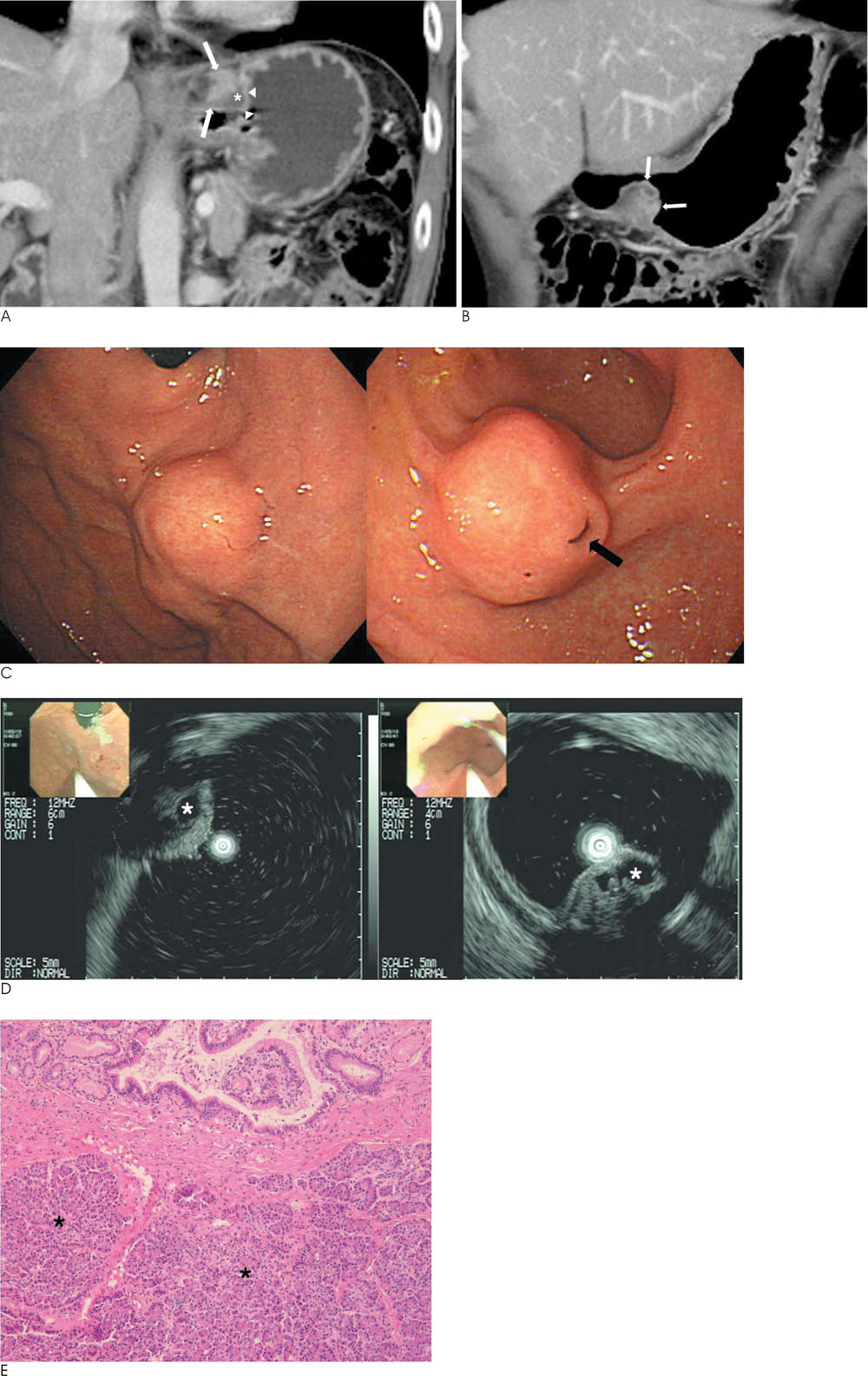
- Ectopic pancreas is most commonly found in the antrum of the stomach, duodenum, or proximal jejunum. Rarely ectopic pancreas in the proximal stomach has been reported. Moreover, the coexistence of two ectopic pancreases at gastric cardia and antrum in a patient has not been reported. Ectopic pancreas usually appears as a submucosal mass, and it is difficult to differentiate between ectopic pancreas and other common submucosal tumors, such as a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) or leiomyoma. Here, we present a case of the coexistence of two ectopic pancreases at cardia and antrum of the stomach in a 60-year-old man, which was preoperatively misdiagnosed as GIST.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dolan RV, ReMine WH, Dockerty MB. The fate of heterotopic pancreatic tissue: a study of 212 cases. Arch Surg. 1974; 109:762–765.2. Kim JY, Lee JM, Kim KW, Park HS, Choi JY, Kim SH, et al. Ectopic pancreas: CT findings with emphasis on differentiation from small gastrointestinal stromal tumor and leiomyoma. Radiology. 2009; 252:92–100.3. Shah A, Gordon AR, Ginsberg GG, Furth EE, Levine MS. Case report: ectopic pancreatic rest in the proximal stomach mimicking gastric neoplasms. Clin Radiol. 2007; 62:600–602.4. Levine MS. Benign tumors of the stomach and duodenum. In : Gore RM, Levine MS, editors. Textbook of gastrointestinal radiology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2008. p. 602–615.5. Copleman B. Aberrant pancreas in the gastric wall. Radiology. 1963; 81:107–111.6. Cho JS, Shin KS, Kwon ST, Kim JW, Song CJ, Noh SM, et al. Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach: CT findings. Radiology. 2000; 217:139–144.7. Tang Z, Jing W, Lindeman N, Harris NL, Ferry JA. One Patient, Two Lymphomas. Simultaneous primary gastric marginal zone lymphoma and primary duodenal follicular lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004; 128:1035–1038.8. Chen SH, Huang WH, Feng CL, Chou JW, Hsu CH, Peng CY, et al. Clinical analysis of ectopic pancreas with endoscopic ultrasonography: an experience in a medical center. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008; 12:877–881.9. Hsia CY, Wu CW, Lui WY. Heterotopic pancreas: a difficult diagnosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999; 28:144–147.10. Khashab MA, Cummings OW, DeWitt JM. Ligation-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection of gastric heterotopic pancreas. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:2805–2808.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Case of an Ectopic Pancreas in the Stomach and Presenting as a Cystic Abscess
- A Case of Synchronous Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Esophagus and Stomach
- Gastric Ectopic Pyloric Opening with Gastric Ulcer: A Rare Case
- Serrated Adenoma with Adenocarcinoma of Stomach Treated by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Synchronous Occurrence of a Gastric Adenocarcinoma and a GIST (Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor): A Case Report