Yonsei Med J.
2018 Jan;59(1):72-79. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.72.
Effectiveness and Safety of Biolimus A9â„¢-Eluting stEnt in Patients with AcUTe Coronary sYndrome; A Multicenter, Observational Study (BEAUTY Study)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. myungho@chollian.net
- 3Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 4Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Presbyterian Medical Center, Jeonju, Korea.
- 8Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 9Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 10Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 11Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 12Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea.
- 13Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 14Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 15Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 16Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 17Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Saint Carollo Hospital, Suncheon, Korea.
- 18Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 19Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 20Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 21Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gwangju Veterans Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 22Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2418851
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.72
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study sought to determine the 1-year clinical effectiveness and safety of a biodegradable, polymer-containing Biolimus A9â„¢-eluting stent (BES) in Korean patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
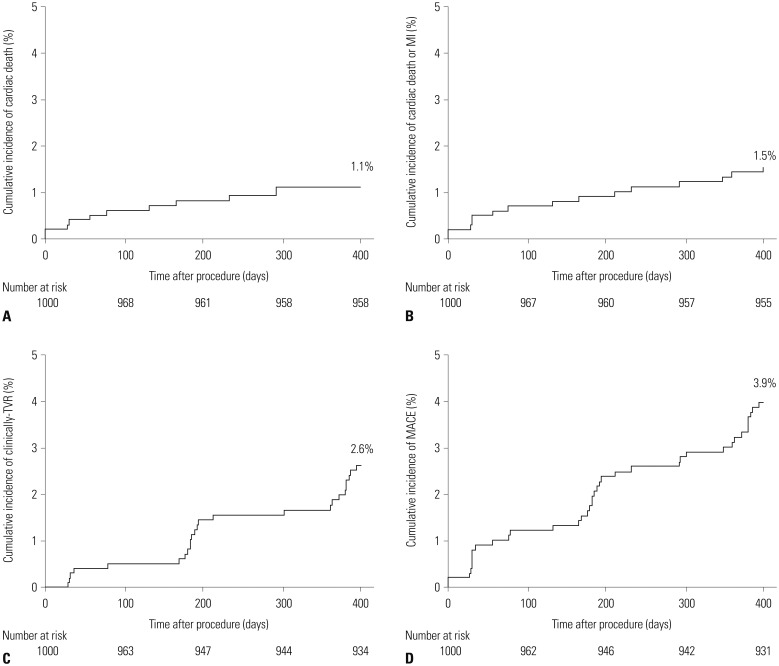
A total of 1000 ACS patients with 1251 lesions who underwent implantation of BESs at 22 centers in Korea were enrolled between May 2011 and July 2013. We assessed major adverse cardiac events (MACE) defined as the composite of cardiac death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and clinical-driven target vessel revascularization at 12 months.
RESULTS
Patient mean age was 62.6±11.4 years. 72.8% of the patients were male, 28.5% had diabetes, 32.8% had multi-vessel disease (MVD), and 47.9% presented with acute MI (AMI). The mean global registry of acute coronary events risk score of all patients was 103.0±27.6. The number of stents per patient was 1.3±0.6. The incidences of MACE and definite stent thrombosis at 12 months were 3.9% and 0.2%, respectively. On multivariate Cox-regression analysis, age ≥65 years was identified as an independent predictors of 1-year MACE (hazard ratio=2.474; 95% confidence interval=1.202−5.091). Subgroup analyses revealed no significant differences in the incidence of MACE between patients with and without diabetes (4.3% vs. 3.7%, p=0.667), between those who presented with and without AMI (4.4% vs. 3.4%, p=0.403), and between those with and without MVD (4.6% vs. 3.5%, p=0.387).
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrated excellent 1-year clinical outcomes of BES implantation in patients at low-risk for ACS.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Coronary Syndrome/*drug therapy
Aged
Drug-Eluting Stents/*adverse effects
Female
Humans
Incidence
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Middle Aged
Multivariate Analysis
Proportional Hazards Models
Republic of Korea
Sirolimus/adverse effects/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Time Factors
Treatment Outcome
Sirolimus
Figure
Reference
-
1. Joner M, Finn AV, Farb A, Mont EK, Kolodgie FD, Ladich E, et al. Pathology of drug-eluting stents in humans: delayed healing and late thrombotic risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 48:193–202. PMID: 16814667.2. Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Joner M, Ladich E, Kutys R, Mont EK, et al. Delayed arterial healing and increased late stent thrombosis at culprit sites after drug-eluting stent placement for acute myocardial infarction patients: an autopsy study. Circulation. 2008; 118:1138–1145. PMID: 18725485.3. Nasuno T, Tokura M, Kageyama M, Toyoda S, Sakuma M, Komatsu T, et al. The wound healing response after implantation of a drug-eluting stent is impaired persistently in the long term. Heart Vessels. 2016; 31:985–989. PMID: 25939630.
Article4. Byrne RA, Kastrati A, Kufner S, Massberg S, Birkmeier KA, Laugwitz KL, et al. Randomized, non-inferiority trial of three limus agent-eluting stents with different polymer coatings: the Intracoronary Stenting and Angiographic Results: Test Efficacy of 3 Limus-Eluting Stents (ISAR-TEST-4) Trial. Eur Heart J. 2009; 30:2441–2449. PMID: 19720642.
Article5. Windecker S, Serruys PW, Wandel S, Buszman P, Trznadel S, Linke A, et al. Biolimus-eluting stent with biodegradable polymer versus sirolimus-eluting stent with durable polymer for coronary revascularisation (LEADERS): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2008; 372:1163–1173. PMID: 18765162.
Article6. Stefanini GG, Byrne RA, Serruys PW, de Waha A, Meier B, Massberg S, et al. Biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents reduce the risk of stent thrombosis at 4 years in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a pooled analysis of individual patient data from the ISAR-TEST 3, ISAR-TEST 4, and LEADERS randomized trials. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33:1214–1222. PMID: 22447805.
Article7. Grube E, Buellesfeld L. BioMatrix Biolimus A9-eluting coronary stent: a next-generation drug-eluting stent for coronary artery disease. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2006; 3:731–741. PMID: 17280537.8. Byrne RA, Joner M, Kastrati A. Polymer coatings and delayed arterial healing following drug-eluting stent implantation. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2009; 57:567–584. PMID: 19838148.9. Finn AV, Nakazawa G, Joner M, Kolodgie FD, Mont EK, Gold HK, et al. Vascular responses to drug eluting stents: importance of delayed healing. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007; 27:1500–1510. PMID: 17510464.10. Smits PC, Hofma S, Togni M, Vázquez N, Valdés M, Voudris V, et al. Abluminal biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent (COMPARE II): a randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2013; 381:651–660. PMID: 23374650.
Article11. Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, Mariani A, Sabaté M, Smits PC, et al. Clinical outcomes with bioabsorbable polymer-versus durable polymer-based drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:299–307. PMID: 24211507.12. Tantawy A, Ahn CM, Shin DH, Kim JS, Kim BK, Ko YG, et al. Nobori-Biolimus-eluting stents versus Resolute Zotarolimus-eluting stents in patients undergoing coronary intervention: a propensity score matching. Yonsei Med J. 2017; 58:290–295. PMID: 28120558.
Article13. Levine GN, Jeong YH, Goto S, Anderson JL, Huo Y, Mega JL, et al. Expert consensus document: World Heart Federation expert consensus statement on antiplatelet therapy in East Asian patients with ACS or undergoing PCI. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014; 11:597–606. PMID: 25154978.14. Lüscher TF, Creager MA, Beckman JA, Cosentino F. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part II. Circulation. 2003; 108:1655–1661. PMID: 14517152.15. Moreno PR, Fuster V. New aspects in the pathogenesis of diabetic atherothrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 44:2293–2300. PMID: 15607389.
Article16. Mahmud E, Bromberg-Marin G, Palakodeti V, Ang L, Creanga D, Demaria AN. Clinical efficacy of drug-eluting stents in diabetic patients: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:2385–2395. PMID: 18565394.17. Kang SH, Park KH, Ahn HS, Park KW, Hong YJ, Koo BK, et al. Everolimus-eluting versus sirolimus-eluting coronary stents in patients with and without diabetes mellitus. EuroIntervention. 2014; 10:74–82. PMID: 24345385.
Article18. Kubo T, Akasaka T, Tanimoto T, Takano M, Seino Y, Nasu K, et al. Assessment of vascular response after drug-eluting stents implantation in patients with diabetes mellitus: an optical coherence tomography sub-study of the J-DESsERT. Heart Vessels. 2016; 31:465–473. PMID: 25630713.
Article19. Kim BK, Hong MK, Shin DH, Kim JS, Ko YG, Choi D, et al. Optical coherence tomography analysis of strut coverage in biolimus- and sirolimus-eluting stents: 3-month and 12-month serial follow-up. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 168:4617–4623. PMID: 23932862.
Article20. Park KH, Jeong MH, Kim JM, Park DS, Kim JH, Lim KS, et al. The impact of triple anti-platelet therapy for endothelialization and inflammatory response at overlapping bioabsorbable polymer coated drug-eluting stents in a porcine coronary model. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 168:1853–1858. PMID: 23347613.
Article21. Nakazawa G, Shinke T, Ijichi T, Matsumoto D, Otake H, Torii S, et al. Comparison of vascular response between durable and biodegradable polymer-based drug-eluting stents in a porcine coronary artery model. EuroIntervention. 2014; 10:717–723. PMID: 25330504.
Article22. Lim KS, Jeong MH, Bae IH, Park DS, Kim JM, Kim JH, et al. Histopathological comparison among biolimus, zotarolimus and everolimus-eluting stents in porcine coronary restenosis model. Korean Circ J. 2013; 43:744–751. PMID: 24363750.
Article23. de Waha A, Stefanini GG, King LA, Byrne RA, Serruys PW, Kufner S, et al. Long-term outcomes of biodegradable polymer versus durable polymer drug-eluting stents in patients with diabetes a pooled analysis of individual patient data from 3 randomized trials. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 168:5162–5166. PMID: 23993323.
Article24. Räber L, Kelbæk H, Taniwaki M, Ostojic M, Heg D, Baumbach A, et al. Biolimus-eluting stents with biodegradable polymer versus bare-metal stents in acute myocardial infarction: two-year clinical results of the COMFORTABLE AMI trial. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014; 7:355–364. PMID: 24847017.25. Tomai F, De Luca L, Altamura L, Versaci F, Pennacchi M, Proietti I, et al. One-year outcome from an all-comers population of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction treated with biolimus-eluting stent with biodegradable polymer. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015; 85:352–358. PMID: 25115927.
Article26. Zhang YJ, Iqbal J, Windecker S, Linke A, Antoni D, Sohn HY, et al. Biolimus-eluting stent with biodegradable polymer improves clinical outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Heart. 2015; 101:271–278. PMID: 25423953.
Article27. Cockburn J, Pareek N, Poliacikova P, Saraf S, Williams R, Dhillon G, et al. Clinical outcomes with 6 months dual antiplatelet therapy after implantation of biolimus-A9 drug eluting coronary stents. Int J Cardiol. 2014; 172:185–189. PMID: 24462139.
Article28. Camenzind E, Boersma E, Wijns W, Mauri L, Rademaker-Havinga T, Ordoubadi FF, et al. Modifying effect of dual antiplatelet therapy on incidence of stent thrombosis according to implanted drugeluting stent type. Eur Heart J. 2014; 35:1932–1948. PMID: 24627416.29. Colombo A, Chieffo A. Dual antiplatelet therapy after drug-eluting stents--how long to treat. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:2225–2226. PMID: 25399657.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Simultaneous Multivessel Acute Stent Thrombosis in a Patient with Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Kounis Syndrome Presenting as Very Late Stent Thrombosis in an Everolimus-Eluting Stent Following Wasp Stings
- Drug-Eluting Stent Strut Fracture as a Cause of Restenosis
- Drug-Eluting Stent: Present and Future
- Drug-Eluting Stent Used to Treat a Case of Recurrent Right Coronary Artery In-Stent Restenoses often Accompanied by Acute Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction