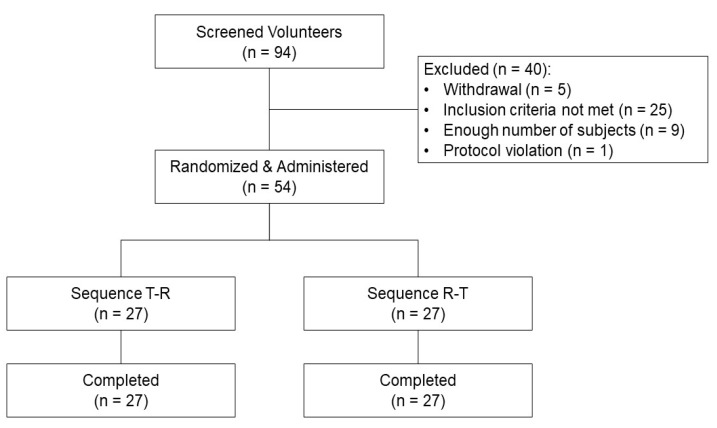
Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2017 Dec;25(4):196-201. 10.12793/tcp.2017.25.4.196.
Comparison of pharmacokinetics and safety of fixed-dose combination of SKI306X and aceclofenac versus separate tablets in healthy subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmaceutical Medicine and Regulatory Sciences, Colleges of Medicine and Pharmacy, Yonsei University, Incheon 21983, Republic of Korea.
- 2Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Clinical Trials Center, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea. DELIVERY98@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Republic of Korea.
- 4Head of Pharma R&D Center, Life Science Business Group, SK Chemicals, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2407002
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2017.25.4.196
Abstract
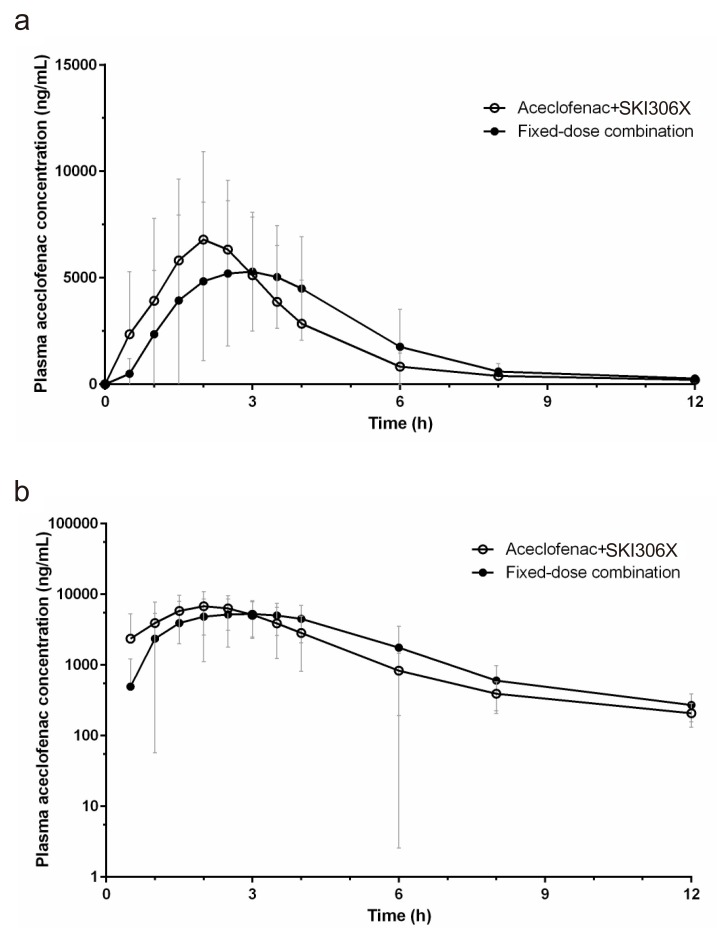
- JOINS (SKI306X) is an herbal anti-arthritic medicine that is widely used with aceclofenac for treating osteoarthritis in Korea. A fixed-dose combination (FDC) tablet containing SKI306X and aceclofenac was developed to improve patient compliance. This study aimed to compare the pharmacokinetics (PK) and safety of the FDC tablet with those of co-administered SKI306X and aceclofenac in healthy subjects. In this randomized, open-label, two-way crossover, single-dose study, the FDC tablet (SKI306X 300 mg/aceclofenac 100 mg) (test) was given or co-administration of 300 mg of SKI306X and 100 mg of aceclofenac (reference) was performed followed by a 7-day wash-out period. Blood samples were collected before and after drug administration to evaluate aceclofenac PK parameters, and safety was assessed throughout the study. A total of 54 healthy male subjects were enrolled in and completed the study. T(max) and t(1/2) of aceclofenac of the FDC tablet were similar to those of aceclofenac co-administered with SKI306X (T(max): test 2.96 h and reference 2.14 h; t(1/2): test 3.46 h and reference 4.04 h). The geometric mean ratios (90% confidence intervals) of C(max) and AUC(last) (T/R) were 0.85 (0.81 to 0.91) and 1.03 (1.01 to 1.06) respectively; these results were within the predefined range (0.8 to 1.25). There was only one drug-related adverse event (dizziness) occurred after administration of the FDC tablet; however, it was mild in severity and resolved without any complications. The FDC tablet was well tolerated and exhibited an absorption rate and extent comparable to those of SKI306X and aceclofenac administered simultaneously.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JI, Choi JY, Kim KG, Lee MC. Efficacy of JOINS on Cartilage Protection in Knee Osteoarthritis: Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2017; 29:217–224. DOI: 10.5792/ksrr.17.004. PMID: 28854768.
Article2. Lee S, Kim SJ. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, risk factors, and quality of life: The Fifth Korean National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017; 20:809–817. DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.12795. PMID: 26578271.
Article3. McAlindon TE, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, Arden NK, Berenbaum F, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014; 22:363–388. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2014.01.003. PMID: 24462672.
Article4. Prieto-Alhambra D, Wilson N. Use of Drug Combinations in Patients with Osteoarthritis: a Population-based Cohort Study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; S160.
Article5. Raza K, Kumar M, Kumar P, Malik R, Sharma G, Kaur M, et al. Topical Delivery of Aceclofenac: Challenges and Promises of Novel Drug Delivery Systems. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:406731. DOI: 10.1155/2014/406731. PMID: 25045671.
Article6. Kim JH, Ryu KH, Jung KW, Han CK, Kwak WJ, Cho YB. Effects of SKI306X on Arachidonate Metabolism and Other Inflammatory Mediators. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005; 28:1615–1620. PMID: 16141526.
Article7. Kim D, Oh ES, Kim CO, Choi C, Chang MJ, Park MS. Effects of JOINS® on the Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Aceclofenac in Healthy Korean Volunteers: an Open-label, Multiple-dose, One Sequence, Two-period Study. Transl Clin Pharmacol. 2016; 24:169–174.
Article8. Choi JH, Kim DY, Yoon JH, Youn HY, Yi J, Rhee HI, et al. Effects of SKI 306X, a new herbal agent, on proteoglycan degradation in cartilage explant culture and collagenase-induced rabbit osteoarthritis model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002; 10:471–478. PMID: 12056850.
Article9. Choi CH, Kim TH, Sung YK, Choi CB, Na YI, Yoo H. SKI306X Inhibition of Glycosaminoglycan Degradation in Human Cartilage Involves Down-regulation of Cytokine-induced Catabolic Genes. Korean J Intern Med. 2014; 29:647–655. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2014.29.5.647. PMID: 25228841.
Article10. Rhim SY, Park JH, Park YS, Lee MH, Shaw LM, Kang JS. Bioequivalence and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Two Branded Formulations of Aceclofenac 100 mg: A Single-Dose, Randomized, Open-Label, Two-Period Crossover Comparison in Healthy Korean Adult Volunteers. Clin Ther. 2008; 30:633–640. PMID: 18498912.
Article11. Guidance for Industry: Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies Submitted in NDAs or INDs - General Considerations. Accessed 10 November 2017. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm389370.pdf.12. Felson DT, Naimark A, Anderson J, Kazis L, Castelli W, Meenan RF. The Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis in the Elderly. The Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. 1987; 30:914–918. PMID: 3632732.
Article13. Bangalore S, Kamalakkannan G, Parkar S, Messerli FH. Fixed-dose combinations improve medication compliance: a meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2007; 120:713–719. PMID: 17679131.
Article14. Brogden RN, Wiseman LR. Aceclofenac, A Review of its Pharmacodynamic Properties and Therapeutic Potential in the Treatment of Rheumatic Disorders and in Pain Management. Drugs. 1996; 52:113–124. PMID: 8799688.15. Pareek A, Chandurkar N. Comparison of Gastrointestinal Safety and Tolerability of Aceclofenac with Diclofenac: a Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind Study in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013; 29:849–859. DOI: 10.1185/03007995.2013.795139. PMID: 23581533.
Article16. Dooley M, Spencer CM, Dunn CJ. Aceclofenac: A Reappraisal of its Use in the Management of Pain and Rheumatic Disease. 2001.17. Kim JH, Ryu KH, Jung KW, Han CK, Kwak WJ, Cho YB. Effects of SKI306X on arachidonate metabolism and other inflammatory mediators. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005; 28:1615–1620. PMID: 16141526.
Article18. Lung YB, Seong SC, Lee MC, Shin YU, Kim DH, Kim JM, et al. A Four-Week, Randomized, Double-Blind Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of SKI306X: a Herbal Antiarthritic Agent versus Diclofenac in Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Am J Chin Med. 2004; 32:291–301. PMID: 15315266.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and sustained-release metformin fixed-dose combination tablets: two randomized, open-label, 2-way crossover studies in healthy male subjects under fed conditions
- Pharmacokinetic Equivalence of the High Dose Strength Fixed-Dose Combination Tablet of Gemigliptin/Metformin Sustained Release (SR) and Individual Component Gemigliptin and Metformin XR Tablets in Healthy Subjects
- Bioequivalence of HCP1104, a New Fixed Dose Combination Drug and Co-administration of Eperisone 50 mg and Aceclofenac 100 mg: A Partial Replicated Crossover Study Design to Estimate the Pharmacokinetics of Highly Variable Drugs
- Pharmacokinetics of fixed-dose combination of rosuvastatin 20 mg and ezetimibe 10 mg compared to concurrent administration of individual tablets in healthy Korean subjects
- Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a fixed-dose combination of gemigliptin/metformin sustained release 25/500 mg compared to the loose combination in healthy male subjects