Korean J Adult Nurs.
2017 Dec;29(6):587-603. 10.7475/kjan.2017.29.6.587.
The Effects of Exercise Intervention for Fall Prevention in Persons with Arthritis: A Meta Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Sunlin University, Pohang, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Keimyung University, Deagu, Korea. hopark@kmu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2406538
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2017.29.6.587
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was a meta-analysis of the effects of exercise intervention in preventing falls among persons with arthritis.
METHODS
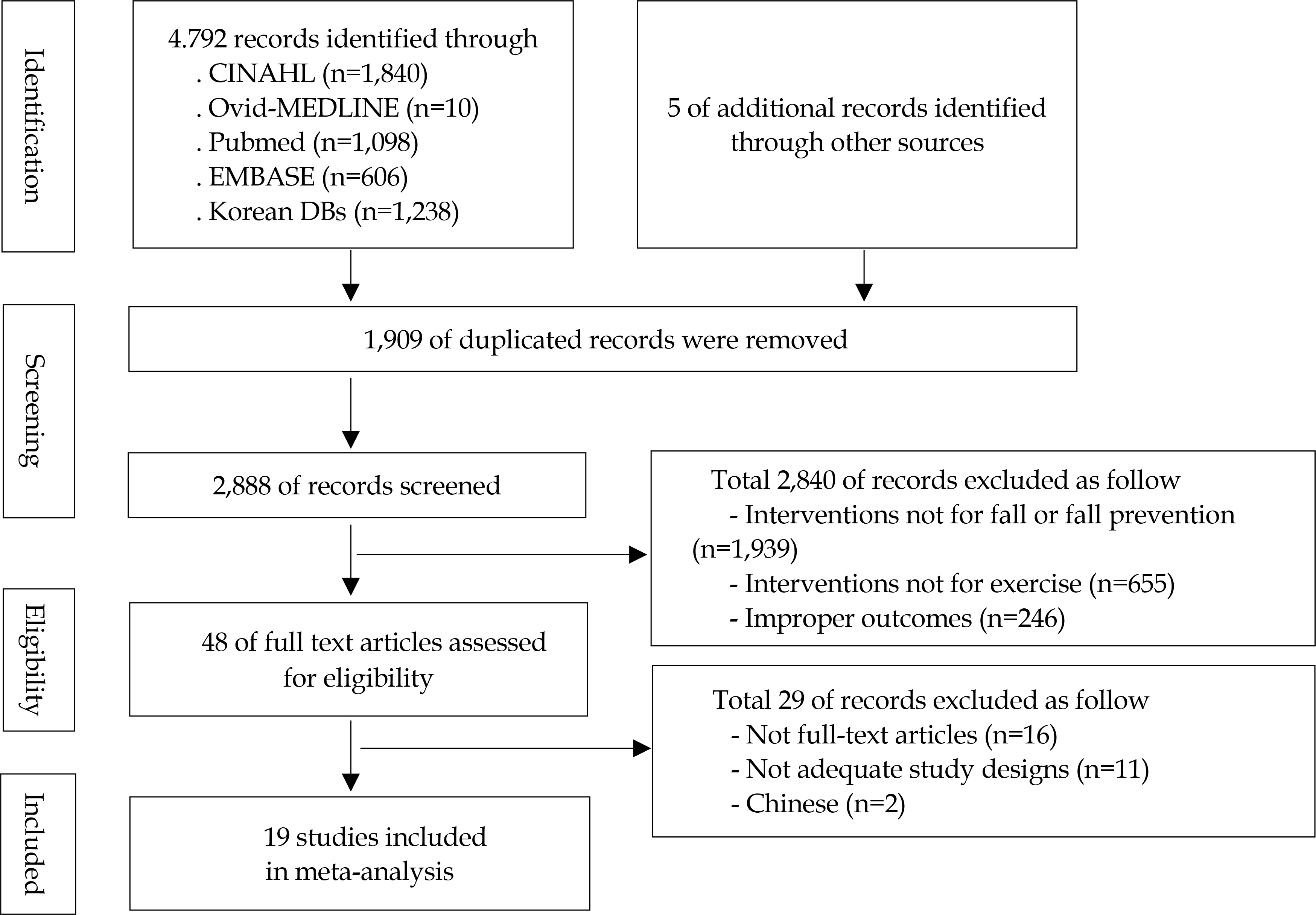
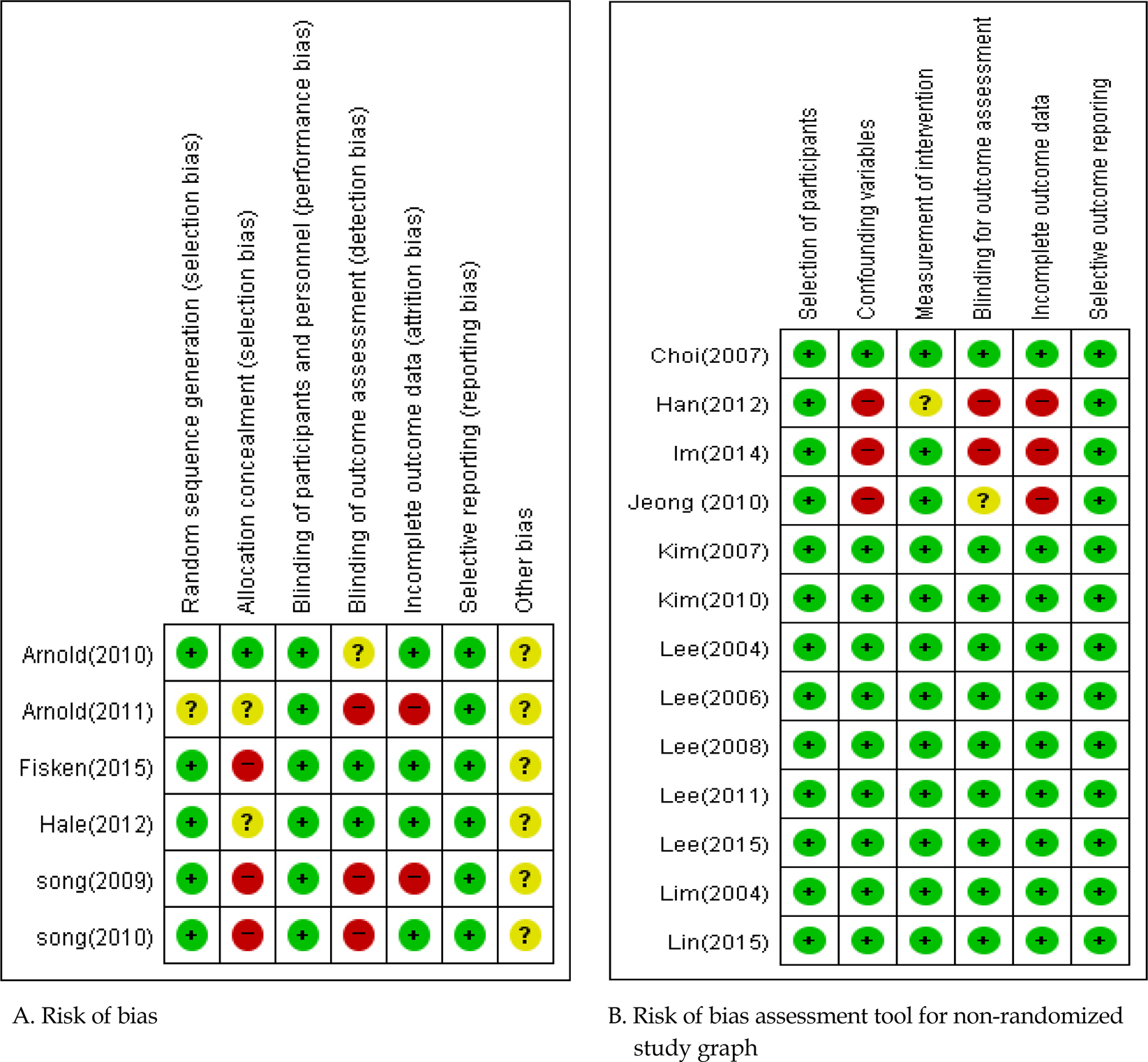
The review consisted of searches from Pubmed, Ovid-MEDLINE, CINAHL, EMBASE and Korean DBs using PICO-SD format. Key words for searching included "˜arthritis', "˜exercise', "˜fall' and the articles published until January 2017 were selected for this study. Methodological quality was assessed using Cochrane's Risk of Bias for randomized studies and Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non randomized studies. Data were analyzed by the RevMan 5.3 program of Cochrane Library.
RESULTS
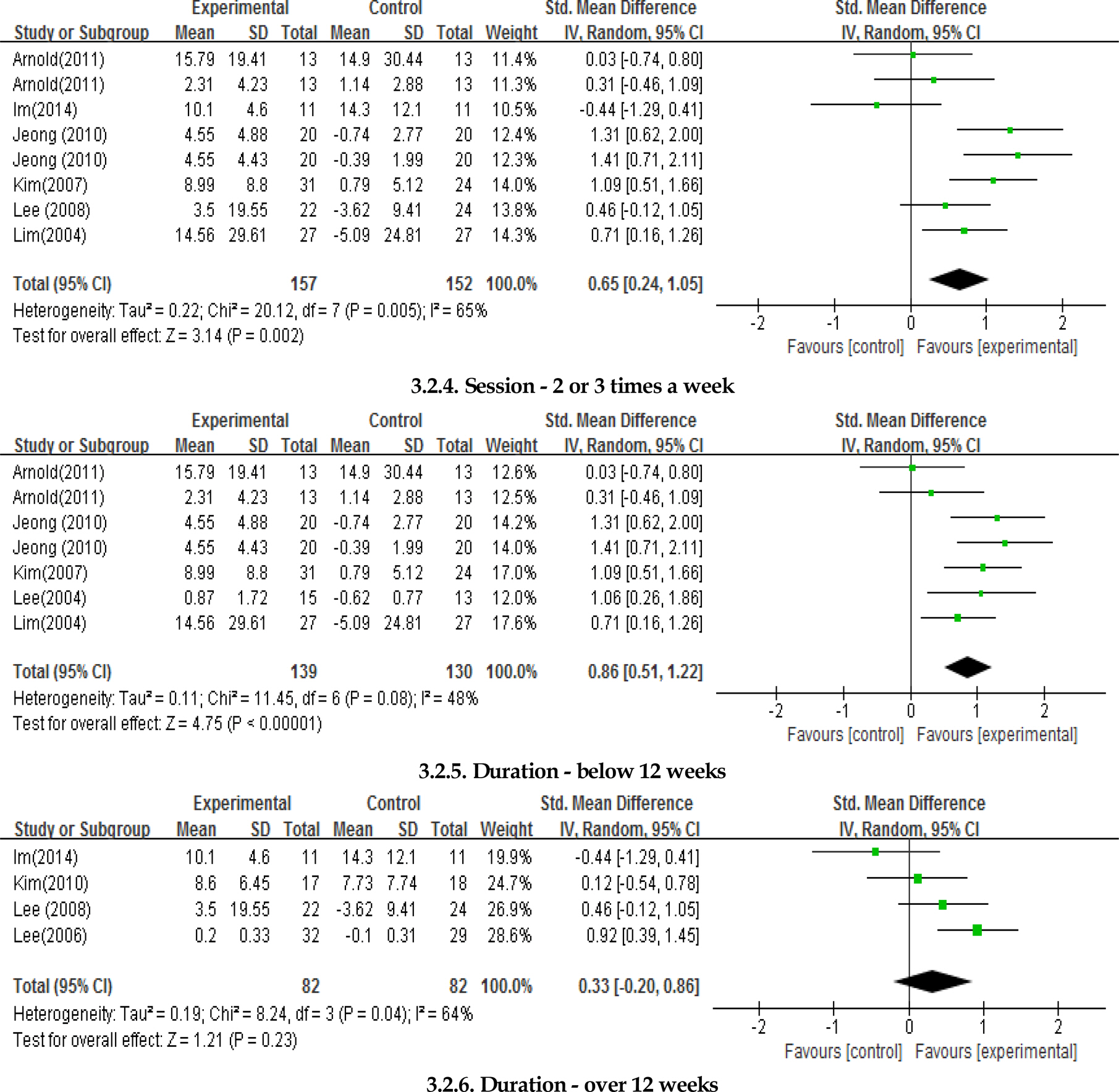
Nineteen clinical trials met the inclusion criteria with a total of 832 participants. There were significant differences in Tai Chi exercise (ES=0.76), exercise interventions performed over 60 minutes at one time (ES=0.98), exercise interventions provided once a week (ES=0.69) or 2~3 times a week (ES=0.65), exercise interventions provided for a total of 12 weeks or less (ES=0.86). The outcome measures such as balance (ES=0.66), fall efficacy (ES=0.70), and fear of falling (ES=−0.70) showed the significant difference, and their effect sizes were ranged from moderate to large.
CONCLUSION
The results of the study show that the exercise intervention is effective to prevent fall in persons with arthritis. It is necessary to include the comprehensive exercise interventions to enhance balance and fall efficacy and reduce fear of falling for the fall prevention program in persons with arthritis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Barbour KE., Stevens JA., Helmick CG., Luo YH., Murphy LB., Hootman JM, et al. Falls and fall injuries among adults with arthritis-United States, 2012. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). 2014. 63(17):379–83.2.National Health Insurance Service. Annual health insurance statistics for 2015 [Internet]. Wonju: National Health Insurance Service;2016. [cited 2016 October 25]. Available from. http://www.nhis.or.kr/menu/boardRetriveMenuSet.xx?menuId=F3321.3.Kim JM. An analysis of falls in the elderly: a PRECEDE model approach [dissertation]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;2009.4.Furuya T., Yamagiwa K., Ikai T., Inoue E., Taniguchi A., Momo-hara S, et al. Associated factors for falls and fear of falling in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Rheumatology. 2009. 28(11):1325–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1229-5.
Article5.Sohng KY., Moon JS. A survey on activities and fear of falling in the home-dwelling elderly in Seoul and Gyonggi-do. Jounal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing. 2003. 14(4):676–85.6.Kendrick D., Kumar A., Carpenter H., Zijlstra GA., Skelton DA., Cook JR, et al. Exercise for reducing fear of falling in older peo-ple living in the community. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014. 28(11):CD009848. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009848.
Article7.Kim YJ., Seo NS., Lim YN., Kim HS., Kim YS., Kim SJ. Effects of Taekwondo exercise program in women with osteoarthritis. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 2012. 19(2):210–22. https://doi.org/10.5953/jmjh.2012.19.2.210.
Article8.Kim SN. Development and evaluation of multifactorial fall prevention program for community dwelling low-income eld-erly people [dissertation]. Seoul: Korea University;2011.9.Park SY., Shin IS. Muscle strengthening effects of exercise programs for preventing falls among the elderly in Korea: a meta-analysis. Physical Therapy Korea. 2011. 18(3):38–48.10.Sherrington C., Whitney JC., Lord SR., Herbert RD., Cumming RG., Close JC. Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2008. 56(12):2234–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.02014.x.
Article11.Park MK., Song LY. Effects of TaiChi on fall risk factors: a meta-analysis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2013. 43(3):341–51. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.341.12.Son YJ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of exercise for fall prevention in the elderly [dissertation]. Seoul: Ajou University;2013.13.Yun CG., An CS. The effect of exercise program on pain and quality of life for patients with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Jounal of Muscle Joint Health. 2014. 21(3):173–83. https://doi.org/10.5953/jmjh.2014.21.3.173.
Article14.Juhl C., Christensen R., Roos EM., Zhang W., Lund H. Impact of exercise type and dose on pain and disability in knee osteo-arthritis: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatology. 2014. 66(3):622–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38290.
Article15.Kim YI., Park JS. A meta-analysis of intervention studies on the effects of self-management in knee osteoarthritis. Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society. 2015. 16(3):1946–56. https://doi.org/10.5762/kais.2015.16.3.1946.
Article16.Kim YI., Choi HS., Han JH., Kim JY., Kim GE. Aquatic exercise for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review & meta analysis. Journal of the Korea Academia- Industrial co-operation Society. 2015. 16(9):6099–111. https://doi.org/10.5762/kais.2015.16.9.6099.17.Oh HS., Seo YO. The comparison between the effects of inte-grated arthritis self-helf programs and the effects of arthritis exercise programs through meta-analysis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 1998. 28(4):941–57. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.4.941.18.Li Y., Su Y., Chen S., Zhang Y., Zhang Z., Liu C, et al. The effects of resistance exercisein patients with knee osteoarthritis: a sys-tematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Rehabilitation. 2016. 30(10):947–59. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269215515610039.19.Panel on Prevention of Falls in Older Persons, American Geriatrics Society and British Geriatrics Society. Summary of the up-dated American geriatrics society/British geriatrics society clinical practice guideline for prevention of falls in older persons. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2011. 59(1):148–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03234.x.20.Kim SY., Park JE., Seo YJ., Jang BH., Son HJ., Suh HS, et al. NECA's guidance for undertaking systematic reviews and meta-analyses for intervention. Seoul: National Evidencebased HealthCare Collaborating Agency;2011. p. 65–78.21.Cohen J. Review: statistical power analysis for the behavioral science,. 2nd ed.Journal of the American Statistical Association;1989. 408(84):p. 1096. https://doi.org/10.2307/2290095.22.Borenstein M., Hedges LV., Higgins JPT., Rothstein HR. Intro-duction to meta-analysis. West Sussex:. John Wiley & Sons;Ltd. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470743386.23.Tufanaru C., Munn Z., Stephenson M., Aromataris E. Fixed or random effects meta-analysis? Common methodological issues in systematic reviews of effectiveness. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare. 2015. 13(3):196–207. https://doi.org/10.1097/xeb.0000000000000065.
Article24.Levinger P., Wallman S., Hill K. Balance dysfunction and falls in people with lower limb arthritis: factors contributing to risk and effectiveness of exercise interventions. European Review of Aging and Physical Activity. 2012. 9(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11556-011-0086-9.
Article25.Vincent KR., Vincent HK. Resistance exercise for knee osteo-arthritis. PM&R. 2012. 4(5):S45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.01.019.
Article26.Hart LE., Haaland DA., Baribeau DA., Mukovozov IM., Sabljic TF. The relationship between exercise and osteoarthritis in the elderly. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine. 2008. 18(6):508–21. https://doi.org/10.1097/jsm.0b013e3181865ed4.
Article27.Hill KD., Williams SB., Chen J., Moran H., Hunt S., Brand C. Balance and falls risk in women with lower limb osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Clinical Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2013. 4(1):22–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcgg.2012.10.003.
Article28.Park SM. Meta-analysis of the interventions for preventing falls by the elderly in the eight countries: comparison between aged 70's and 80's. Journal of the Korean Gerontological Society. 2010. 30(1):49–63.29.Arnold CM., Gyurcsik NC. Risk factors for falls in older adults with lower extremity arthritis: a conceptual framework of cur-rent knowledge and future directions. Physiotherapy Canada. 2012. 64(3):302–14. https://doi.org/10.3138/ptc.2011-12BH.
Article30.Logghe IH., Verhagen AP., Rademaker AC., Bierma SM., Ros-sum E., Faber MJ, et al. The effects of Tai Chi on fall prevention, fear of falling and balance in older people: a meta- analysis. Preventive Medicine. 2010. 51(3):222–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2010.06.003.Fisken AL., Waters DL., Hing WA., Steele M., Keogh JW. Com-parative effects of 2aqua exercise programs on physical function, balance, and perceived quality of life in older adults with osteoarthritis. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy. 2015. 38(1):17–27. https://doi.org/10.1519/jpt.0000000000000019.Lin X., Meijer OG., Lin J., Wu W., Lin X., Liang B, et al. Frontal plane kinematics in walking with moderate hip osteoarthritis: stability and fall risk. Clinical Biomechanics. 2015. 30(8):874–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2015.05.014.
ArticleHale LA., Waters D., Herbison P. A randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of water-based exercise to improve falls risk and physical function in older adults with lower-ex-tremity osteoarthritis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2012. 93(1):27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2011.08.004.
ArticleArnold CM., Faulkner RA., Gyurcsik NC. The relationship between falls efficacy and improvement in fall risk factors fol-lowing an exercise plus educational intervention for older adults with hip osteoarthritis. Physiotherapy Canada. 2011. 63(4):410–20. https://doi.org/10.3138/ptc.2010-29.
ArticleArnold CM., Faulkner RA. The effect of aquatic exercise and education on lowering fall risk in older adults with hip osteo-arthritis. Journal of Aging and Physical Activity. 2010. 18(3):245–60. https://doi.org/10.1123/japa.18.3.245.
ArticleSong R., Roberts BL., Lee EO., Lam P., Bae SC. A randomized study of the effects of T'ai Chi on muscle strength, bone miner-al density, and fear of falling in women with osteoarthritis. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2010. 16(3):227–33. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2009.0165.Lee SS., So YS. The effects of aquatic rehabilitation exercise on pain, physical function, walking ability and falls efficacy in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Korea Journal of Sports Science. 2015. 24(5):1241–51.Im SY., Kim SJ., Hur SH., An KJ., Lee JS. The effect of regular aquatic exercise on balance capacity, physical fitness and per-formance level, and muscular activity in elderly women ar-thritis patients. Journal of Korean Association of Physical Edu-cation and Sport for Girls and Women. 2014. 28(1):37–54.Han SW., Kim KT. The effect of aquarobic and swimming exercise for female elderly suffering from degenerative arthritis on body composition, gait function and pain. Korean Journal of Sports Science. 2012. 21(3):1077–89.Lee MS. Effects of a health diary program on fall-related out-comes in low-income elderly women with osteoarthritis. Journal of Agricultural Medicine and Community Health. 2011. 36(3):167–78. https://doi.org/10.5393/JAMCH.2011.36.3.167.
ArticleJeong YH., Kim JI. Effects of a 9-week self-help management aquatic exercise program on pain, flexibility, balance, fatigue and self-efficacy in the patients with osteoarthritis. Journal of Muscle Joint Health. 2010. 17(1):47–57. https://doi.org/10.5953/jmjh.2010.17.1.047.Kim SA., Kim JI. The effects of the BeHaS exercise program on balance and walking ability in middle-aged women with knee osteoarthritis. Journal of the Korean Academy of Fundamen-tals of Nursing. 2010. 17(1):55–63.Song RY., Eam AY., Lee EO., Lam P., Bae SC. Effects of Tai Chi combined with self-help program on arthritic symptoms and fear of falling in women with osteoarthritis. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 2009. 16(1):46–54.Lee HY., Lee KJ. Effects of Tai Chi exercise in elderly with knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008. 38(1):11–8. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.11.
ArticleKim JL., Lee KJ., Kim SI., Min SH. Effects of BeHaS exercise program on pain, balance, and fall efficacy in elderly with osteoarthritis. Journal of the Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2007. 14(2):181–8.Choi JH., Yoo IY. Effects of Tai Chi self-help program on functional status of knee joint, fatigue, fear of falling for elderly woman patients with knee osteoarthritis. Journal of the Korean Gerontological Society. 2007. 27(4):). 913–27.Lee KY., Jeong OY. The effect of Tai Chi movement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006. 36(2):278–85. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.2.278.
ArticleLee EN., Yoo YW. Effects of a 8-week Tai Chi exercise program on the risk factors for falls in the elderly with osteoarthritis. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 2004. 11(1):61–73.Lim NY., Kim SH., Choi MK., Kim BK., Kim MS., Kim SA, et al. The effects of TaiChi for patients with chronic arthritis. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 2004. 11(2):153–64.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of a Fall Prevention Program on Physical Fitness, Fall Efficacy and Fall Prevention Behavior among Community-dwelling Older Adults
- Characteristics and Effects of Fall Prevention Interventions among the Korean Older Adults: A Systematic Review
- Effects of Nursing Interventions for Fall Prevention in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-analysis
- The Literature Review for Fall in the Elderly
- A Review of Exercise Interventions for Fall Prevention in the Elderly