Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2017 Nov;5(6):307-311. 10.4168/aard.2017.5.6.307.
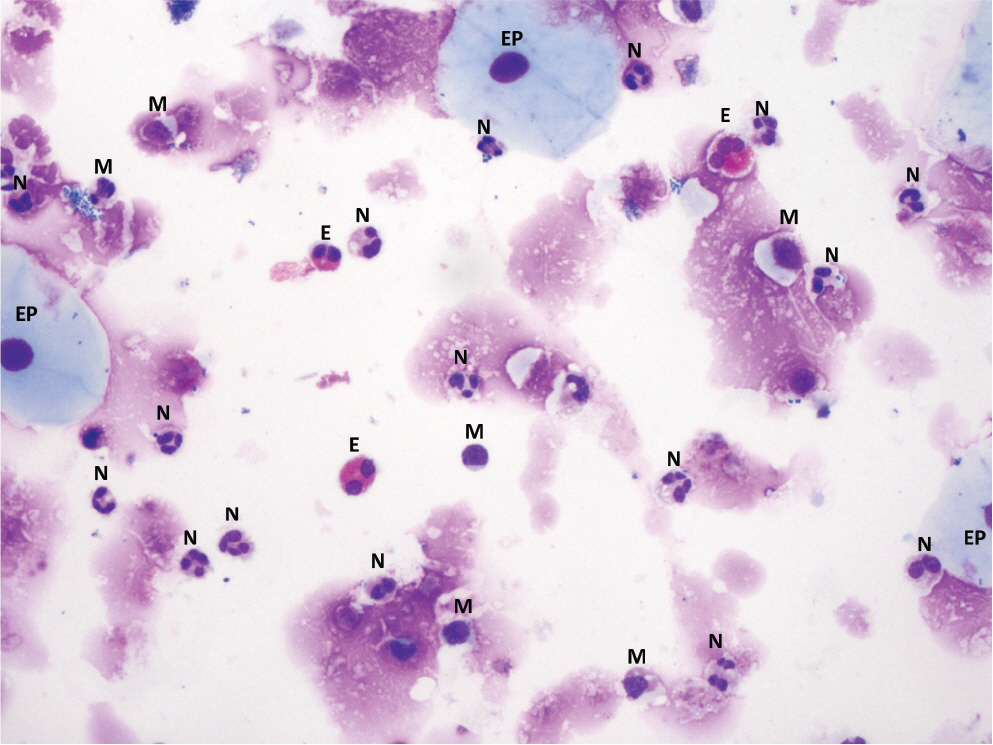
KAAACI Standardization Committee report on the procedure and application of induced sputum examination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government - Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 7Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Division of Allergy, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwjung@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2396670
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2017.5.6.307
Abstract
- Induced sputum and sputum cell count analysis is a test for the diagnosis of various respiratory diseases. In particular, it has long been used as an important biomarker in the diagnosis or characterization of asthma or eosinophilic bronchitis. Despite a relatively long history of this test, there has been no consensus report for conducting and interpreting the analyses in Korea. Based on this awareness and necessity, the Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology launched the Standardization Committee to review the international guidelines and the literature and to develop a consensus report on the diagnostic procedure and interpretation of the sputum induction test.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
KAAACI Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Cough in Adults and Children in Korea
Dae Jin Song, Woo-Jung Song, Jae-Woo Kwon, Gun-Woo Kim, Mi-Ae Kim, Mi-Yeong Kim, Min-Hye Kim, Sang-Ha Kim, Sang-Heon Kim, Sang Hyuck Kim, Sun-Tae Kim, Sae-Hoon Kim, Ja Kyoung Kim, Joo-Hee Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Hyo-Bin Kim, Kyung-Hee Park, Jae Kyun Yoon, Byung-Jae Lee, Seung-Eun Lee, Young Mok Lee, Yong Ju Lee, Kyung-Hwan Lim, You Hoon Jeon, Eun-Jung Jo, Young-Koo Jee, Hyun Jung Jin, Sun Hee Choi, Gyu Young Hur, Sang-Heon Cho, Sang-Hoon Kim, Dae Hyun Lim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(6):591-613. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.6.591.
Reference
-
1. Bickerman HA, Sproul EE, Barach AL. An aerosol method of producing bronchial secretions in human subjects: a clinical technic for the detection of lung cancer. Dis Chest. 1958; 33:347–62.
Article2. Pin I, Gibson PG, Kolendowicz R, Girgis-Gabardo A, Denburg JA, Hargreave FE, et al. Use of induced sputum cell counts to investigate airway inflammation in asthma. Thorax. 1992; 47:25–9.
Article3. Fahy JV, Wong H, Liu J, Boushey HA. Comparison of samples collected by sputum induction and bronchoscopy from asthmatic and healthy subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995; 152:53–8.
Article4. Pizzichini E, Pizzichini MM, Efthimiadis A, Dolovich J, Hargreave FE. Measuring airway inflammation in asthma: eosinophils and eosinophilic cationic protein in induced sputum compared with peripheral blood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:539–44.
Article5. al-Ali MK, Howarth PH. Nitric oxide and the respiratory system in health and disease. Respir Med. 1998; 92:701–15.
Article6. Weiszhar Z, Horvath I. Induced sputum analysis: step by step. Breathe. 2013; 9:300–6.
Article7. Cataldo D, Foidart JM, Lau L, Bartsch P, Djukanovic R, Louis R. Induced sputum: comparison between isotonic and hypertonic saline solution inhalation in patients with asthma. Chest. 2001; 120:1815–21.8. Efthimiadis A, Spanevello A, Hamid Q, Kelly MM, Linden M, Louis R, et al. Methods of sputum processing for cell counts, immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridisation. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2002; 37:19s–23s.9. Spanevello A, Confalonieri M, Sulotto F, Romano F, Balzano G, Migliori GB, et al. Induced sputum cellularity. Reference values and distribution in normal volunteers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 162(3 Pt 1):1172–4.10. Belda J, Leigh R, Parameswaran K, O'Byrne PM, Sears MR, Hargreave FE. Induced sputum cell counts in healthy adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161(2 Pt 1):475–8.
Article11. Kim MY, Jo EJ, Lee SE, Lee SY, Song WJ, Kim TW, et al. Reference ranges for induced sputum eosinophil counts in Korean adult population. Asia Pac Allergy. 2014; 4:149–55.
Article12. Jatakanon A, Lim S, Barnes PJ. Changes in sputum eosinophils predict loss of asthma control. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:64–72.
Article13. Pavord ID, Brightling CE, Woltmann G, Wardlaw AJ. Non-eosinophilic corticosteroid unresponsive asthma. Lancet. 1999; 353:2213–4.14. Green RH, Brightling CE, McKenna S, Hargadon B, Parker D, Bradding P, et al. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 360:1715–21.
Article15. Reddel HK, Taylor DR, Bateman ED, Boulet LP, Boushey HA, Busse WW, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: asthma control and exacerbations: standardizing end-points for clinical asthma trials and clinical practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180:59–99.16. Lougheed MD, Lemiere C, Ducharme FM, Licskai C, Dell SD, Rowe BH, et al. Canadian Thoracic Society 2012 guideline update: diagnosis and management of asthma in preschoolers, children and adults. Can Respir J. 2012; 19:127–64.
Article17. Maestrelli P, Calcagni PG, Saetta M, Di Stefano A, Hosselet JJ, Santonas-taso A, et al. Sputum eosinophilia after asthmatic responses induced by isocyanates in sensitized subjects. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994; 24:29–34.
Article18. Jayaram L, Parameswaran K, Sears MR, Hargreave FE. Induced sputum cell counts: their usefulness in clinical practice. Eur Respir J. 2000; 16:150–8.
Article19. Eltboli O, Brightling CE. Eosinophils as diagnostic tools in chronic lung disease. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2013; 7:33–42.
Article20. D'Urso V, Doneddu V, Marchesi I, Collodoro A, Pirina P, Giordano A, et al. Sputum analysis: non-invasive early lung cancer detection. J Cell Physiol. 2013; 228:945–51.21. Olivieri D, D'Ippolito R, Chetta A. Induced sputum: diagnostic value in interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2000; 6:411–4.
Article22. Bothamley GH, Ditiu L, Migliori GB, Lange C. TBNET contributors. Active case finding of tuberculosis in Europe: a Tuberculosis Network European Trials Group (TBNET) survey. Eur Respir J. 2008; 32:1023–30.
Article23. LaRocque RC, Katz JT, Perruzzi P, Baden LR. The utility of sputum induction for diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in immunocompro-mised patients without human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 37:1380–3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Application of Induced Sputum
- Comparison of Induced Sputum and Bronchoscopy in Diagnosis of Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Brief History of Standardization of Korean Terminology in the Field of Pathology
- Application of Standardization for Causal Inference in Observational Studies: A Step-by-step Tutorial for Analysis Using R Software
- The KAAACI Standardization Committee Report on the procedure and application of the bronchial provocation tests