J Korean Fract Soc.
2011 Jul;24(3):267-270.
Multiple Non-contiguous Spine Fractures with Concomitant Injuries: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. oschae@naver.com
Abstract
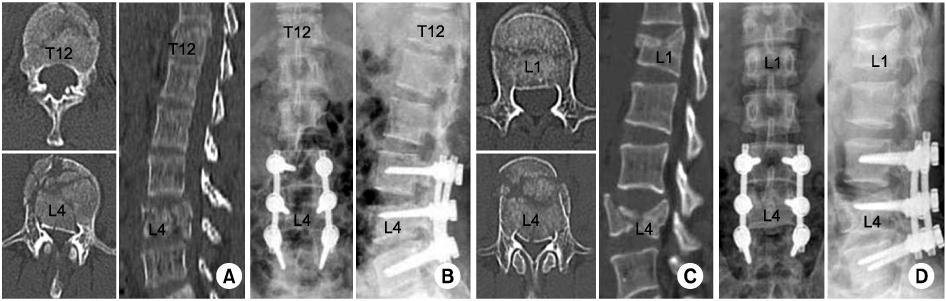
- Multiple non-contiguous spinal fracture is a special type of multi-level spinal injury, which is rare but most frequently occur in motor vehicle accident or a falling from a height. We report five patients of multiple non-contiguous spinal fractures. All patients underwent segmental pedicle screws fixation without fusion for preserving facet joints and minimizing blood loss and operation time. We performed necessary operation for any concomitant injuries at the same day.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chang HG, Kim YW, Kim YC, Kwon DJ, Seo KN, Lee KB. Multiple spine fracture of young adult (Over 3 Vertebrae). J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2005. 12:206–213.
Article2. Dai LY, Jia LS. Multiple non-contiguous injuries of the spine. Injury. 1996. 27:573–575.
Article3. Gardner VO, Amstrong GW. Long-term lumbar facet joint change in spinal fracture patients treated with Harrington rods. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990. 15:479–484.
Article4. Huler RJ. Frymoyer JW, editor. Thoracolumbar Spine Fracture. The adult spine-principles and practice. 1997. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;1473.5. Jorgensen DR, Joseph J Jr. Multiple noncontiguous spine fractures at four levels in a neurologically intact patient. J Trauma. 1996. 41:750–753.
Article6. Kim YM, Kim DS, Choi ES, et al. Results of non-fusion methods in thoracolumbar and lumbar spinal fractures. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2005. 12:132–139.
Article7. Knop C, Fabian HF, Bastian L, Blauth M. Late results of thoracolumbar fractures after posterior instrumentation and transpedicular bone grafting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:88–99.
Article8. Lian XF, Zhao J, Hou TS, Yuan JD, Jin GY, Li ZH. The treatment for multilevel noncontiguous spinal fractures. Int Orthop. 2007. 31:647–652.
Article9. Powell JN, Waddell JP, Tucker WS, Transfeldt EE. Multiple-level noncontiguous spinal fractures. J Trauma. 1989. 28:1146–1150.
Article10. Wittenberg RH, Hargus S, Steffen R, Muhr G, Bötel U. Noncontiguous unstable spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002. 27:254–257.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Multiple Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Spine Fractures: Comparison of Contiguous and Non-Contiguous Fractures in Non-Osteoporotic Patients
- Multiple Noncontiguous Fractures in Cervical Spine: Cases Report
- Non - Contiguous Multiple Spine Fracture
- Twelve Contiguous Spinous Process Fracture of Cervico-Thoracic Spine
- Eleven Levels of Spinous Process Fractures in Thoracolumbar Spine