Clin Endosc.
2017 Sep;50(5):491-494. 10.5946/ce.2017.006.
Long-Term Survival in Stage IV Esophageal Adenocarcinoma with Chemoradiation and Serial Endoscopic Cryoablation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA.
- 2Division of Digestive Diseases, Department of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA. field.willingham@emory.edu
- 3Emory Winship Cancer Institute, Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA.
- 4Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA.
- KMID: 2394750
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.006
Abstract
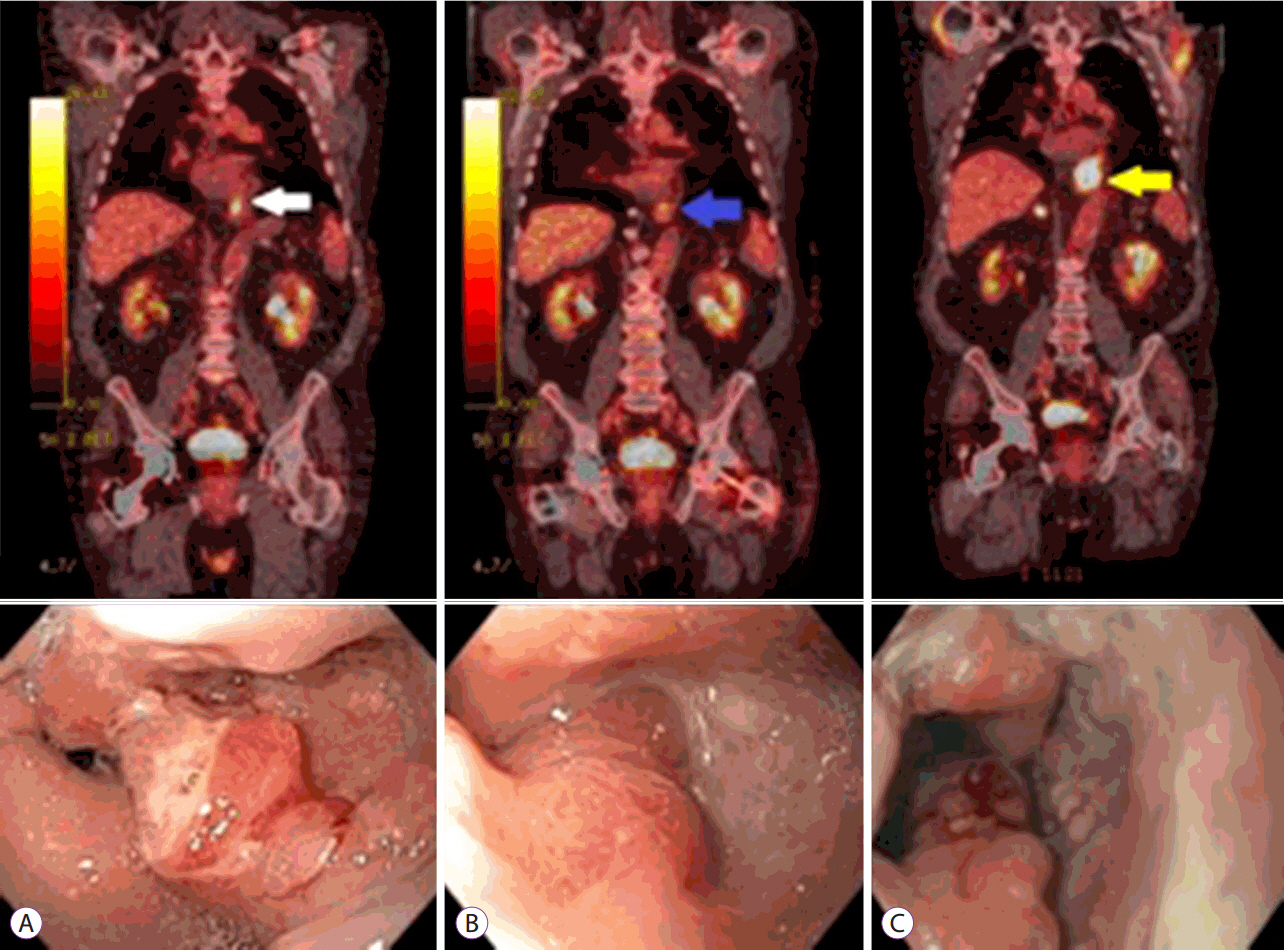
- Esophageal cancer has a poor overall prognosis and is frequently diagnosed at a late stage. Conventional treatment for metastatic esophageal cancer involves chemotherapy and radiation. Local disease control plays a significant role in improving survival. Endoscopic spray cryotherapy is a novel modality that involves freezing and thawing to produce local ablation of malignant tissue via ischemic mechanisms. Spray cryotherapy has been shown to be effective, particularly for early T-stage, superficial esophageal adenocarcinomas. We present the case of a 72-year-old-male with locally recurrent stage IV esophageal adenocarcinoma and long-term survival of 7 years to date, with concurrent chemoradiation and serial cryoablation. He remains asymptomatic and continues to undergo chemotherapy and sequential cryoablation. The findings highlight the long-term safety and efficacy of cryotherapy in combination with chemoradiation, and suggest that cryoablation may have an additive role in the treatment of advanced stage esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Khangura SK, Greenwald BD. Endoscopic management of esophageal cancer after definitive chemoradiotherapy. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:1477–1485.
Article2. Greenwald BD, Dumot JA. Cryotherapy for Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011; 27:363–367.
Article3. Gan S, Watson DI. New endoscopic and surgical treatment options for early esophageal adenocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:1478–1484.
Article4. Greenwald BD, Dumot JA, Abrams JA, et al. Endoscopic spray cryotherapy for esophageal cancer: safety and efficacy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:686–693.
Article5. Ilson DH. Esophageal cancer chemotherapy: recent advances. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2008; 2:85–92.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long Term Survival after the Resection of Esophageal Cancer
- Long-term survival after concurrent chemoradiation therapy for esophageal cancer with tracheal invasion
- Management of Clinical T1N0M0 Esophageal Cancer
- A Case of Recurrence after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Arising from Barrett's Esophagus
- Epidemiology of and Risk Factors for Esophageal Cancer in Korea