Imaging Sci Dent.
2017 Jun;47(2):123-127. 10.5624/isd.2017.47.2.123.
Therapeutic effect of intraductal irrigation of the salivary gland: A technical report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology and Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. hmslsh@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2389893
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2017.47.2.123
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Obstructive and inflammatory disease often occurs in the major salivary glands, and no predictive treatment has yet been developed for this condition. The aim of this report was to introduce an intraductal irrigation procedure and to illustrate its application to practical patient cases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
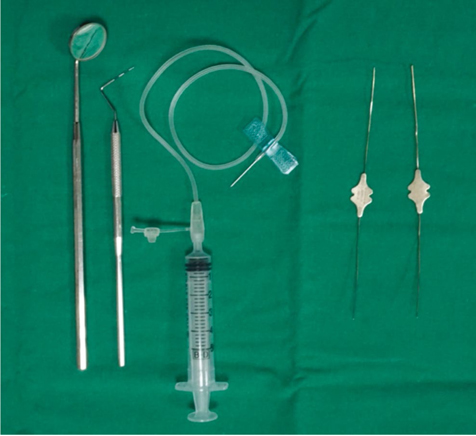
Two patients complaining of pain and swelling in the parotid gland during meals who underwent sialography were diagnosed as having sialodochitis with sialadenitis. Intraductal irrigation was then performed on the parotid gland on the side of the complaint. The irrigation procedure was conducted in the same manner as the sialography procedure, except that saline was used as the filling solution. Symptom severity was evaluated with a numerical rating scale (NRS) at the initial visit and a month after the irrigation.
RESULTS
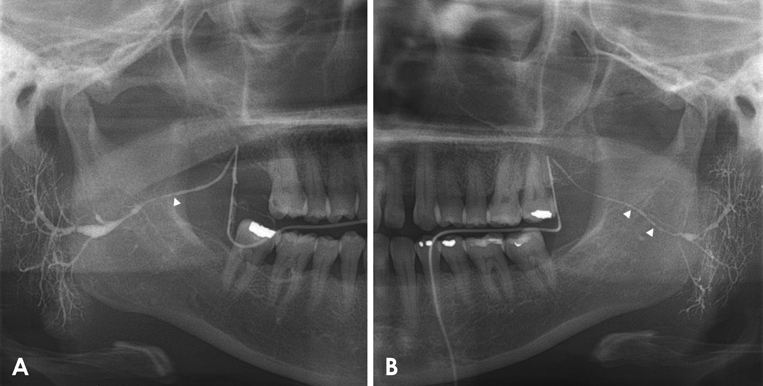
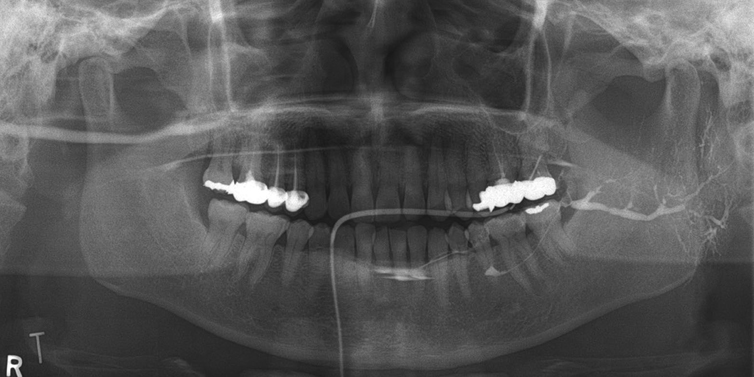
The initial NRS value of patient 1 was 10. The value decreased to 6 and then to 0 after 2 irrigation procedures. The NRS value of patient 2 regarding the symptoms involving the left parotid gland decreased from 4-5 to 1 after 4 irrigation procedures performed at 1-month intervals.
CONCLUSION
Intraductal irrigation of the salivary gland may be a simple, safe, and effective treatment option for patients with obstructive and inflammatory disease of the salivary gland that is capable of resolving their symptoms.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Epker BN. Obstructive and inflammatory diseases of the major salivary glands. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1972; 33:2–27.
Article2. Kim JH, Aoki EM, Cortes AR, Abdala-Júnior R, Asaumi J, Arita ES. Comparison of the diagnostic performance of panoramic and occlusal radiographs in detecting submandibular sialoliths. Imaging Sci Dent. 2016; 46:87–92.
Article3. Abdel-Wahed N, Amer ME, Abo-Taleb NS. Assessment of the role of cone beam computed sialography in diagnosing salivary gland lesions. Imaging Sci Dent. 2013; 43:17–23.
Article4. Triantafyllou A, Harrison JD, Garrett JR. Analytical ultrastructural investigation of microliths in salivary glands of cat. Histochem J. 1993; 25:183–190.
Article5. Eisenbud L, Cranin N. The role of sialography in the diagnosis and therapy of chronic obstructive sialadenitis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1963; 16:1181–1199.
Article6. Bates D, O'Brien CJ, Tikaram K, Painter DM. Parotid and submandibular sialadenitis treated by salivary gland excision. Aust N Z J Surg. 1998; 68:120–124.
Article7. Hsu AK, Kutler DI. Indications, techniques and complications of major salivary gland extirpation. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009; 21:313–321.
Article8. Izumi M, Eguchi K, Nakamura H, Takagi Y, Kawabe Y, Nakamura T. Corticosteroid irrigation of parotid gland for treatment of xerostomia in patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998; 57:464–469.9. Antoniades D, Harrison JD, Epivatianos A, Papanayotou P. Treatment of chronic sialadenitis by intraductal penicillin or saline. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 62:431–434.
Article10. Pace CG, Hwang KG, Papadaki M, Troulis MJ. Interventional sialoendoscopy for treatment of obstructive sialadenitis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72:2157–2166.
Article11. Drage NA, Brown JE, Wilson RF. Pain and swelling after sialography: is it a significant problem? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000; 90:385–388.
Article12. Hawker GA, Mian S, Kendzerska T, French M. Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011; 63:Suppl 11. S240–S252.13. Buckenham TM, Page JE, Jeddy T. Technical report: interventional sialography - balloon dilatation of a Stensen's duct stricture using digital subtraction sialography. Clin Radiol. 1992; 45:34.
Article14. Choi JS, Lim JY, Kim YM. Sialendoscopy. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2011; 54:819–827.
Article15. Walvekar RR, Razfar A, Carrau RL, Schaitkin B. Sialendoscopy and associated complications: a preliminary experience. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118:776–779.
Article16. Nahlieli O, Baruchin AM. Long-term experience with endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of salivary gland inflammatory diseases. Laryngoscope. 2000; 110:988–993.
Article