Korean J Pain.
2017 Jul;30(3):220-228. 10.3344/kjp.2017.30.3.220.
Comparison of clinical efficacy in epidural steroid injections through transforaminal or parasagittal approaches
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea. swon13@daum.net
- 2Department of Psychiatry, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicin, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2385355
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2017.30.3.220
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The transforaminal (TF) epidural steroid injection (ESI) is suggested as more effective than the interlaminar (IL) route due to higher delivery of medication at the anterior epidural space. However, serious complications such as spinal cord injury and permanent neural injury have been reported. The purpose of this study is to evaluate and compare the clinical effectiveness, technical ease, and safety of the TF and parasagittal IL (PIL) ESI.
METHODS
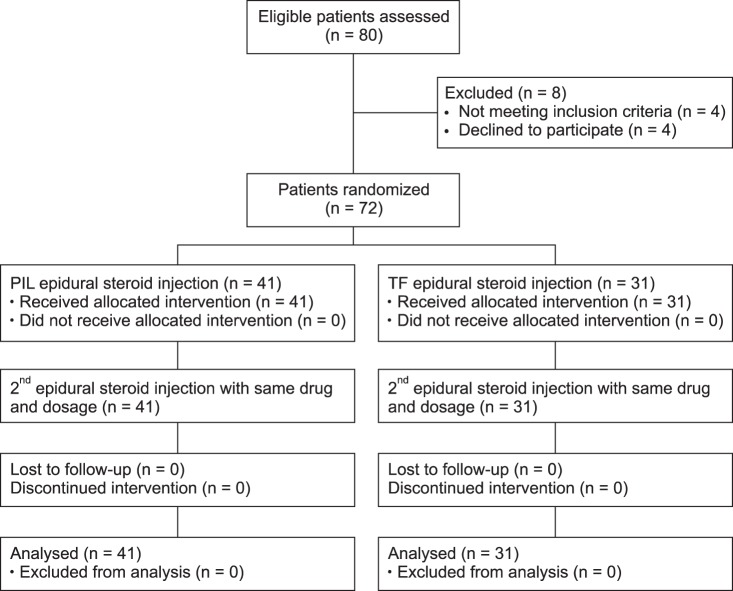
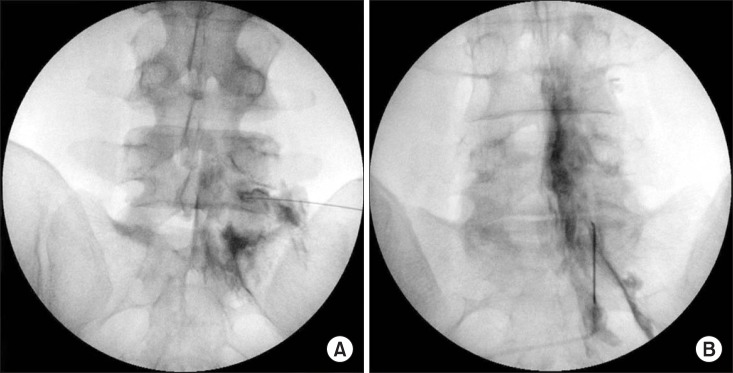
A total of 72 patients were randomized to either the PIL group (n = 41) or the TF group (n = 31) under fluoroscopic guidance. Patients were evaluated for effective pain relief by the numerical rating scale (NRS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) (%) before and 2 weeks after the ESI. The presence of concordant paresthesia, anterior epidural spread, total procedure time, and exposed radiation dose were also evaluated.
RESULTS
Both the PIL and TF approach produced similar clinically significant improvements in pain and level of disability. Among the 72 patients, 27 PIL (66%) and 20 TF (64%) patients showed concordant paresthesia while 14 (34%) and 11 (36%) patients in the same respective order showed disconcordant or no paresthesia. Radiation dose and total procedure time required were compared; the PIL group showed a significantly lower radiation dose (30.2 ± 12 vs. 80.8 ± 26.8 [Cgy/cm²]) and shorter procedure time (96.2 ± 31 vs. 141.6 ± 30 seconds).
CONCLUSIONS
ESI under fluoroscopic guidance with PIL or TF approach were effective in reducing the NRS and ODI. PIL ESI was a technically easier and simple method compared to TF ESI.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Unintentional lumbar facet joint injection guided by fluoroscopy during interlaminar epidural steroid injection: a retrospective analysis
Min Jae Kim, Yun Suk Choi, Hae Jin Suh, You Jin Kim, Byeong Jin Noh
Korean J Pain. 2018;31(2):87-92. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.2.87.Effect of needle type on intravascular injection in transforaminal epidural injection: a meta-analysis
Jae Yun Kim, Soo Nyoung Kim, Chulmin Park, Ho Young Lim, Jae Hun Kim
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(1):39-46. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.1.39.
Reference
-
1. Manchikanti L, Buenaventura RM, Manchikanti KN, Ruan X, Gupta S, Smith HS, et al. Effectiveness of therapeutic lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections in managing lumbar spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:E199–E245. PMID: 22622912.2. Chou R, Baisden J, Carragee EJ, Resnick DK, Shaffer WO, Loeser JD. Surgery for low back pain: a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:1094–1109. PMID: 19363455.3. Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Howard J. Fusion and non-surgical treatment for symptomatic lumbar degenerative disease: a systematic review of Oswestry Disability Index and MOS Short Form-36 outcomes. Spine J. 2008; 8:747–755. PMID: 18037354.
Article4. Cohen SP, Bicket MC, Jamison D, Wilkinson I, Rathmell JP. Epidural steroids: a comprehensive, evidence-based review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013; 38:175–200. PMID: 23598728.5. Manchikanti L, Knezevic NN, Boswell MV, Kaye AD, Hirsch JA. Epidural injections for lumbar radiculopathy and spinal stenosis: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 2016; 19:E365–E410. PMID: 27008296.6. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Pampati V, Falco FJ, Hirsch JA. Comparison of the efficacy of caudal, interlaminar, and transforaminal epidural injections in managing lumbar disc herniation: is one method superior to the other? Korean J Pain. 2015; 28:11–21. PMID: 25589942.
Article7. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, Pampati V, Falco FJ. Transforaminal epidural injections in chronic lumbar disc herniation: a randomized, double-blind, active-control trial. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:E489–E501. PMID: 25054399.8. Kraiwattanapong C, Wechmongkolgorn S, Chatriyanuyok B, Woratanarat P, Udomsubpayakul U, Chanplakorn P, et al. Outcomes of fluoroscopically guided lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis patients. Asian Spine J. 2014; 8:119–128. PMID: 24761192.
Article9. Gharibo CG, Varlotta GP, Rhame EE, Liu EC, Bendo JA, Perloff MD. Interlaminar versus transforaminal epidural steroids for the treatment of subacute lumbar radicular pain: a randomized, blinded, prospective outcome study. Pain Physician. 2011; 14:499–511. PMID: 22086091.10. Ghai B, Bansal D, Kay JP, Vadaje KS, Wig J. Transforaminal versus parasagittal interlaminar epidural steroid injection in low back pain with radicular pain: a randomized, double-blind, active-control trial. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:277–290. PMID: 25054387.11. Ghai B, Vadaje KS, Wig J, Dhillon MS. Lateral parasagittal versus midline interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injection for management of low back pain with lumbosacral radicular pain: a double-blind, randomized study. Anesth Analg. 2013; 117:219–227. PMID: 23632053.
Article12. Kennedy DJ, Dreyfuss P, Aprill CN, Bogduk N. Paraplegia following image-guided transforaminal lumbar spine epidural steroid injection: two case reports. Pain Med. 2009; 10:1389–1394. PMID: 19863744.
Article13. Candido KD, Katz JA, Chinthagada M, McCarthy RA, Knezevic NN. Incidence of intradiscal injection during lumbar fluoroscopically guided transforaminal and interlaminar epidural steroid injections. Anesth Analg. 2010; 110:1464–1467. PMID: 20418306.
Article14. Thefenne L, Dubecq C, Zing E, Rogez D, Soula M, Escobar E, et al. A rare case of paraplegia complicating a lumbar epidural infiltration. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2010; 53:575–583. PMID: 20870478.
Article15. Lyders EM, Morris PP. A case of spinal cord infarction following lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injection: MR imaging and angiographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:1691–1693. PMID: 19369604.
Article16. Levi D, Horn S, Corcoran S. The incidence of intradiscal, intrathecal, and intravascular flow during the performance of retrodiscal (infraneural) approach for lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections. Pain Med. 2016; 17:1416–1422. PMID: 26814293.
Article17. Candido KD, Raghavendra MS, Chinthagada M, Badiee S, Trepashko DW. A prospective evaluation of iodinated contrast flow patterns with fluoroscopically guided lumbar epidural steroid injections: the lateral parasagittal interlaminar epidural approach versus the transforaminal epidural approach. Anesth Analg. 2008; 106:638–644. PMID: 18227326.
Article18. Hong J, Jung S. Clinical effectiveness and prognostic indicators of parasagittal interlaminar epidural injection. Pain Physician. 2016; 19:E877–E884. PMID: 27454278.19. Gupta R, Singh S, Kaur S, Singh K, Aujla K. Correlation between epidurographic contrast flow patterns and clinical effectiveness in chronic lumbar discogenic radicular pain treated with epidural steroid injections via different approaches. Korean J Pain. 2014; 27:353–359. PMID: 25317285.
Article20. Jo SA, Park MH, Jo I, Ryu SH, Han C. Usefulness of Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) in the Korean elderly population. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007; 22:218–223. PMID: 17044132.
Article21. Botwin KP, Natalicchio J, Hanna A. Fluoroscopic guided lumbar interlaminar epidural injections: a prospective evaluation of epidurography contrast patterns and anatomical review of the epidural space. Pain Physician. 2004; 7:77–80. PMID: 16868616.22. Hashemi M, Mofrad MK, Mohajerani SA, Kazemi SM, Radpey B, Zali A. Anatomical flow pattern of contrast in lumbar epidural space: a human study with a midline vs. parasagittal interlaminar approach under fluoroscopy. Pain Physician. 2015; 18:317–324. PMID: 26218934.23. Candido KD, Rana MV, Sauer R, Chupatanakul L, Tharian A, Vasic V, et al. Concordant pressure paresthesia during interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injections correlates with pain relief in patients with unilateral radicular pain. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:497–511. PMID: 24077196.24. Sinofsky AH, Aydin SM, Kim E, Gharibo CG. Concordant provocation as a prognostic indicator during interlaminar lumbosacral epidural steroid injections. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:247–253. PMID: 24850106.25. McCormick Z, Margolis S, Temme K, Rivers E, Cameron SA, Smith MC, et al. Concordant pain provocation during transforaminal epidural steroid injection for lumbosacral radiculopathy: effect on pain outcome and predictive factors. Pain Physician. 2015; 18:E19–E26. PMID: 25675066.26. Kim S, Shin JH, Lee JW, Kang HS, Lee GY, Ahn JM. Factors affecting radiation exposure during lumbar epidural steroid injection: a prospective study in 759 patients. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:405–412. PMID: 27134528.
Article27. Derby R, Melnik I, Choi J, Lee SH, Lee JE. Reliability and safety of contra-lateral oblique view for interlaminar epidural needle placement. Pain Physician. 2017; 20:E65–E73. PMID: 28072798.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between Epidurographic Contrast Flow Patterns and Clinical Effectiveness in Chronic Lumbar Discogenic Radicular Pain Treated with Epidural Steroid Injections Via Different Approaches
- Lumbar Ventral Epidural Approach
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Caudal, Interlaminar, and Transforaminal Epidural Injections in Managing Lumbar Disc Herniation: Is One Method Superior to the Other?
- Comparison of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection and Lumbar/Caudal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
- Epidural Steroid Injection