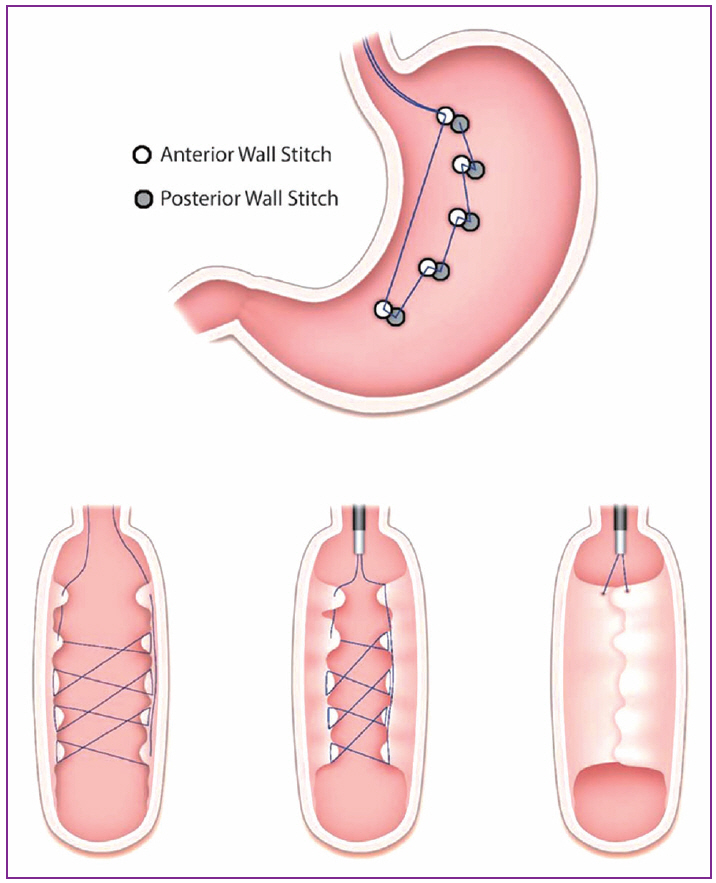
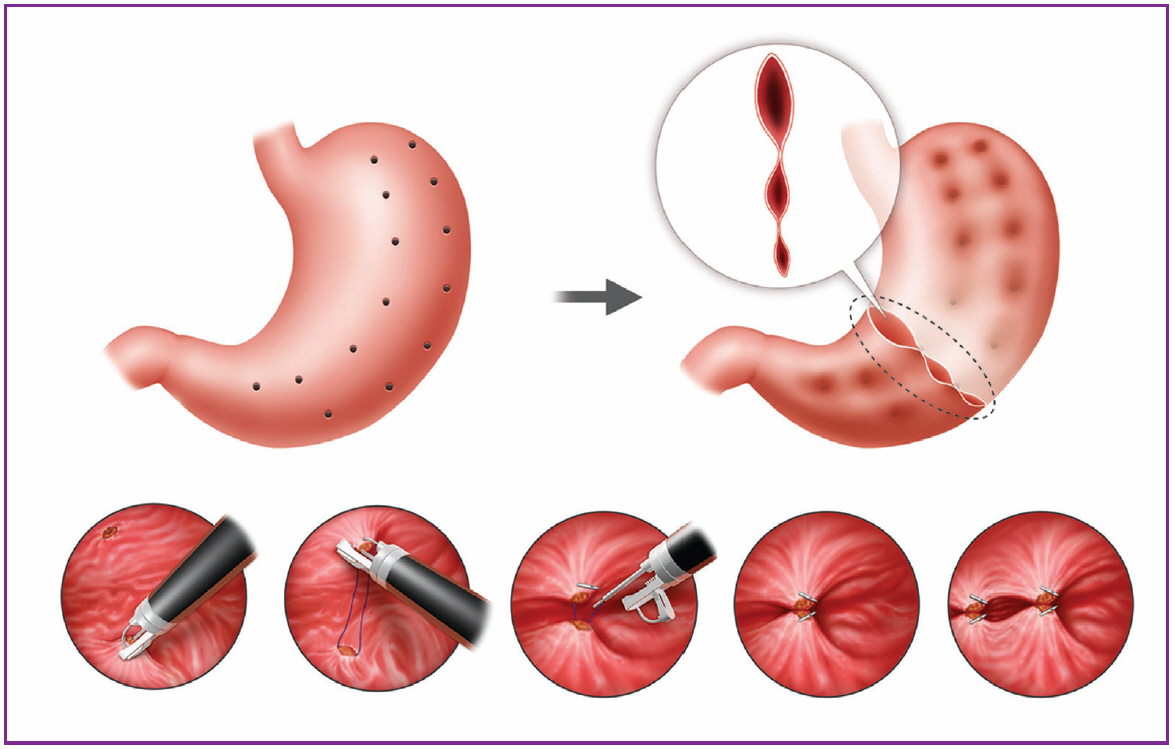
Clin Endosc.
2017 Jan;50(1):21-25. 10.5946/ce.2016.147.
Role of Endoscopic Gastroplasty Techniques in the Management of Obesity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. c73138@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2383486
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.147
Abstract
- Health and wellness represent a major global concern. Trends such as a lack of exercise and excessive consumption of calories are major causes of the rapid increase in obesity worldwide. Obesity should be controlled because it can result in other illnesses, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, coronary artery disease, stroke, breathing disorders, or cancer. However, many people have difficulty in managing obesity through exercise, dietary control, behavioral modifications, and drug therapy. Bariatric surgery is not commonly used due to a variety of complications, even though it has been demonstrated to produce reliable results with respect to adequate weight loss when performed using an open or a laparoscopic approach. Endoscopic bariatric procedures are emerging techniques that are less invasive and safer compared with current surgical approaches. However, the evaluation of endoluminal procedures is limited by the small number of studies and their short-term follow-up.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim CH, Kim KJ, Kim BY, et al. Prediabetes is not independently associated with microalbuminuria in Korean general population: the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2011-2012 (KNHANES V-2,3). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014; 106:e18–e21.
Article2. Kannel WB, Cupples LA, Ramaswami R, Stokes J 3rd, Kreger BE, Higgins M. Regional obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease; the Framingham study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991; 44:183–190.
Article3. Mathus-Vliegen EM. Obesity and the gastroenterologist. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:608–611.
Article4. Ponce J, Nguyen NT, Hutter M, Sudan R, Morton JM. American society for metabolic and bariatric surgery estimation of bariatric surgery procedures in the United States, 2011-2014. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015; 11:1199–1200.
Article5. Pandolfino JE, Krishnamoorthy B, Lee TJ. Gastrointestinal complications of obesity surgery. MedGenMed. 2004; 6:15.6. Fobi MA. Surgical treatment of obesity: a review. J Natl Med Assoc. 2004; 96:61–75.7. Mason EE. Vertical banded gastroplasty for obesity. Arch Surg. 1982; 117:701–706.
Article8. Laws HL. Standardized gastroplasty orifice. Am J Surg. 1981; 141:393–394.
Article9. Chua TY, Mendiola RM. Laparoscopic vertical banded gastroplasty: the Milwaukee experience. Obes Surg. 1995; 5:77–80.
Article10. Sugerman HJ, Londrey GL, Kellum JM, et al. Weight loss with vertical banded gastroplasty and Roux-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity with selective versus random assignment. Am J Surg. 1989; 157:93–102.
Article11. Stimac D, Majanović SK. Endoscopic approaches to obesity. Dig Dis. 2012; 30:187–195.
Article12. Thompson CC. Endoscopic therapy of obesity: a new paradigm in bariatric care. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:505–507.
Article13. Devière J, Ojeda Valdes G, Cuevas Herrera L, et al. Safety, feasibility and weight loss after transoral gastroplasty: first human multicenter study. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:589–598.
Article14. Familiari P, Boškoski I, Marchese M, Perri V, Costamagna G. Endoscopic treatment of obesity. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 5:689–701.
Article15. Moreno C, Closset J, Dugardeyn S, et al. Transoral gastroplasty is safe, feasible, and induces significant weight loss in morbidly obese patients: results of the second human pilot study. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:406–413.
Article16. Jafri SM, Arora G, Triadafilopoulos G. What is left of the endoscopic antireflux devices? Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009; 25:352–357.
Article17. Mahmood Z, McMahon BP, Arfin Q, et al. Endocinch therapy for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a one year prospective follow up. Gut. 2003; 52:34–39.
Article18. Fogel R, De Fogel J, Bonilla Y, De La Fuente R. Clinical experience of transoral suturing for an endoluminal vertical gastroplasty: 1-year follow-up in 64 patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:51–58.
Article19. Brethauer SA, Chand B, Schauer PR, Thompson CC. Transoral gastric volume reduction as intervention for weight management: 12-month follow-up of TRIM trial. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2012; 8:296–303.
Article20. López-Nava G, Bautista-Castaño I, Jimenez A, de Grado T, Fernandez-Corbelle JP. The primary obesity surgery endolumenal (POSE) procedure: one-year patient weight loss and safety outcomes. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015; 11:861–865.
Article21. Abu Dayyeh BK, Rajan E, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: a potential endoscopic alternative to surgical sleeve gastrectomy for treatment of obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:530–535.
Article22. Lopez-Nava G, Galvão MP, da Bautista-Castaño I, Jimenez A, De Grado T, Fernandez-Corbelle JP. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for the treatment of obesity. Endoscopy. 2015; 47:449–452.
Article23. Lopez-Nava G, Sharaiha RZ, Neto MG, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for obesity: a multicenter study of 242 patients with 18 months follow-up. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150(4 Suppl 1):S26.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Bariatric Endoscopy in Obesity Control
- Role of Malabsorptive Endoscopic Procedures in Obesity Treatment
- Endoluminal Gastroplasty for Obesity Treatment: Emerging Technology and Obstacles
- Recent Trends in Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies
- The Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty as an Alternative to Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy