J Pathol Transl Med.
2015 Sep;49(5):382-388. 10.4132/jptm.2015.07.10.
Membranous Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF1R) Expression Is Predictive of Poor Prognosis in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chungjh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2381393
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.10
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) is a membrane receptor-type tyrosine kinase that has attracted considerable attention as a potential therapeutic target, although its clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is controversial. This study aimed to clarify the clinical significance of IGF1R expression in human NSCLC.
METHODS
IGF1R protein expression was evaluated using immunohistochemistry in 372 patients with NSCLC who underwent curative surgical resection (146 squamous cell carcinomas [SqCCs] and 226 adenocarcinomas [ADCs]). We then analyzed correlations between expression of IGF1R and clinicopathological and molecular features and prognostic significance.
RESULTS
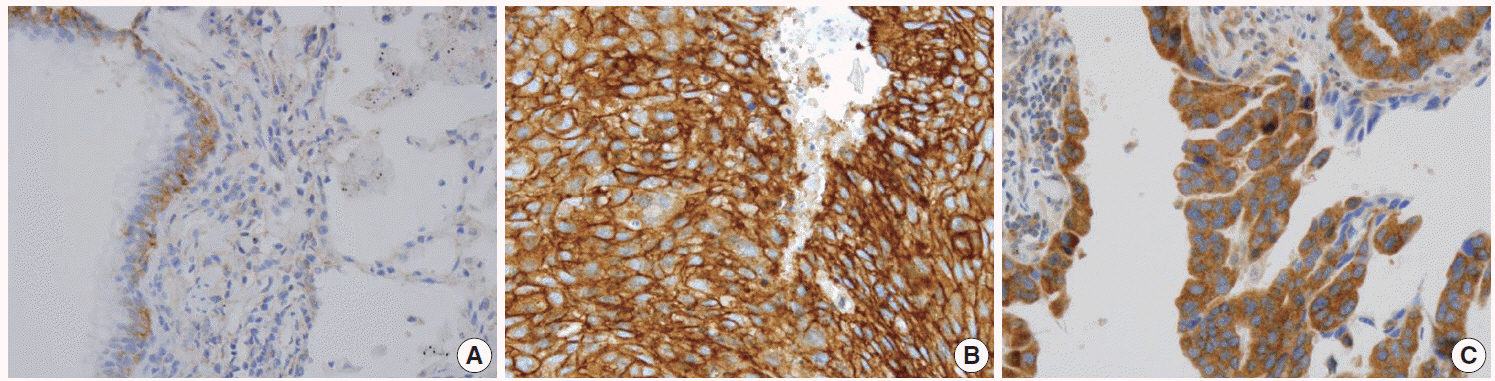
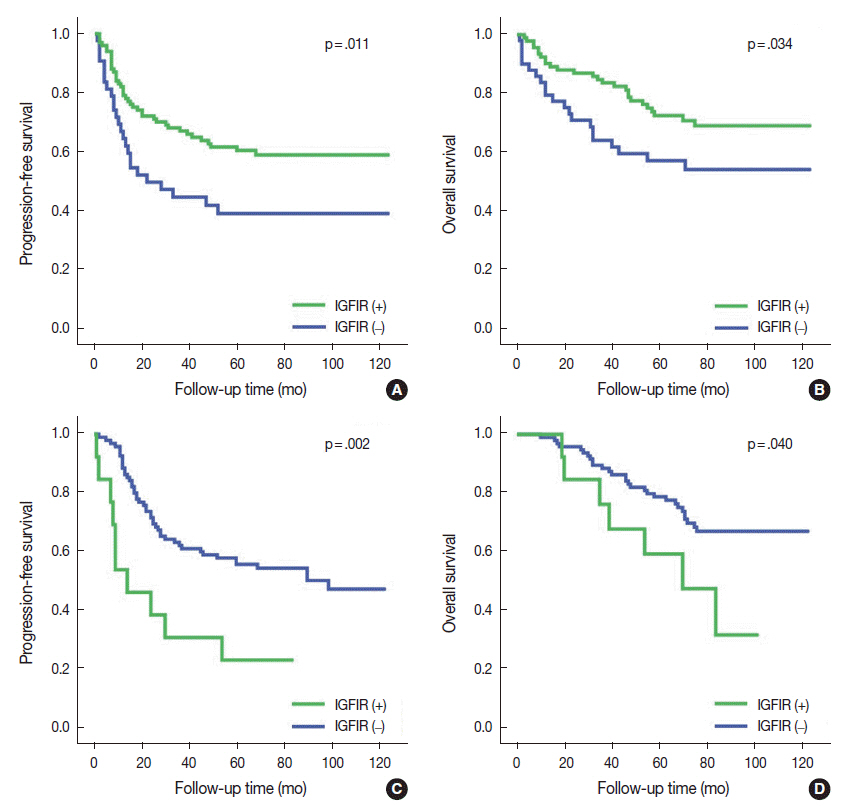
Membranous and cytoplasmic IGF1R expression were significantly higher in SqCCs than in ADCs. In patients with SqCC, membranous IGF1R expression was associated with absence of vascular, lymphatic, and perineural invasion; lower stage; and better progression-free survival (PFS) (hazard ratio [HR], 0.586; p = .040). In patients with ADC, IGF1R expression did not have a significant prognostic value; however, in the subgroup of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant ADC, membranous IGF1R expression was associated with lymphatic and perineural invasion, solid predominant histology, and higher cancer stage and was significantly associated with worse PFS (HR, 2.582; p = .009).
CONCLUSIONS
Lung ADC and SqCC showed distinct IGF1R expression profiles that demonstrated prognostic significance. High membranous IGF1R expression was predictive of poor PFS in EGFR-mutant lung ADC, while it was predictive of better PFS in SqCC. These findings will help improve study design for subsequent investigations and select patients for future anti-IGF1R therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma*
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell
Cytoplasm
Disease-Free Survival
Epidermal Growth Factor*
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Lung
Membranes
Prognosis*
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor*
Epidermal Growth Factor
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:947–57.
Article2. Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:2866–74.
Article3. Yun CH, Mengwasser KE, Toms AV, et al. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:2070–5.4. Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007; 316:1039–43.5. Ward CW, Garrett TP, McKern NM, et al. The three dimensional structure of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Mol Pathol. 2001; 54:125–32.
Article6. Blakesley VA, Stannard BS, Kalebic T, Helman LJ, LeRoith D. Role of the IGF-I receptor in mutagenesis and tumor promotion. J Endocrinol. 1997; 152:339–44.
Article7. Bianconi F, Baldelli E, Ludovini V, Crino L, Flacco A, Valigi P. Computational model of EGFR and IGF1R pathways in lung cancer: a systems biology approach for translational oncology. Biotechnol Adv. 2012; 30:142–53.
Article8. Ludovini V, Bellezza G, Pistola L, et al. High coexpression of both insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGFR-1) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is associated with shorter disease-free survival in resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:842–9.
Article9. Dziadziuszko R, Merrick DT, Witta SE, et al. Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) gene copy number is associated with survival in operable non-small-cell lung cancer: a comparison between IGF1R fluorescent in situ hybridization, protein expression, and mRNA expression. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:2174–80.
Article10. Cappuzzo F, Tallini G, Finocchiaro G, et al. Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) expression and survival in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21:562–7.
Article11. van der Veeken J, Oliveira S, Schiffelers RM, Storm G, van Bergen En Henegouwen PM, Roovers RC. Crosstalk between epidermal growth factor receptor- and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling: implications for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009; 9:748–60.12. Morgillo F, Hong WK, Lee H. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) heterodimerization and resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:13032.13. Kikuchi R, Sonobe M, Kobayashi M, et al. Expression of IGF1R is associated with tumor differentiation and survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19 Suppl 3:S412–20.
Article14. Tsuta K, Mimae T, Nitta H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor protein expression and gene copy number alterations in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2013; 44:975–82.
Article15. Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer;2010.16. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A, Nicholson AG. WHO classification of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2015.17. Lee HJ, Xu X, Kim H, et al. Comparison of direct sequencing, PNA clamping-real time polymerase chain reaction, and pyrosequencing methods for the detection of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung carcinoma and the correlation with clinical responses to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Korean J Pathol. 2013; 47:52–60.18. Kim H, Yoo SB, Choe JY, et al. Detection of ALK gene rearrangement in non-small cell lung cancer: a comparison of fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromogenic in situ hybridization with correlation of ALK protein expression. J Thorac Oncol. 2011; 6:1359–66.19. Jin Y, Sun PL, Kim H, et al. MET gene copy number gain is an independent poor prognostic marker in Korean stage I lung adenocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:621–8.20. Jin Y, Sun PL, Kim H, et al. ROS1 gene rearrangement and copy number gain in non-small cell lung cancer. Virchows Arch. 2015; 466:45–52.21. Reinmuth N, Kloos S, Warth A, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 pathway mutations and protein expression in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Hum Pathol. 2014; 45:1162–8.
Article22. Sutherland KD, Berns A. Cell of origin of lung cancer. Mol Oncol. 2010; 4:397–403.
Article23. Gately K, Forde L, Cuffe S, et al. High coexpression of both EGFR and IGF1R correlates with poor patient prognosis in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2014; 15:58–66.
Article24. Yeo CD, Park KH, Park CK, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) predicts poor responses to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring activating EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer. 2015; 87:311–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinicopathologic Analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Status in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Protein Expression, Gene Amplification and Survival Analysis
- Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor, Transforming Growth Factor-alphaand Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Human Trophoblast and Decidua
- Small Cell Lung Cancer with Mutation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma Resistant to Gefitinib
- Cell proliferatiion status, p53 protein and epidermal growth factor receptor(EGFR) expression-correlation with early recurrence in colorectal adenocarcinoma
- Correlation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression with prognostic factors in patients with ovarian neoplasms