Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jul;56(4):1155-1157. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1155.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome after the Use of Gadolinium Contrast Media
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2366361
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.4.1155
Abstract
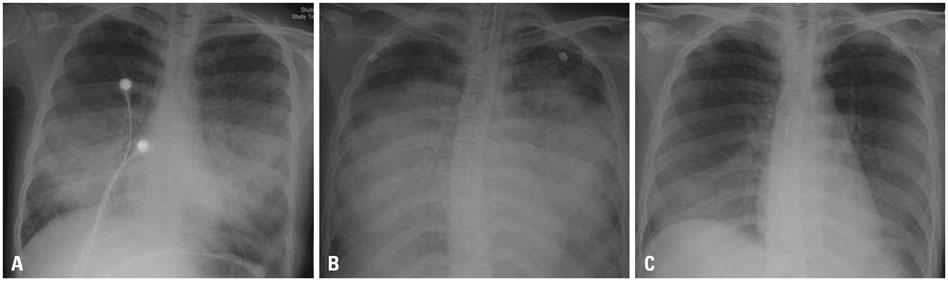
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a medical emergency that threatens life. To this day, ARDS is very rarely reported by iodine contrast media, and there is no reported case of ARDS induced by gadolinium contrast media. Here, we present a case with ARDS after the use of gadobutrol (Gadovist) as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast medium. A 26 years old female without any medical history, including allergic diseases and without current use of drugs, visited the emergency room for abdominal pain. Her abdominopelvic computed tomography with iodine contrast media showed a right ovarian cyst and possible infective colitis. Eighty-three hours later, she underwent pelvis MRI after injection of 7.5 mL (0.1 mL/kg body weight) of gadobutrol (Gadovist) to evaluate the ovarian cyst. She soon presented respiratory difficulty, edema of the lips, nausea, and vomiting, and we could hear wheezing upon auscultation. She was treated with dexamethasone, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. Her chest X-ray showed bilateral central bat-wing consolidative appearance. Managed with mechanical ventilation, she was extubated 3 days later and discharged without complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Scott LJ. Gadobutrol: a review of its use for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in adults and children. Clin Drug Investig. 2013; 33:303–314.
Article2. Boden WE. Anaphylactoid pulmonary edema ("shock lung") and hypotension after radiologic contrast media injection. Chest. 1982; 81:759–761.
Article3. Solomon DR. Anaphylactoid reaction and non-cardiac pulmonary edema following intravenous contrast injection. Am J Emerg Med. 1986; 4:146–149.
Article4. Herborn CU, Honold E, Wolf M, Kemper J, Kinner S, Adam G, et al. Clinical safety and diagnostic value of the gadolinium chelate gadoterate meglumine (Gd-DOTA). Invest Radiol. 2007; 42:58–62.
Article5. Nicholas BA, Vricella GJ, Smith M, Passalacqua M, Gulani V, Ponsky LE. Contrast-induced nephropathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: minimizing the risk. Can J Urol. 2012; 19:6074–6080.6. Bakowitz M, Bruns B, McCunn M. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in the injured patient. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2012; 20:54.
Article7. Brockow K, Sánchez-Borges M. Hypersensitivity to contrast media anddyes. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2014; 34:547–564.8. Forsting M, Palkowitsch P. Prevalence of acute adverse reactions to gadobutrol--a highly concentrated macrocyclic gadolinium chelate: review of 14,299 patients from observational trials. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 74:e186–e192.
Article9. Hasdenteufel F, Luyasu S, Renaudin JM, Paquay JL, Carbutti G, Beaudouin E, et al. Anaphylactic shock after first exposure to gadoterate meglumine: two case reports documented by positive allergy assessment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:527–528.
Article10. Jung JW, Kang HR, Kim MH, Lee W, Min KU, Han MH, et al. Immediate hypersensitivity reaction to gadolinium-based MR contrast media. Radiology. 2012; 264:414–422.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Anaphylactoid Reaction to Gadolinium Contrast Media and Propranolol Complicated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A Case Report
- Anaphylaxis and Acute Coronary Syndrome Secondary to Intravenous Gadolinium-based Contrast Agent: Kounis Syndrome
- Treatment of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- A Case Report on a Severe Anaphylaxis Reaction to Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Media
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome