Effects of applying nerve blocks to prevent postherpetic neuralgia in patients with acute herpes zoster: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jgleem@amc.seoul.kr
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2365337
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2017.30.1.3
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a common and painful complication of acute herpes zoster. In some cases, it is refractory to medical treatment. Preventing its occurrence is an important issue. We hypothesized that applying nerve blocks during the acute phase of herpes zoster could reduce PHN incidence by attenuating central sensitization and minimizing nerve damage and the anti-inflammatory effects of local anesthetics and steroids.
METHODS
This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the efficacy of using nerve blocks to prevent PHN. We searched the MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, ClinicalTrials.gov and KoreaMed databases without language restrictions on April, 30 2014. We included all randomized controlled trials performed within 3 weeks after the onset of herpes zoster in order to compare nerve blocks vs active placebo and standard therapy.
RESULTS
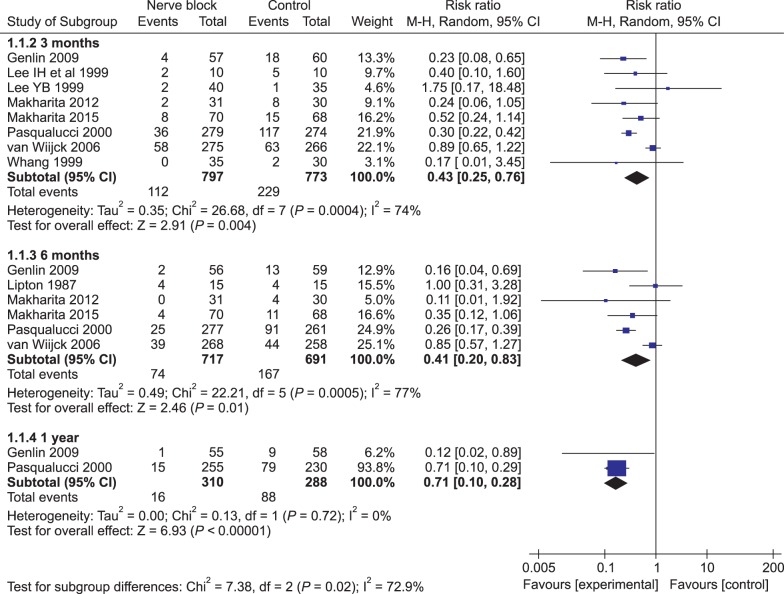
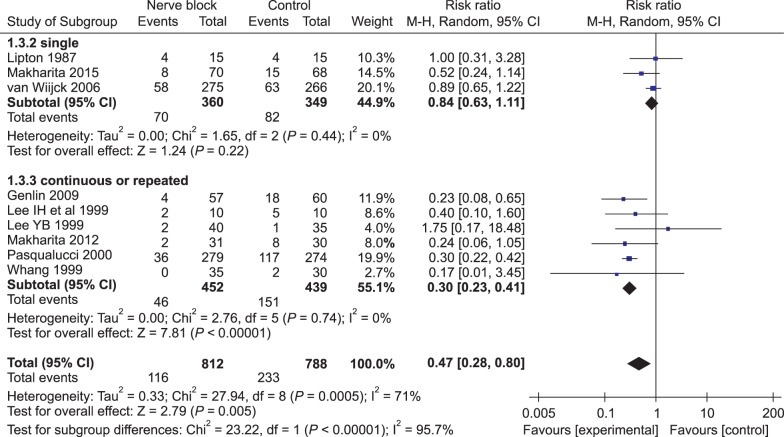
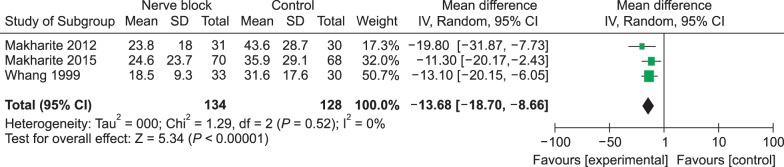
Nine trials were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. Nerve blocks reduced the duration of herpes zoster-related pain and PHN incidence of at 3, 6, and 12 months after final intervention. Stellate ganglion block and single epidural injection did not achieve positive outcomes, but administering paravertebral blockage and continuous/repeated epidural blocks reduced PHN incidence at 3 months. None of the included trials reported clinically meaningful serious adverse events.
CONCLUSIONS
Applying nerve blocks during the acute phase of the herpes zoster shortens the duration of zoster-related pain, and somatic blocks (including paravertebral and repeated/continuous epidural blocks) are recommended to prevent PHN. In future studies, consensus-based PHN definitions, clinical cutoff points that define successful treatment outcomes and standardized outcome-assessment tools will be needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Dexamethasone treatment for bilateral lingual nerve injury following orotracheal intubation
Saeyoung Kim, Seung-Yeon Chung, Si-Jeong Youn, Younghoon Jeon
J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2018;18(2):115-117. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.2.115.The efficacy of selective nerve root block for the long-term outcome of postherpetic neuralgia
A Ram Doo, Jin-Wook Choi, Ju-Hyung Lee, Ye Sull Kim, Min-Jong Ki, Young Jin Han, Ji-Seon Son
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(3):215-222. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.3.215.Pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies for preventing postherpetic neuralgia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Junhyeok Kim, Min Kyoung Kim, Geun Joo Choi, Hwa Yong Shin, Beom Gyu Kim, Hyun Kang
Korean J Pain. 2021;34(4):509-533. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2021.34.4.509.Modalities in managing postherpetic neuralgia
Meera Shrestha, Aijun Chen
Korean J Pain. 2018;31(4):235-243. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.4.235.
Reference
-
1. Head H, Campbell AW, Kennedy PG. The pathology of herpes zoster and its bearing on sensory localisation. Rev Med Virol. 1997; 7:131–143. PMID: 10398478.
Article2. Arvin A. Aging, immunity, and the varicella-zoster virus. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:2266–2267. PMID: 15930416.
Article3. Schmader KE, Dworkin RH. Natural history and treatment of herpes zoster. J Pain. 2008; 9:S3–S9. PMID: 18166460.
Article4. Dworkin RH, Portenoy RK. Pain and its persistence in herpes zoster. Pain. 1996; 67:241–251. PMID: 8951917.
Article5. Kawai K, Gebremeskel BG, Acosta CJ. Systematic review of incidence and complications of herpes zoster: towards a global perspective. BMJ Open. 2014; 4:e004833.
Article6. Oxman MN, Levin MJ, Johnson GR, Schmader KE, Straus SE, Gelb LD, et al. A vaccine to prevent herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in older adults. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:2271–2284. PMID: 15930418.
Article7. Chen N, Li Q, Yang J, Zhou M, Zhou D, He L. Antiviral treatment for preventing postherpetic neuralgia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; CD006866. PMID: 24500927.
Article8. Nahm FS, Kim SH, Kim HS, Shin JW, Yoo SH, Yoon MH, et al. Survey on the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in Korea; multicenter study of 1,414 patients. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:21–26. PMID: 23342203.
Article9. Sacks GM. Unmet need in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Am J Manag Care. 2013; 19:S207–S213. PMID: 23448093.10. Schmader KE. Epidemiology and impact on quality of life of postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Clin J Pain. 2002; 18:350–354. PMID: 12441828.
Article11. Eaglstein WH, Katz R, Brown JA. The effects of early corticosteroid therapy on the skin eruption and pain of herpes zoster. JAMA. 1970; 211:1681–1683. PMID: 4905733.
Article12. Levin MJ, Gershon AA, Dworkin RH, Brisson M, Stanberry L. Prevention strategies for herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia. J Clin Virol. 2010; 48(Suppl 1):S14–S19. PMID: 20510262.
Article13. Klenerman P, Luzzi GA. Acyclovir and postherpetic neuralgia. Biomed Pharmacother. 1990; 44:455–459. PMID: 2081273.
Article14. Chen N, Li Q, Zhang Y, Zhou M, Zhou D, He L. Vaccination for preventing postherpetic neuralgia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; CD007795. PMID: 21412911.
Article15. Han Y, Zhang J, Chen N, He L, Zhou M, Zhu C. Corticosteroids for preventing postherpetic neuralgia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013; CD005582. PMID: 23543541.
Article16. Opstelten W, van Wijck AJ, Stolker RJ. Interventions to prevent postherpetic neuralgia: cutaneous and percutaneous techniques. Pain. 2004; 107:202–206. PMID: 14736581.
Article17. Wu CL, Marsh A, Dworkin RH. The role of sympathetic nerve blocks in herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. Pain. 2000; 87:121–129. PMID: 10924805.
Article18. Doran C, Yi X. The anti-inflammatory effect of local anesthetics. Pain Clin. 2007; 19:207–213.
Article19. Yanagida H, Suwa K, Corssen G. No prophylactic effect of early sympathetic blockade on postherpetic neuralgia. Anesthesiology. 1987; 66:73–76. PMID: 3800039.
Article20. Riopelle JM, Naraghi M, Grush KP. Chronic neuralgia incidence following local anesthetic therapy for herpes zoster. Arch Dermatol. 1984; 120:747–750. PMID: 6721540.
Article21. Tajima K, Iseki M, Inada E, Miyazaki T. The effects of early nerve blocks for prevention of postherpetic neuralgia and analysis of prognostic factors. Masui. 2009; 58:153–159. PMID: 19227166.22. Winnie AP, Hartwell PW. Relationship between time of treatment of acute herpes zoster with sympathetic blockade and prevention of post-herpetic neuralgia: clinical support for a new theory of the mechanism by which sympathetic blockade provides therapeutic benefit. Reg Anesth. 1993; 18:277–282. PMID: 8268115.23. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. Oxford: The Cochrane Collaboration;2011.24. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010; 8:336–341. PMID: 20171303.
Article25. Bhala BB, Ramamoorthy C, Bowsher D, Yelnoorker KN. Shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. Clin J Pain. 1988; 4:169–174.
Article26. Ahn SY, Lee YB, Lee KH, Lim HK, Lee WS, Ahn SK, et al. The effect of stellate ganglion block on herpes zoster. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:681–687.27. Tenicela R, Lovasik D, Eaglstein W. Treatment of herpes zoster with sympathetic blocks. Clin J Pain. 1985; 1:63–67.
Article28. Hwang SM, Kang YC, Lee YB, Yoon KB, Ahn SK, Choi EH. The effects of epidural blockade on the acute pain in herpes zoster. Arch Dermatol. 1999; 135:1359–1364. PMID: 10566834.
Article29. Ji G, Niu J, Shi Y, Hou L, Lu Y, Xiong L. The effectiveness of repetitive paravertebral injections with local anesthetics and steroids for the prevention of postherpetic neuralgia in patients with acute herpes zoster. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109:1651–1655. PMID: 19713253.
Article30. Lee IH, Kim BS, Lee SC, Jo DH. The effect of stellate ganglion block on the pain of acute stage and the prevention of postherpetic neuralgin in the treatment of senile herpes zoster patients. Korean J Dermatol. 1999; 37:571–579.31. Lee YB, Park JT, Han JW, Yoon KB. The efficacy of epidural blockade on acute herpes zoster. J Korean Pain Soc. 1999; 12:183–187.32. Lipton JR, Harding SP, Wells JC. The effect of early stellate ganglion block on postherpetic neuralgia in herpes zoster ophthalmicus. Pain Clin. 1987; 1:247–251.33. Makharita MY, Amr YM, El-Bayoumy Y. Effect of early stellate ganglion blockade for facial pain from acute herpes zoster and incidence of postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:467–474. PMID: 23159962.34. Makharita MY, Amr YM, El-Bayoumy Y. Single paravertebral injection for acute thoracic herpes zoster: a randomized controlled trial. Pain Pract. 2015; 15:229–235. PMID: 24528531.
Article35. Pasqualucci A, Pasqualucci V, Galla F, De Angelis V, Marzocchi V, Colussi R, et al. Prevention of post-herpetic neuralgia: acyclovir and prednisolone versus epidural local anesthetic and methylprednisolone. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2000; 44:910–918. PMID: 10981565.
Article36. van Wijck AJ, Opstelten W, Moons KG, van Essen GA, Stolker RJ, Kalkman CJ, et al. The PINE study of epidural steroids and local anaesthetics to prevent postherpetic neuralgia: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2006; 367:219–224. PMID: 16427490.
Article37. Tajima K, Kawagoe I, Kanai M, Mitsuhata H. Effective treatment of acute pain and related symptoms in elderly with herpes zoster. Masui. 2008; 57:874–878. PMID: 18649643.38. Rutgers MJ, Dirksen R. The prevention of postherpetic neuralgia: a retrospective view of patients treated in the acute phase of herpes zoster. Br J Clin Pract. 1988; 42:412–414. PMID: 3255420.39. Manabe H, Dan K, Hirata K, Hori K, Shono S, Tateshi S, et al. Optimum pain relief with continuous epidural infusion of local anesthetics shortens the duration of zoster-associated pain. Clin J Pain. 2004; 20:302–308. PMID: 15322436.
Article40. Higa K, Hori K, Harasawa I, Hirata K, Dan K. High thoracic epidural block relieves acute herpetic pain involving the trigeminal and cervical regions: comparison with effects of stellate ganglion block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 1998; 23:25–29. PMID: 9552775.
Article41. Koh WS, Park SM, Kim BS, Shin DY. The effect of sympathetic blocks in the prevention of postherpetic neuralgia. Korean J Dermatol. 1997; 35:620–626.42. Dworkin RH, O'Connor AB, Kent J, Mackey SC, Raja SN, Stacey BR, et al. Interventional management of neuropathic pain: NeuPSIG recommendations. Pain. 2013; 154:2249–2261. PMID: 23748119.
Article43. Gabutti G, Serenelli C, Cavallaro A, Ragni P. Herpes zoster associated hospital admissions in Italy: review of the hospital discharge forms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2009; 6:2344–2353. PMID: 19826547.
Article44. Gil A, Gil R, Alvaro A, San Martín M, González A. Burden of herpes zoster requiring hospitalization in Spain during a seven-year period (1998-2004). BMC Infect Dis. 2009; 9:55. PMID: 19422687.
Article45. Opstelten W, Zuithoff NP, van Essen GA, van Loon AM, van Wijck AJ, Kalkman CJ, et al. Predicting postherpetic neuralgia in elderly primary care patients with herpes zoster: prospective prognostic study. Pain. 2007; 132(Suppl 1):S52–S59. PMID: 17379412.
Article46. Gialloreti LE, Merito M, Pezzotti P, Naldi L, Gatti A, Beillat M, et al. Epidemiology and economic burden of herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia in Italy: a retrospective, population-based study. BMC Infect Dis. 2010; 10:230. PMID: 20682044.
Article47. Bicket MC, Gupta A, Brown CH 4th, Cohen SP. Epidural injections for spinal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the “control” injections in randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology. 2013; 119:907–931. PMID: 24195874.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Sympathetic Blocks in the Prevention of Postherpetic Neuralgia
- Treatment of Herpes Zoster: Nerve Block
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatement of the Stellate Ganglion in Acute Herpes Zoster: A case report
- The Effect of a Sympathectomy Using Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation in Patients with Acute Herpes Zoster: A case report
- Administration of Vitamin C in a Patient with Herpes Zoster: A case report