Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jan;35(1):165-168. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.165.
Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Measurement of Leukocyte Arylsulfatase A Activity Using a Natural Substrate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. songjhcp@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363170
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.165
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Cerebroside-Sulfatase/*metabolism
Child, Preschool
*Chromatography, High Pressure Liquid
Enzyme Assays/instrumentation/*methods
Female
Humans
Kinetics
Leukocytes/*enzymology
Leukodystrophy, Metachromatic/diagnosis/enzymology
Male
Middle Aged
Reference Standards
Substrate Specificity
Sulfoglycosphingolipids/analysis/metabolism/standards
*Tandem Mass Spectrometry/standards
Cerebroside-Sulfatase
Sulfoglycosphingolipids
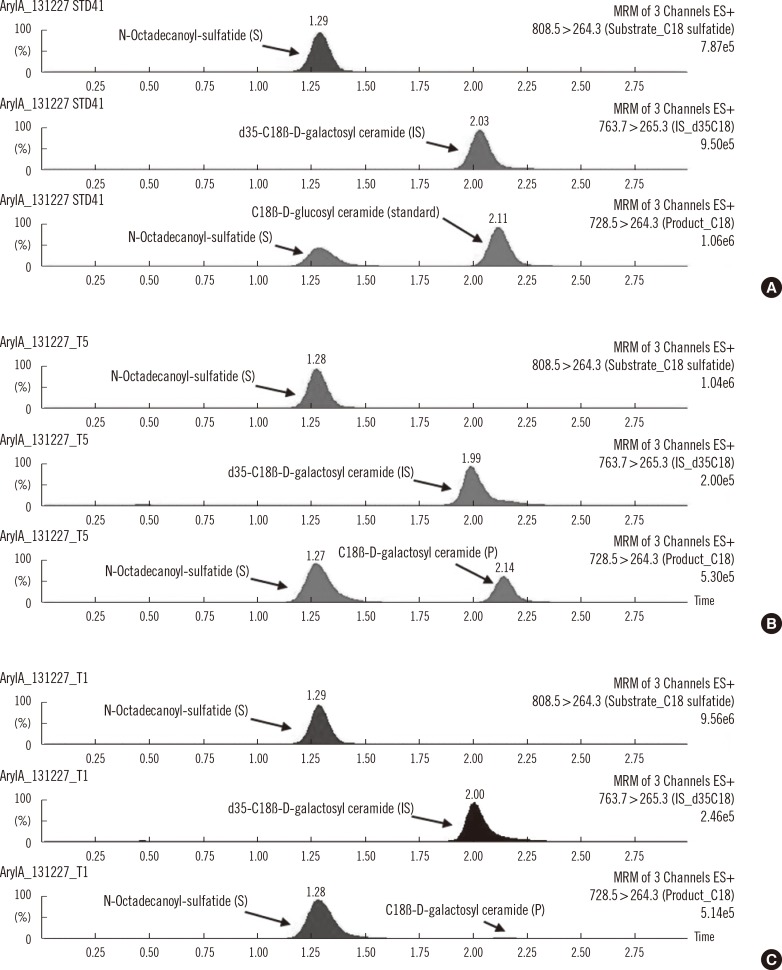
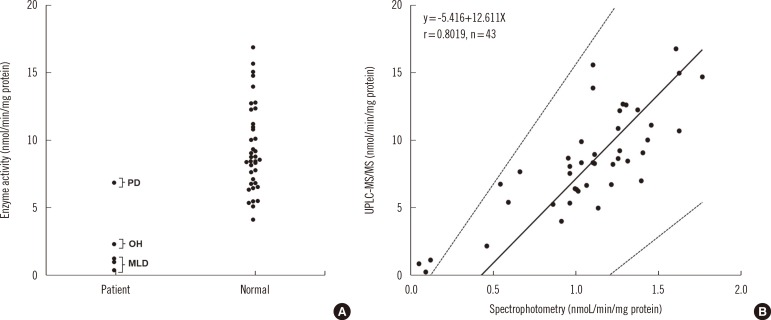
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baum H, Dodgson KS, Spencer B. The assay of arylsulphatases A and B in human urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1959; 4:453–455. PMID: 13663253.
Article2. Harinath BC, Robins E. Arylsulphatases in human brain: assay, some properties, and distribution. J Neurochem. 1971; 18:237–244. PMID: 5550089.
Article3. Lee-Vaupel M, Conzelmann E. A simple chromogenic assay for arylsulfatase A. Clin Chim Acta. 1987; 164:171–180. PMID: 2885112.
Article4. Rip JW, Gordon BA. A simple spectrophotometric enzyme assay with absolute specificity for arylsulfatase A. Clin Biochem. 1998; 31:29–31. PMID: 9559221.
Article5. Spacil Z, Tatipaka H, Barcenas M, Scott CR, Turecek F, Gelb MH. High-throughput assay of 9 lysosomal enzymes for newborn screening. Clin Chem. 2013; 59:502–511. PMID: 23315484.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Simultaneous Screening of 177 Drugs of Abuse in Urine Using Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Drug-intoxicated Patients
- Measurement of Serum Levels of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D2 Using Diels-Alder Derivatization and Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Metabolism and excretion of novel pulmonary-targeting docetaxel liposome in rabbits
- Bioanalytical methods for the detection of duloxetine and thioctic acid in plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS)
- Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Thirteen Marker Components in Traditional Korean Formula, Samryeongbaekchul-san using an Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Equipped with Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry