Ann Surg Treat Res.
2016 Oct;91(4):207-211. 10.4174/astr.2016.91.4.207.
Complete tubular duplication of colon in an adult: a rare cause of colovaginal fistula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. bestoperator@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2354329
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.91.4.207
Abstract
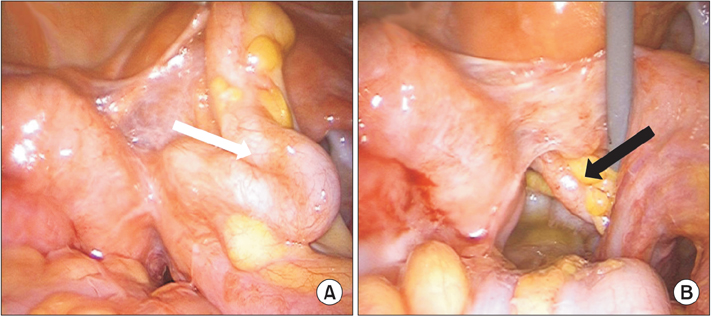
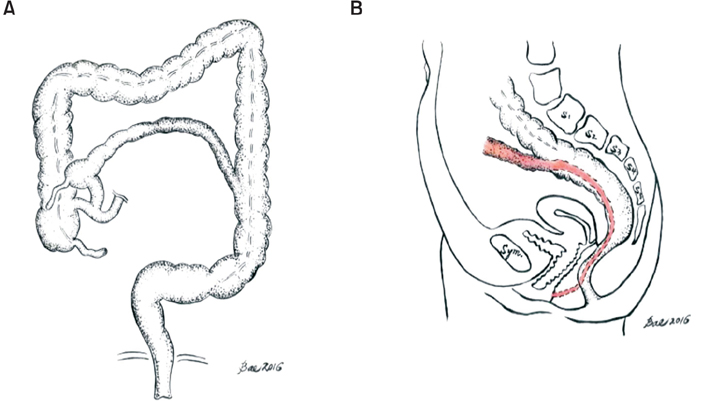
- Alimentary tract duplications are uncommon congenital anomalies that usually present during the first decade of life. Complete duplication of the colon in adults is very rare and difficult to diagnose preoperatively. We report a case of a 40-year-old female with complete tubular duplication which was initially misdiagnosed as a salpingeal abscess due to colovaginal fistula.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ildstad ST, Tollerud DJ, Weiss RG, Ryan DP, McGowan MA, Martin LW. Duplications of the alimentary tract. Clinical characteristics, preferred treatment, and associated malformations. Ann Surg. 1988; 208:184–189.2. Caklili OT, Tuncer I, Colak Y, Kosemetin D, Ceyran AB. Colonic duplication in adulthood presenting with diarrhea. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:Suppl 2 UCTN. E430–E431.3. Banchini F, Delfanti R, Begnini E, Tripodi MC, Capelli P. Duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: case report and review. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:586–589.4. Yong YG, Jung KU, Cho YB, Yun SH, Kim HC, Lee WY, et al. Large tubular colonic duplication in an adult treated with a small midline incision. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 82:190–194.5. Sarin YK, Manchanda V, Sharma A, Singhal A. Triplication of colon with diphallus and complete duplication of bladder and urethra. J Pediatr Surg. 2006; 41:1924–1926.6. Shah KR, Joshi A. Complete genitourinary and colonic duplication: a rare presentation in an adult patient. J Ultrasound Med. 2006; 25:407–411.7. Holcomb GW 3rd, Gheissari A, O'Neill JA Jr, Shorter NA, Bishop HC. Surgical management of alimentary tract duplications. Ann Surg. 1989; 209:167–174.8. Kokoska ER, Steinhardt GF, Tomita SS, Weber TR. Prostatorectal fistula associated with tubular colorectal duplication. J Pediatr Surg. 1999; 34:1546–1548.9. Kim TW, Jung PM. A clinical study of intestinal duplication. J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2004; 10:9–16.10. Kwak JM, Boo YJ, Kim J. Tubular colorectal duplication presenting as rectovaginal fistula. ANZ J Surg. 2014; 84:289–290.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tubular Colonic Duplication Presenting as Rectovestibular Fistula
- Asymptomatic Tubular Duplication of the Transverse Colon in an Adult
- A Case of Tubular Duplication of the Esophagus
- A Case of Tubular Esophageal Duplication
- Large tubular colonic duplication in an adult treated with a small midline incision