Yonsei Med J.
2015 Jan;56(1):103-111. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.103.
Efficacy of Surgical Treatment for Brain Metastasis in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. littmann@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2352795
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.103
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and simultaneously having brain metastases at the initial diagnosis, presenting symptoms related brain metastasis, survived shorter duration and showed poor quality of life. We analyzed our experiences on surgical treatment of brain metastasis in patients with NSCLC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed a single-center, retrospective review of 36 patients with NSCLC and synchronous brain metastases between April 2006 and December 2011. Patients were categorized according to the presence of neurological symptoms and having a brain surgery. As a result, 14 patients did not show neurological symptoms and 22 patients presented neurological symptoms. Symptomatic 22 patients were divided into two groups according to undergoing brain surgery (neurosurgery group; n=11, non-neurosurgery group; n=11). We analyzed overall surgery (OS), intracranial progression-free survival (PFS), and quality of life.
RESULTS
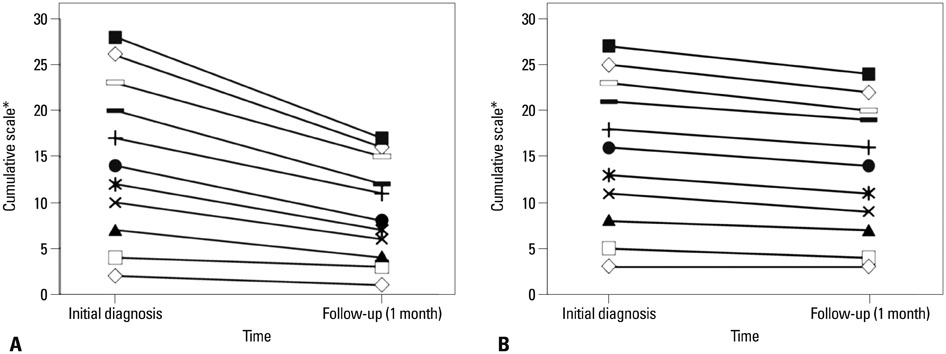
Survival analysis showed there was no difference between patients with neurosurgery (OS, 12.1 months) and non-neurosurgery (OS, 10.2 months; p=0.550). Likewise for intracranial PFS, there was no significant difference between patients with neurosurgery (PFS, 6.3 months) and non-neurosurgery (PFS, 5.3 months; p=0.666). Reliable neurological one month follow up by the Medical Research Council neurological function evaluation scale were performed in symptomatic 22 patients. The scale improved in eight (73%) patients in the neurosurgery group, but only in three (27%) patients in the non-neurosurgery group (p=0.0495).
CONCLUSION
Patients with NSCLC and synchronous brain metastases, presenting neurological symptoms showed no survival benefit from neurosurgical resection, although quality of life was improved due to early control of neurological symptoms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yawn BP, Wollan PC, Schroeder C, Gazzuola L, Mehta M. Temporal and gender-related trends in brain metastases from lung and breast cancer. Minn Med. 2003; 86:32–37.2. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:494–500.
Article3. Billing PS, Miller DL, Allen MS, Deschamps C, Trastek VF, Pairolero PC. Surgical treatment of primary lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001; 122:548–553.
Article4. Cairncross JG, Kim JH, Posner JB. Radiation therapy for brain metastases. Ann Neurol. 1980; 7:529–541.5. Shen KR, Meyers BF, Larner JM, Jones DR. American College of Chest Physicians. Special treatment issues in lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest. 2007; 132:3 Suppl. 290S–305S.6. Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, et al. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997; 37:745–751.
Article7. Sawaya R, Hammoud M, Schoppa D, Hess KR, Wu SZ, Shi WM, et al. Neurosurgical outcomes in a modern series of 400 craniotomies for treatment of parenchymal tumors. Neurosurgery. 1998; 42:1044–1055.
Article8. van den Bent MJ, Afra D, de Witte O, Ben Hassel M, Schraub S, Hoang-Xuan K, et al. Long-term efficacy of early versus delayed radiotherapy for low-grade astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma in adults: the EORTC 22845 randomised trial. Lancet. 2005; 366:985–990.
Article9. Schuette W. Treatment of brain metastases from lung cancer: chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2004; 45:Suppl 2. S253–S257.
Article10. Sørensen JB, Hansen HH, Hansen M, Dombernowsky P. Brain metastases in adenocarcinoma of the lung: frequency, risk groups, and prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 1988; 6:1474–1480.
Article11. Lagerwaard FJ, Levendag PC, Nowak PJ, Eijkenboom WM, Hanssens PE, Schmitz PI. Identification of prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases: a review of 1292 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:795–803.
Article12. Schouten LJ, Rutten J, Huveneers HA, Twijnstra A. Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer. 2002; 94:2698–2705.
Article13. Louie AV, Rodrigues G, Yaremko B, Yu E, Dar AR, Dingle B, et al. Management and prognosis in synchronous solitary resected brain metastasis from non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009; 10:174–179.
Article14. Rades D, Raabe A, Bajrovic A, Alberti W. Treatment of solitary brain metastasis. Resection followed by whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) and a radiation boost to the metastatic site. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004; 180:144–147.15. Granone P, Margaritora S, D'Andrilli A, Cesario A, Kawamukai K, Meacci E. Non-small cell lung cancer with single brain metastasis: the role of surgical treatment. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001; 20:361–366.
Article16. Bonnette P, Puyo P, Gabriel C, Giudicelli R, Regnard JF, Riquet M, et al. Surgical management of non-small cell lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. Chest. 2001; 119:1469–1475.
Article17. Barker FG 2nd. Craniotomy for the resection of metastatic brain tumors in the U.S., 1988-2000: decreasing mortality and the effect of provider caseload. Cancer. 2004; 100:999–1007.
Article18. Paek SH, Audu PB, Sperling MR, Cho J, Andrews DW. Reevaluation of surgery for the treatment of brain metastases: review of 208 patients with single or multiple brain metastases treated at one institution with modern neurosurgical techniques. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:1021–1034.19. Stark AM, Tscheslog H, Buhl R, Held-Feindt J, Mehdorn HM. Surgical treatment for brain metastases: prognostic factors and survival in 177 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2005; 28:115–119.
Article20. Jazieh AR, Bamefleh H, Demirkazik A, Gaafar RM, Geara FB, Javaid M, et al. Modification and implementation of NCCN guidelines on non-small cell lung cancer in the Middle East and North Africa region. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010; 8:Suppl 3. S16–S21.
Article21. Park SJ, Kim HT, Lee DH, Kim KP, Kim SW, Suh C, et al. Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring either exon 19 or 21 mutation. Lung Cancer. 2012; 77:556–560.
Article22. Kalikaki A, Koutsopoulos A, Trypaki M, Souglakos J, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V, et al. Comparison of EGFR and K-RAS gene status between primary tumours and corresponding metastases in NSCLC. Br J Cancer. 2008; 99:923–929.
Article23. Gow CH, Chang YL, Hsu YC, Tsai MF, Wu CT, Yu CJ, et al. Comparison of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations between primary and corresponding metastatic tumors in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-naive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:696–702.
Article24. Galluzzi S, Payne PM. Brain metastases from primary bronchial carcinoma: a statistical study of 741 necropsies. Br J Cancer. 1956; 10:408–414.
Article25. Penel N, Brichet A, Prevost B, Duhamel A, Assaker R, Dubois F, et al. Pronostic factors of synchronous brain metastases from lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2001; 33:143–154.
Article26. Vogelbaum MA, Suh JH. Resectable brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:1289–1294.
Article27. Sánchez de Cos J, Sojo González MA, Montero MV, Pérez Calvo MC, Vicente MJ, Valle MH. Non-small cell lung cancer and silent brain metastasis. Survival and prognostic factors. Lung Cancer. 2009; 63:140–145.
Article28. Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet. 2004; 363:1665–1672.
Article29. Noordijk EM, Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H, Padberg GW, Voormolen JH, Hoekstra FH, et al. The choice of treatment of single brain metastasis should be based on extracranial tumor activity and age. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994; 29:711–717.
Article30. Alexander E 3rd, Moriarty TM, Davis RB, Wen PY, Fine HA, Black PM, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the definitive, non-invasive treatment of brain metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995; 87:34–40.
Article31. Kondziolka D, Patel A, Lunsford LD, Kassam A, Flickinger JC. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 45:427–434.
Article32. Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villá S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, et al. Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:134–141.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Cutaneous Metastasis from Small Cell Lung Cancer
- A case of leptomeningeal metastasis from adenocarcinoma of the lung improved by treatment with Gefitinib
- A Case of Iris Metastasis from Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Durable response to first-line treatment with AZD3759 (zorifertinib) in a patient with epithelial growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer and untreated multiple brain metastasis
- Radiotherapy of Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer