J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Oct;63(4):391-394.
Metastasis of Breast Carcinoma to Intercostal Muscle Detected by Breast MRI: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea. ejsonrd@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
Abstract
- Breast cancer can metastasize to any organ; however, distant metastases are unusual at the time of diagnosis. Furthermore metastasis to skeletal muscle is an uncommon manifestation of malignancy. We report a case of a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with cancer of the left breast with metastases to the ipsilateral intercostal muscle. To the best of our knowledge this is the first report of intercostal muscle metastasis from breast cancer in the English literature.
MeSH Terms
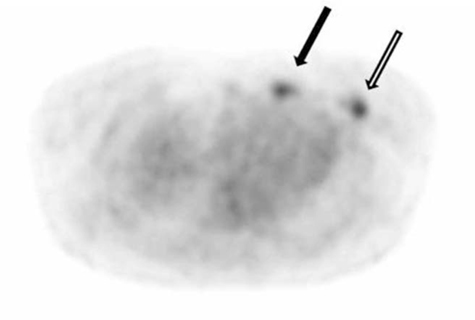
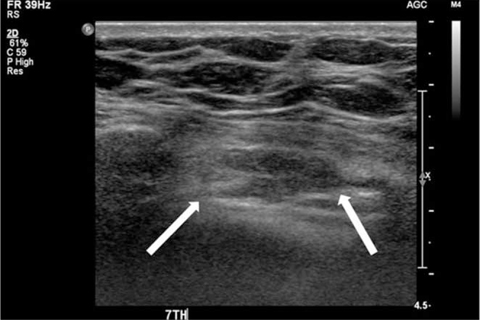
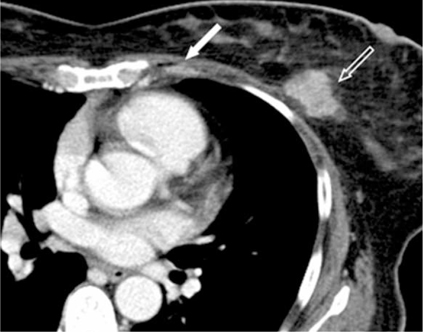
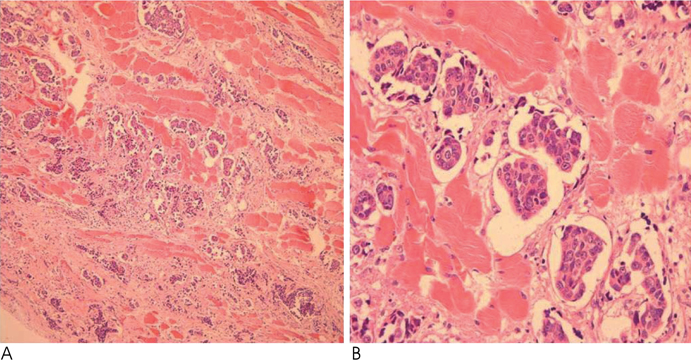
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006; 56:106–130.2. Batista RR, Marchiori E, Takayassu TC, Cabral FC, Carbral RF, Zanetti G. Sternal metastasis as an initial presentation of renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Cases J. 2009; 2:9045.3. Bruneton JN, Caramella E, Hery M, Aubanel D, Manzino JJ, Picard JL. Axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: preoperative detection with US. Radiology. 1986; 158:325–326.4. Carlini M, Lonardo MT, Carboni F, Petric M, Vitucci C, Santoro R, et al. Liver metastases from breast cancer. Results of surgical resection. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002; 49:1597–1601.5. Lee YT. Breast carcinoma: pattern of metastasis at autopsy. J Surg Oncol. 1983; 23:175–180.6. Brookes M, MacVicar D, Husband J. Metastatic carcinoma of the breast: the appearances of metastatic spread to the abdomen and pelvis as demonstrated by CT. Br J Radiol. 2007; 80:284–292.7. Mat Saad AZ, McGuire E, O'shea J, Kneafsey B. Synchronous intramuscular metastases of malignant melanoma-case report and literature review. Eur J Plast Surg. 2007; 30:35–37.8. Herring CL Jr, Harrelson JM, Scully SP. Metastatic carcinoma to skeletal muscle. A report of 15 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 355:272–281.9. Liu Y, Ghesani N, Mirani N, Zuckier LS. PET-CT demonstration of extensive muscle metastases from breast cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2006; 31:266–268.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Alopecia Neoplastica Metastasis from Breast Carcinoma
- Occult Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of Breast Detected by Stomach Metastasis: A Case Report
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast: A Case Report
- Nodular Metastatic Carcinoma from Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer
- A Case of Radiotheraphy of Choroidal Metastasis of Breast Carcinoma