J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc.
2012 Nov;51(6):395-401.
The Clinical Characteristics of Pathological Gamblers Who Completed about 10 Weeks' Admission Treatment Programs : The Change of Depression and Anxiety after Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1St. Andrew's Neuropsychiatric Hospital, Icheon, Korea. indichoi@gmail.com
- 2Department of Psychiatry, Seoul Metropolitan Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation & Welfare, Korean National College of Welfare, Pyeongtaek, Korea.
- 4Department of Social Welfare, Yong-In Songdam College, Yongin, Korea.
- 5Kangwon Land Addiction Care Center, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study is investigate the clinical characteristics and the change of depression and anxiety in pathological gamblers who completed 10-week admission treatment programs.
METHODS
To investigate the clinical characteristics, we included 40 pathological gamblers who completed admission treatment programs from Jan 2006 to Jun 2010. To measure the change through treatment, we included 16 patients who completed pre-treatment and post-treatment assessment scales, including the Korean-National Opinion Research Center DSM-IV Screen for Gambling Problems (K-NODS), Beck's Depression Inventory (BDI), and the State-trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), from May 2008 to Aug 2008.
RESULTS
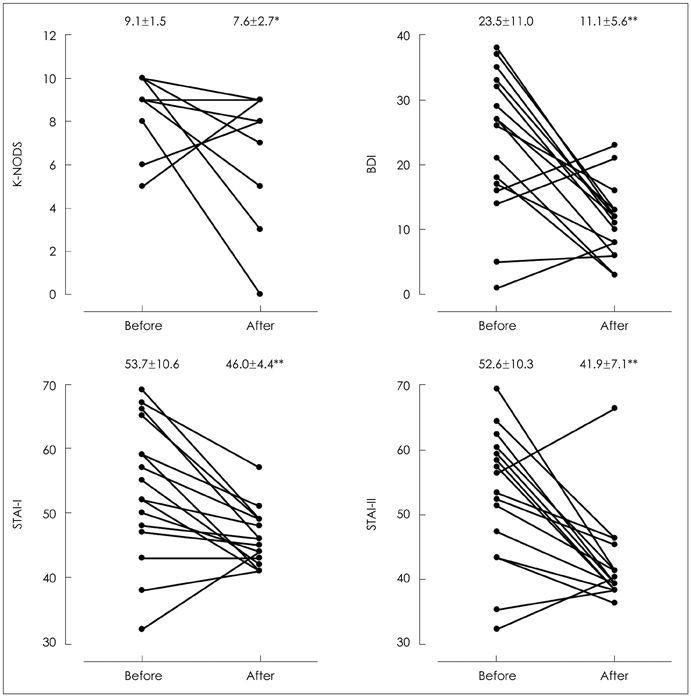
Mean age of the patients was 42.9+/-9.0 years and mean intelligent quotient was 109.7+/-10.4. Thirty (75%) patients showed comorbid disorders, including depression (14 patients, 35%), anxiety disorder (five patients, 12.5%), alcohol use disorder (five patients, 12.5%), and personality disorder (four patients, 10%). After treatment, K-NODS, BDI, STAI-I, and STAI-II scores showed improvement, from 9.1+/-1.5 to 7.6+/-2.7, from 23.5+/-5.8 to 11.1+/-3.2, from 52.6+/-10.3 to 41.9+/-7.1, and from 53.7+/-10.6 to 46.0+/-4.4, respectively.
CONCLUSION
In treatment of pathological gambling, comorbid psychiatric risk factors, such as depression and anxiety should be considered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 2000. 4th ed. Text Revision. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association;671.2. Petry NM, Ammerman Y, Bohl J, Doersch A, Gay H, Kadden R, et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for pathological gamblers. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2006. 74:555–567.
Article3. Leung KS, Cottler LB. Treatment of pathological gambling. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2009. 22:69–74.
Article4. Lowengrub K, Iancu I, Aizer A, Kotler M, Dannon PN. Pharmacotherapy of pathological gambling: review of new treatment modalities. Expert Rev Neurother. 2006. 6:1845–1851.
Article5. Dannon P, Sason M, Shalgi B, Tusan L, Sapir Y, Kotler M. [Comorbid psychiatric symptoms in pathological gamblers: anxiety, depression and substance abuse]. Harefuah. 2004. 143:643–646. 6956. Lorains FK, Cowlishaw S, Thomas SA. Prevalence of comorbid disorders in problem and pathological gambling: systematic review and meta-analysis of population surveys. Addiction. 2011. 106:490–498.
Article7. Kessler RC, Hwang I, LaBrie R, Petukhova M, Sampson NA, Winters KC, et al. DSM-IV pathological gambling in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Psychol Med. 2008. 38:1351–1360.
Article8. Hodgins DC, Peden N, Cassidy E. The association between comorbidity and outcome in pathological gambling: a prospective follow-up of recent quitters. J Gambl Stud. 2005. 21:255–271.
Article9. Ladouceur R, Sylvain C, Sévigny S, Poirier L, Brisson L, Dias C, et al. Pathological gamblers: inpatients' versus outpatients' characteristics. J Gambl Stud. 2006. 22:443–450.
Article10. Breen RB, Kruedelbach NG, Walker HI. Cognitive changes in pathological gamblers following a 28-day inpatient program. Psychol Addict Behav. 2001. 15:246–248.
Article11. Jung SY, Son DS, Choi YS, Shin HH, Kim SH, Choi YS, et al. A study on the development and effectiveness of social-psychological rehabilitation program for gamblers. Ment Health Soc Work. 2009. 32:285–320.12. Yeom TH, Park YS, Oh KJ, Kim JG, Lee YH. K-WAIS Guidlines. 1992. Seoul: Korea Guidance.13. Kim JS, Han KH, Lim JY, Lee JH, Min BB, Moon KJ. MMPI-2 manual. 2005. Seoul: Mamumsarang.14. Derogatis LR. SCL-90-R: Administration, scoring, and procedures manual. 1994. Minneapolis, MN: National Computer Systems, Inc..15. Min BB, Oh HS, Lee JY. TCI manual. 2007. Seoul: Maumsarang.16. Kim KH. Reliability and validity of Korean NODS. Korean J Health Psychol. 2003. 8:487–509.17. Lee YH, Song JY. A study of the reliability and the validity of the BDI, SDS, and MMPI-D Scales. Korean J Clin Psychol. 1991. 10:98–113.18. Kim JT. 1978. Seoul: Korea University.19. Suurvali H, Cordingley J, Hodgins DC, Cunningham J. Barriers to seeking help for gambling problems: a review of the empirical literature. J Gambl Stud. 2009. 25:407–424.
Article20. Ledgerwood DM, Orr ES, Kaploun KA, Milosevic A, Frisch GR, Rupcich N, et al. Executive function in pathological gamblers and healthy controls. J Gambl Stud. 2012. 28:89–103.
Article21. Moravec JD, Munley PH. Psychological test findings on pathological gamblers in treatment. Int J Addict. 1983. 18:1003–1009.
Article22. Graham JR. MMPI-2: Assessing personality and psychopathology. 2006. 4th ed. New York: Oxford University Press.23. Han YO, Kim HW, Kim TW, Lee JG, Jeong JY. The characteristics of male pathological gamblers based on MMPI-2 profiles. Korean J Clin Psychol. 2011. 30:519–536.
Article24. Shin YC. The Temperament and Character Dimensions in Pathological Gambling Patients. 2002. Seoul: Chung-Ang University.25. Petry NM, Stinson FS, Grant BF. Comorbidity of DSM-IV pathological gambling and other psychiatric disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. 66:564–574.
Article26. el-Guebaly N, Patten SB, Currie S, Williams JV, Beck CA, Maxwell CJ, et al. Epidemiological associations between gambling behavior, substance use & mood and anxiety disorders. J Gambl Stud. 2006. 22:275–287.
Article27. Rocca P, Mingrone C, Mongini T, Montemagni C, Pulvirenti L, Rocca G, et al. Outcome and length of stay in psychiatric hospitalization, the experience of the University Clinic of Turin. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2010. 45:603–610.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Influencing Recognition of Motivation for Change in Pathological Gamblers
- The Clinical Characteristics of Female Gamblers: Focusing on Casino Visitors
- Stress, Coping Style and Depression in Pathological Gamblers
- Factors Influencing Family-function in Families of Pathological Gamblers
- The Psychological and Behavioral Characteristics of the Pathological Gamblers in Horse Racing