J Korean Med Assoc.
2008 Jan;51(1):5-15.
Introduction to Radiosurgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Korea. gknife@plaza.snu.ac.kr, htchung@korea.com
Abstract
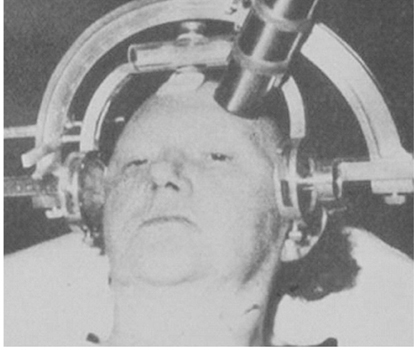
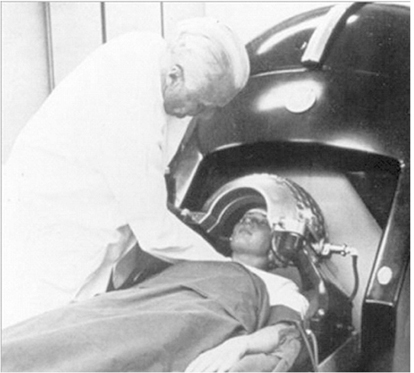
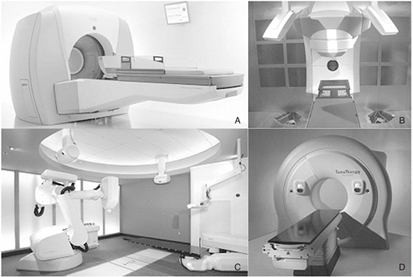
- Radiosurgery, or stereotactic radiosurgery, is a minimally invasive modality to treat a lesion with stereotactically focused ionizing radiation without surgical incision. Because there are no incision procedures, general anesthesia or transfusion is not required, and complications related to incisional procedures do not occur in radiosurgery. As a result, radiosurgery shows much low rates of complications than conventional open surgery with comparable cure rates. In the beginning, radiosurgery was applied only to a few intracranial diseases because a stereotactic frame was applied to the skull. Along with the development of technologies and accumulation of knowledge on radiosurgery such as medical imaging, computer, radiation physics, and radiobiology, indications of radiosurgery have been expanded in various ways. Nowadays, radiosurgery is accepted as an adjuvant treatment or a primary treatment option for many neurosurgical diseases and cancers. Cranial nerve schwannomas, brain meningiomas, pituitary adenoma, and other benign brain tumors are good indications for radiosurgery. Intracranial arteriovenous malformation, brain metastases from extracranial cancers, and trigeminal neuralgia are also well controlled by radiosurgery. Spinal metastases and various cancers are emerging indications for extracranial radiosurgery, which has been recently introduced. In this article, the authors summarized the basic concept, history, development, and future of radiosurgery as an introduction to radiosurgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Larson DA. Introduction to radiosurgery. Clin Neurosurg. 1992. 38:391–404.2. Larson DA, Gutin PH. Introduction to radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1990. 1:897–908.
Article3. Maciunas RJ. Stereotactic radiosurgery. Nat Med. 1996. 2:712–713.
Article4. Flickinger JC, Barker FG 2nd. Clinical results: Radiosurgery and radiotherapy of cranial nerve schwannomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2006. 17:121–128.
Article5. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Acoustic neuroma radiosurgery. Origins, contemporary use and future expectations. Neurochirurgie. 2004. 50:427–435.6. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Acoustic tumors: operation versus radiation-making sense of opposing viewpoints. Part II. Acoustic neuromas: sorting out management options. Clin Neurosurg. 2003. 50:313–328.7. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Comparison of management options for patients with acoustic neuromas. Neurosurg Focus. 2003. 14:e1.
Article8. Friedman WA, Foote KD. Linear accelerator-based radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Neurosurg Focus. 2003. 14:e2.
Article9. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Clin J Pain. 2002. 18:42–47.
Article10. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Controversies in the management of multiple brain metastases: the roles of radiosurgery and radiation therapy. Forum (Genova). 2001. 11:47–58.11. Friedman WA, Foote KD. Linear accelerator radiosurgery in the management of brain tumours. Ann Med. 2000. 32:64–80.
Article12. Friedman WA. Radiosurgery versus surgery for arteriovenous malformations: the case for radiosurgery. Clin Neurosurg. 1999. 45:18–20.13. Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Stereotactic radiosurgery for meningiomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1999. 10:317–325.
Article14. Kondziolka D. Functional radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 1999. 44:12–20. discussion 20-22.
Article15. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. Clinical applications of stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer Treat Res. 1998. 93:283–297.
Article16. Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Somaza S, Kondziolka D. Radiosurgery: its role in brain metastasis management. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1996. 7:497–504.
Article17. WA Friedman . Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. Clin Neurosurg. 1995. 42:328–347.
Article18. Friedman WA, Bova FJ. Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. Clin Neurosurg. 1993. 40:446–464.
Article19. Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC. Stereotactic radiosurgery for benign intracranial tumors. Clin Neurosurg. 1993. 40:475–497.20. Lunsford LD, Linskey ME. Stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of patients with acoustic tumors. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1992. 25:471–491.
Article21. Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC. Stereotactic radiosurgery: current spectrum and results. Clin Neurosurg. 1992. 38:405–444.22. Deinsberger R, Tidstrand J. Linac radiosurgery as a tool in neurosurgery. Neurosurg Rev. 2005. 28:79–88.
Article23. Gerszten PC, Welch WC. Cyberknife radiosurgery for metastatic spine tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2004. 15:491–501.
Article24. Rock JP, Ryu S, Yin FF. Novalis radiosurgery for metastatic spine tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2004. 15:503–509.
Article25. Thornton AF, Laramore GE. Technical advances in radiotherapy of head and neck tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1999. 13:811–823.
Article26. Mehta MP. The physical, biologic, and clinical basis of radiosurgery. Curr Probl Cancer. 1995. 19:265–329.
Article27. Attia M, Menhel J, Alezra D, Pffefer R, Spiegelmann R. Radiosurgery-LINAC or gamma knife: 20 years of controversy revisited. Isr Med Assoc J. 2005. 7:583–588.28. Phillips MH, Stelzer KJ, Griffin TW, Mayberg MR, Winn HR. Stereotactic radiosurgery: a review and comparison of methods. J Clin Oncol. 1994. 12:1085–1099.
Article29. Luxton G, Petrovich Z, Jozsef G, Nedzi LA, Apuzzo ML. Stereotactic radiosurgery: principles and comparison of treatment methods. Neurosurgery. 1993. 32:241–259. discussion 259.30. Goodman ML. Gamma Knife radiosurgery: Current status and review. South Med J. 1990. 83:551–554.31. Bova FJ. Radiation Physics. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 1990. 1:909–931.
Article32. Leksell L. Stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiarty. 1983. 46:797–803.
Article33. Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Radiobiology of radiosurgery. Prog Neurol Surg. 2007. 20:16–27.
Article34. Willers H, Held KD. Introduction to clinical radiation biology. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006. 20:1–24.
Article35. Niranjan A, Gobbel GT, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. Experimental radiobiological investigations into radiosurgery: present understanding and future directions. Neurosurgery. 2004. 55:495–504. discussion 504-505.
Article36. Shrieve DC, Klish M, Wendland MM, Watson GA. Basic principles of radiobiology, radiotherapy, and radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2004. 15:467–479.
Article37. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. The radiobiology of radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1999. 10:157–166.
Article38. Joensuu H, Tenhunen M. Physical and biological targeting of radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 1999. 38(S13):75–83.
Article39. Altschuler E, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Wu A, Maitz AH, Sclabassi R, Martinez AJ, Flickinger JC. Radiobiologic models for radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1992. 3:61–77.
Article40. Levivier M, Massager N, Wikler D, Devriendt D, Goldman S. Integration of functional imaging in radiosurgery: the example of PET scan. Prog Neurol Surg. 2007. 20:68–81.
Article41. Lee JK, Liu RS, Shiang HR, Pan DH. Usefulness of semiquantitative FDG-PET in the prediction of brain tumor treatment response to gamma knife radiosurgery. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2003. 27:525–529.
Article42. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Loeffler JS, Friedman WA. Radiosurgery and radiotherapy: observations and clarifications. J Neurosurg. 2004. 101:585–589.
Article43. Laitinen LV. Personal memories of the history of stereotactic neurosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2004. 55:1420–1428. discussion 1428-1429.
Article44. Leksell L. A stereotactic apparatus for intracerebral surgery. Acta Chir Scand. 1949. 99:229–233.45. Spiegel EA, Wycis HT, Marks M, Lee AJ. Stereotaxic apparatus for operations on the human brain. Science. 1947. 106:349–350.
Article46. Horsley V, Clarke RH. The structure and funtions of the cerebellum examined by a new method. Brain. 1908. 31:45–124.
Article47. Levy RP, Schulte RW, Slater JD, Miller DW, Slater JM. Stereotactic radiosurgery-the role of charged particles. Acta Oncol. 1999. 38:165–169.48. Levy RP, Fabrikant JI, Frankel KA, Phillips MH, Lyman JT. Charged-particle radiosurgery of the brain. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1990. 1:955–990.
Article49. Fabrikant JI, Levy RP, Steinberg GK, Phillips MH, Frankel KA, Silverberg GD. Stereotactic charged-particle radiosurgery: clinical results of treatment of 1,200 patients with intracranial arteriovenous malformations and pituitary disorders. Clin Neurosurg. 1992. 38:472–492.50. Lyman JT, Phillips MH, Frankel KA, Levy RP, Fabrikant JI. Radiation physics for particle beam radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1992. 3:1–8.
Article51. Wu A. Physics and dosimetry of the gamma knife. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1992. 3:35–50.
Article52. Saw GB, Celi JC, Huq MS. Therapeutic radiation physics primer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006. 20:25–43.
Article53. Friedman WA. Linear accelerator radiosurgery. Clin Neurosurg. 1992. 38:445–471.
Article54. Podgorsak EB. Physics for radiosurgery with linear accelerators. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1992. 3:9–34.
Article55. Friedman WA. LINAC radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 1990. 1:991–1008.
Article56. Podgorsak EB, Pike B, Olivier A, Pla M, Souhami L. Radiosurgery with high energy photon beams: a comparison among techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989. 16:857–865.
Article57. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lunsford LD. Dose selection in stereotactic radiosurgery. Prog Neurol Surg. 2007. 20:28–42.
Article58. Andrews DW, Bednarz G, Evans JJ, Downes B. A review of 3 current radiosurgery systems. Surg Neurol. 2006. 66:559–564.
Article59. Smith RP, Heron DE, Huq MS, Yue NJ. Modern radiation treatment planning and delivery-from Röntgen to real time. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006. 20:45–62.
Article60. Ting JY, Scarbrough TJ. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy and image-guided radiation therapy: small clinic implementation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006. 20:63–86.
Article61. Hogle WP. The state of the art in radiation therapy. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2006. 22:212–220.
Article62. Klish MD, Watson GA, Shrieve DC. Radiation and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for metastatic spine tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2004. 15:481–490.
Article63. Rosenzweig KE, Amols H, Ling CC. New radiotherapy technologies. Semin Surg Oncol. 2003. 21:190–195.
Article64. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. Dose selection in stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1999. 10:271–280.
Article65. Corn BW, Curran WJ Jr, Shrieve DC, Loeffler JS. Stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy: new developments and new directions. Semin Oncol. 1997. 24:707–714.66. Graham JD, Nahum AE, Brada M. A comparison of techniques for stereotactic radiotherapy by linear accelerator based on 3-dimensional dose distributions. Radiother Oncol. 1991. 22:29–35.
Article67. Solberg TD, Boedeker KL, Fogg R, Selch MT, DeSalles AA. Dynamic arc radiosurgery field shaping: a comparison with static field conformal and noncoplanar circular arcs. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001. 49:1481–1491.
Article68. Solberg TD, Selch MT, Smathers JB, DeSalles AA. Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: rationale and methods. Med Dosim. 1998. 23:209–219.
Article69. Romanelli P, Schweikard A, Schlaefer A, Adler J. Computer aided robotic radiosurgery. Comput Aided Surg. 2006. 11:161–174.
Article70. Steffey-Stacy EC. Frameless, image-guided stereotactic radiosurgery. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2006. 22:221–232.
Article71. Kuo JS, Yu C, Petrovich Z, Apuzzo ML. The CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery system: description, installation, and an initial evaluation of use and functionality. Neurosurgery. 2003. 53:1235–1239. discussion 1239.
Article72. Ross PJ, Ashamalla H, Rafla S. Advances in stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic radiation therapy. Radiat Ther. 2001. 10:57–72.73. Mackie TR, Balog J, Ruchala K, Shepard D, Aldridge S, Fitchard E, Reckwerdt P, Olivera G, McNutt T, Mehta M. Tomotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1999. 9:108–117.
Article74. Mackie TR, Holmes T, Swerdloff S, Reckwerdt P, Deasy JO, Yang J, Paliwal B, Kinsella T. Tomotherapy: a new concept for the delivery of dynamic conformal radiotherapy. Med Phys. 1993. 20:1709–1719.
Article75. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Witt TC, Flickinger JC. The future of radiosurgery: radiobiology, technology, and applications. Surg Neurol. 2000. 54:406–414.
Article76. Barnett GH, Linskey ME, Adler JR, Cozzens JW, Friedman WA, Heilbrun MP, Lunsford LD, Schulder M, Sloan AE. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Congress of Neurolofical Surgeons Washington Committee Stereotactic Radiosurgery Task Force. Stereotactic radiosurgery-an organized neurosurgery-sanctioned definition. J Neurosurg. 2007. 106:1–5.
Article77. Kavanagh BD, Timmerman RD. Stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiation therapy: an overview of technical considerations and clinical applications. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006. 20:87–95.
Article78. Pollock BE, Lunsford LD. A call to define stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2004. 55:1371–1373.
Article79. Adler JR Jr, Colombo F, Heilbrun MP, Winston K. Toward an expanded view of radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2004. 55:1374–1376.
Article80. Ostertag ChB. Stereotactic radiation therapy and radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1994. 63:220–232.
Article81. Lunsford LD, Alexander E, Chapman P, Coffey R, Friedman W, Harsh G IV, Maciunas R, Olivier A, Steinberg G, Walsh J, Larson DA, Bova F, Eisert D, Kline R, Loeffler J, Lutz W, Mehta M, Palta J, Schewe K, Schultz C, Shaw E, Wilson JF. Consensus statement on stereotactic radiosurgery: quality improvement. Neurosurgery. 1994. 34:193–195.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Pathological Changes after Stereotactic Radiosurgery for AVM
- LINAC-based High-precision Radiotherapy: Radiosurgery, Image-guided Radiotherapy, and Respiratory-gated Radiotherapy
- Result of Stereotactic LINAC Radiosurgery of AVM
- Complications after Radiosurgery of the Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
- The mixed era of stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy