J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2012 Nov;53(11):1603-1608.
The Efficacy of KR-1W Aberrometer in Assessing the Astigmatism after Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Sungmo Eye Hospital, Busan, Korea. medicalhan@hanmail.net
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of the KR-1W aberrometer in assessing the astigmatism and the achieved axis after AcrySof Toric intraocular lens (IOL) implantation.
METHODS
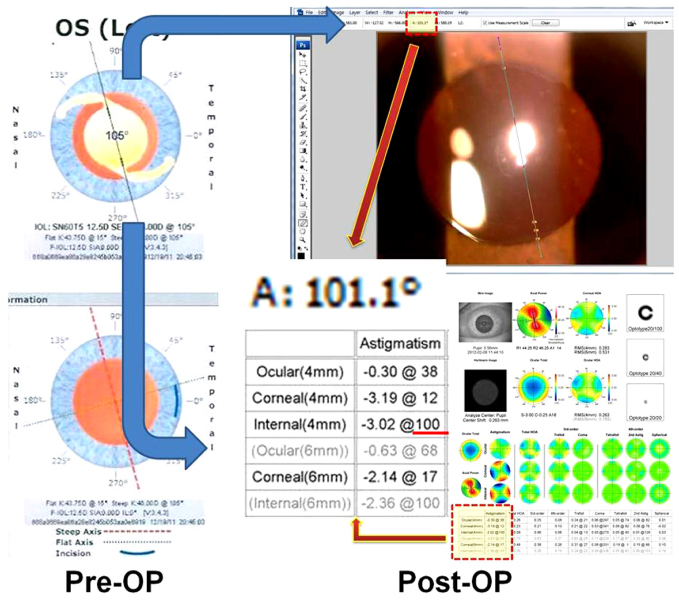
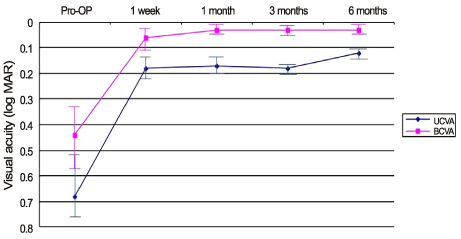
Thirty-nine patients (48 eyes) that had undergone phacoemulsification and AcrySof Toric IOL implantation were included in the present study. At postoperative 1 month, ocular aberrations of all the eyes were measured using the KR-1W aberrometer before mydriasis and the achieved axis of AcrySof Toric IOL was measured by slit lamp examination after mydriasis. The achieved axis measured by slit lamp examination and the astigmatism of the implanted AcrySof Toric IOL were compared with the KR-1W.
RESULTS
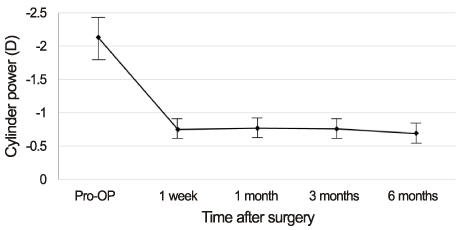
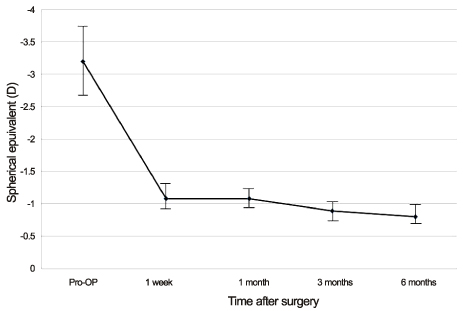
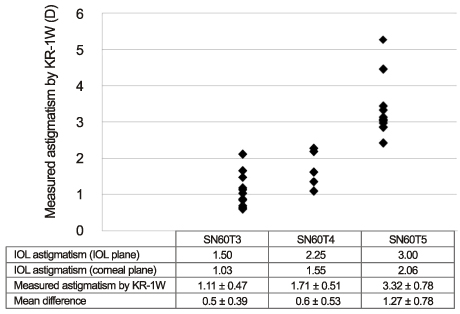
The mean achieved lens axis after mydriasis measured by slit lamp examination and KR-1W was 86.43 +/- 47.49 degrees and 88.93 +/- 41.22 degrees, respectively. The correlation coefficient of the 2 methods was 0.992 (p < 0.001). The measured astigmatism according to the AcrySof Toric IOL model was 1.11 +/- 0.47D in SN60T3, 1.71 +/- 0.51D in SN60T4, and 3.32 +/- 0.78D in SN60T5.
CONCLUSIONS
Without the need to directly evaluate the axis of implanted Toric IOL after mydriasis, the achieved lens axis can be measured by the KR-1W without mydriasis. The AcrySof Toric IOL model could be assessed by the KR-1W without information about the AcrySof Toric IOL model.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shimizu K, Misawa A, Suzuki Y. Toric intraocular lenses: correcting astigmatism while controlling axis shift. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994. 20:523–526.2. Werblin TP. Do three-piece PMMA IOLs rotate after implantation in the capsular bag? J Refract Surg. 1995. 11:468–471.3. Gills JP, Martin RG, Sanders DR. Sutureless Cataract Surgery: An Evolution toward Minimally Invasive Technique. 1992. Thorofare, NJ: Slack Inc;183–197.4. Gills JP, Martin RG, Thornton SP, Sanders DR. Surgical Treatment of Astigmatism. 1994. Thorofare, NJ: Slack Inc;159–164.5. Liang J, Grimm B, Goelz S, Bille JF. Objective measurement of wave aberrations of the human eye with the use of a Hartmann-Shack wave-front sensor. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 1994. 11:1949–1957.6. Thibos LN. Principles of Hartmann-Shack aberrometry. J Refract Surg. 2000. 16:S563–S565.7. MacRae S, Fujieda M. Slit skiascopic-guided ablation using the Nidek laser. J Refract Surg. 2000. 16:S576–S580.8. Molebny VV, Pallikaris IG, Naoumidis LP, et al. Retina ray-tracing technique for eye-refraction mapping. Proc SPIE. 1997. 2971:175–183.9. Navarro R, Moreno-Barriuso E. Laser ray-tracing method for optical testing. Opt Lett. 1999. 24:951–953.10. Ninn-Pedersen K, Stenevi U, Ehinger B. Cataract patients in a defined Swedish population 1986-1990. II. Preoperative observations. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1994. 72:10–15.11. Hoffer KJ. Biometry of 7,500 cataractous eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980. 90:360–368.12. Hoffer KJ. Biometry of 7,500 cataractous eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980. 90:360–368.13. Amesbury EC, Miller KM. Correction of astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009. 20:19–24.14. Poll JT, Wang L, Koch DD, Weikert MP. Correction of astigmatism during cataract surgery: toric intraocular lens compared to peripheral corneal relaxing incisions. J Refract Surg. 2011. 27:165–171.15. Kim MH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Long-term efficacy and rotational stability of acrysof toric intraocular lens implantation in cataract surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010. 24:207–212.16. Pineda R, Denevich S, Lee WC, et al. Economic evaluation of toric intraocular lens: a short- and long-term decision analytic model. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010. 128:834–840.17. Nguyen TM, Miller KM. Digital overlay technique for documenting toric intraocular lens axis orientation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000. 26:1496–1504.18. Sun XY, Vicary D, Montgomery P, Griffiths M. Toric intraocular lenses for correcting astigmatism in 130 eyes. Ophthalmology. 2000. 107:1776–1781.19. Chang DF. Early rotational stability of the longer Staar toric intraocular lens: fifty consecutive cases. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003. 29:935–940.20. Novis C. Astigmatism and toric intraocular lenses. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2000. 11:47–50.21. Bauer NJ, de Vries NE, Webers CA, et al. Astigmatism management in cataract surgery with the AcrySof toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008. 34:1483–1488.22. Na JH, Lee HS, Joo CK. The clinical result of acrysof toric intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009. 50:831–838.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of Miscorrection after Implantation of the Toric Intraocular Lens
- Effect of Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation on Astigmatism in Cataract Surgery
- Comparison of Efficacies in Treating Astigmatism between Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation and Limbal Relaxing Incision
- Intraindividual Comparison of ICL and Toric ICL Implantation in the Correction of High Myopia With Astigmatism
- Modified Capsular Tension Ring Scleral Fixation and Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation in a Patient with Homocystinuria