Nat Prod Sci.
2016 Jun;22(2):111-116. 10.20307/nps.2016.22.2.111.
Chemical Components from the Stems of Pueraria lobata and Their Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 305-764, Korea. yhk@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2328876
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2016.22.2.111
Abstract
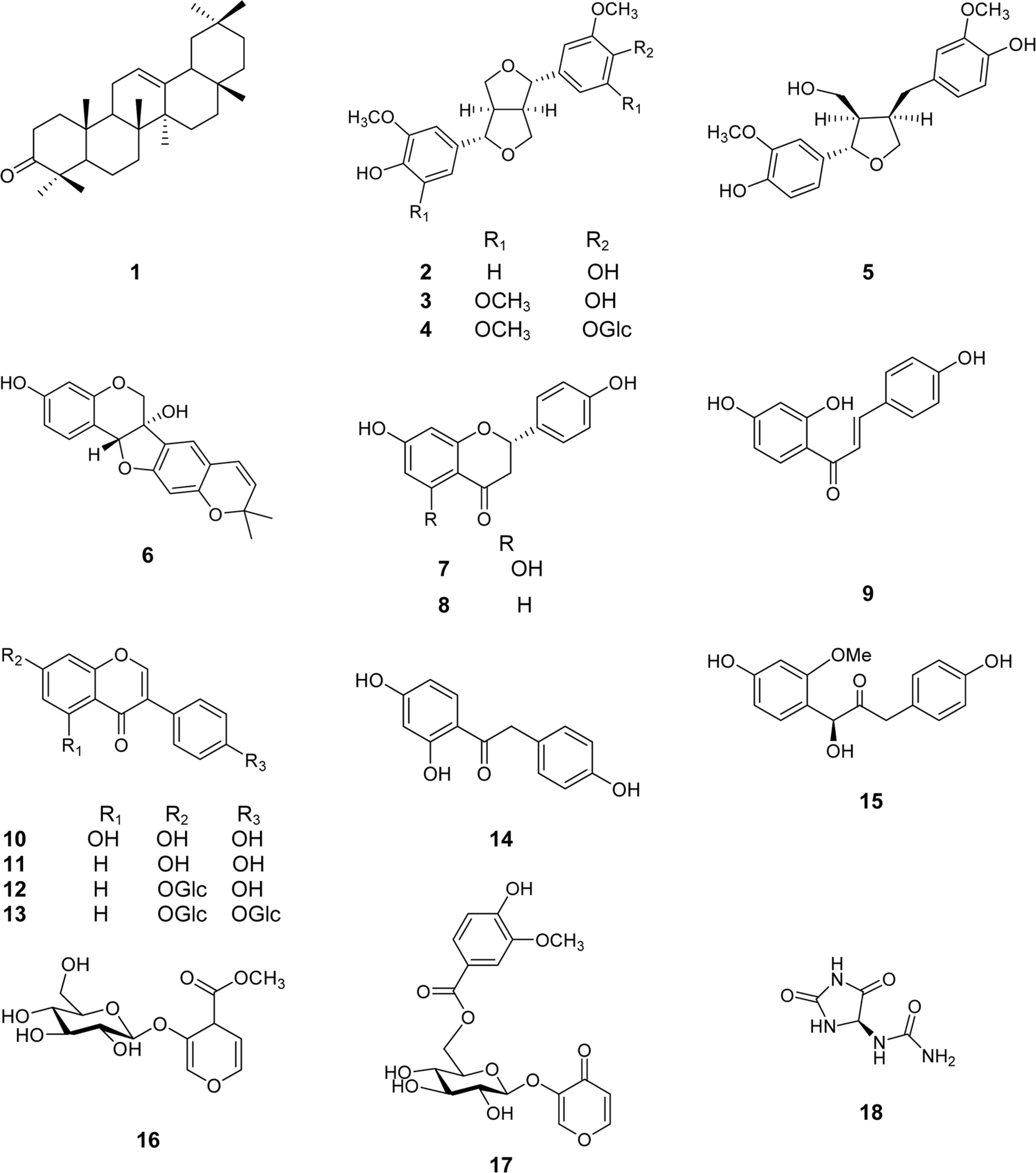
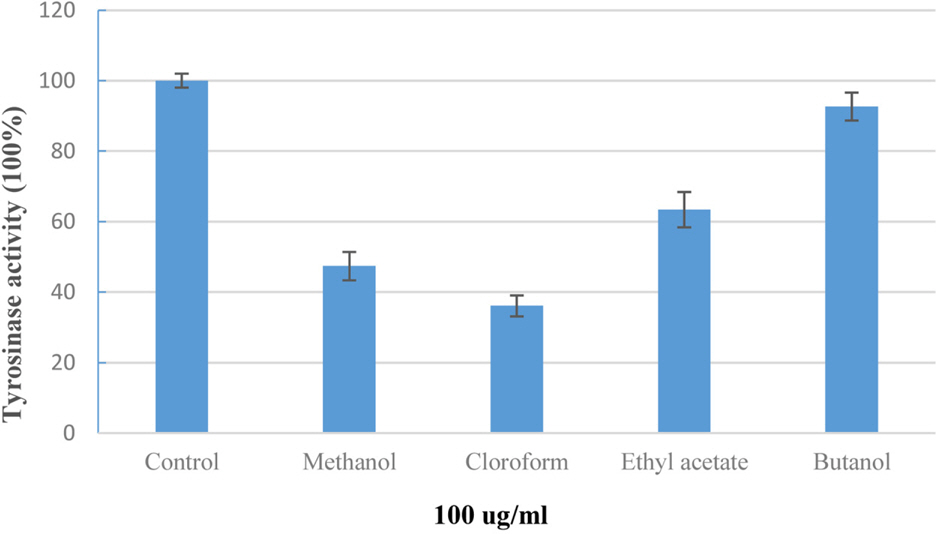
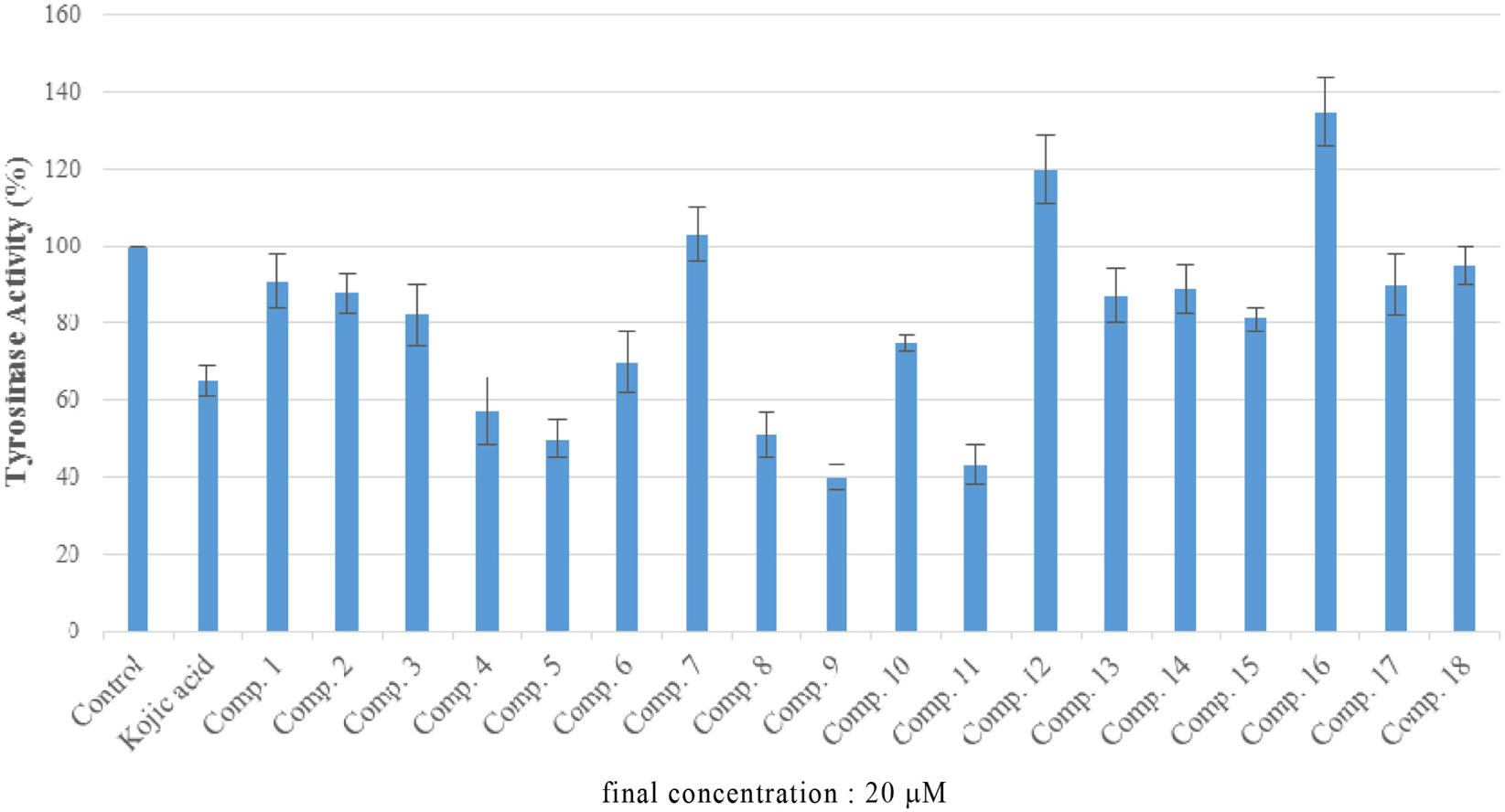
- Phytochemical investigation of the stems of Pueraria lobata (Wild) Ohwi (Leguminosae), led to the isolation of eighteen known compounds: β-amyrone (1), (+)-pinoresinol (2), (+)-syringaresinol (3) (+)-syringaresinol-O-β-D-glucoside (4), (+)-lariciresinol (5), (-)-tuberosin (6), naringenin (7), liquiritigenin (8), isoliquiritigenin (9) genistein (10), daidzein (11) daidzin (12) daidzein 4',7-diglucoside (13) 2,4,4'-trihydroxy deoxybenzoin (14), S-(+)-1-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxy-phenyl)propan-2-one (15), methyl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosylbenzoate (16), pyromeconic acid 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside 6'-(O-4''-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate) (17), and allantion (18). The chemical structures of these compounds were elucidated from spectroscopic data and by comparison of those data with previously published results. The effects of isolated compounds on mushroom tyrosinase enzymatic activity were screened. The results indicated that, chloroform extract of P. lobata stems turned out to be having tyrosinase inhibitory effect, and only compounds 5, 8, 9, and 11 showed enzyme inhibitory activity, with ICâ‚…â‚€ values of 21.49 ± 4.44, 25.24 ± 6.79, 4.85 ± 2.29, and 17.50 ± 1.29 µM, respectively, in comparison with these of positive control, kojic acid (ICâ‚…â‚€ 12.28 ± 2.72 µM). The results suggest that P. lobata stems extract as well as its chemical components may represent as potential candidates for tyrosinase inhibitors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
(1). Seo S. Y., Sharma V. K., Sharma N. J.Agric. Food Chem. 2003; 51:2837–2853.(2). Nhiem N. X., Yen H. T., Luyen B. T. T., Tai B. H., Hoan P. V., Thao N. P., Anh H. L. T., Ban N. K., Kiem P. V., Minh C. V., Kim J. H., Jeon M. N., Kim Y. H.Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2015; 36:703–706.(3). Cho Y. J., Son B. W., Jeong D. Y., Choi H. D., Park J. H. Kor. J.Pharmacogn. 1998; 29:193–197.(4). Chen T. R., Shih S. C., Ping H. P., Wei Q. K. J.Food Drug Anal. 2012; 20:681–685.(5). Hung V. P., Morita N.Food Chem. 2007; 105:749–755.(6). Li G., Zhang Q., Wang Y.Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010; 35:3156–3160.(7). Luo X. D., Wu S. H., Ma Y. B., Wu D. G.Acta Bot. Sin. 2001; 43:426–430.(8). Xie L. H., Akao T., Hamasaki K., Deyama T., Hattori M.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003; 51:508–515.(9). Park J. A., Kim H. J., Jin C. B., Lee K. T., Lee Y. S.Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003; 26:1009–1013.(10). Shahat A. A., Abdel-Azim N. S., Pieters L., Vlietinck A. J.Fitoterapia. 2004; 75:771–773.(11). Wang Q. H., Peng K., Tan L. H., Dai H. F.Molecules. 2010; 15:4011–4016.(12). Shirataki Y., Tsuzuku T., Yokoe I., Hirano R. T., Komatsu M.Chem. Parm. Bull. 1990; 38:1712–1716.(13). Kulesh N. I., Vasilevskaya N. A., Veselova M. V., Denisenko V. A., Fedoreev S. A.Chem. Nat. Compd. 2008; 44:712–714.(14). Yahara S., Ogata T., Saijo R., Konishi R., Yamahara J., Miyahara K., Nohara T.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989; 37:979–987.(15). Veitch N. C., Sutton P. S., Kite G. C., Ireland H. E. J.Nat. Prod. 2003; 66:210–216.(16). Kim B. H., Kim C. M. Kor. J.Pharmacogn. 1995; 26:18–22.(17). Yang M. C., Kim D. S., Jeong S. W., Ma J. Y.Korean J. Medicinal Crop. Sci. 2011; 19:446–455.(18). Jun M., Fu H.-Y., Hong J., Wan X., Yang C. S., Ho C. T. J.Food Sci. 2003; 68:2117–2122.(19). Kinjo J. E., Furusawa J. I., Baba J., Takeshita T., Yamasaki M., Ohara T.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987; 35:4846–4850.(20). Ng L. T., Ko H. H., Lu T. M.Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009; 17:4360–4366.(21). Bezuidenhout S. C., Bezuidenhoudt B. C. B., Ferreira D.Phytochemistry. 1988; 27:2329–2334.(22). Wang C., Zhang T. T., Du G. H., Zhang D. M. J.Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2011; 13:817–825.(23). Chai X., Su Y. F., Guo L. P., Wu D., Zhang J. F., Si C. L., Kim J. K., Bae Z. S.Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008; 36:216–218.(24). Yin F., Hu L., Pan R.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004; 52:1440–1444.(25). Khatib S., Nerya O., Musa R., Shmuel M., Tamir S., Vaya J.Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005; 13:433–441.(26). Wang Y., Curtis-Long M. J., Lee B. W., Yuk H. J., Kim D. W., Tan X. F., Park K. H.Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014; 22:1115–1120.(27). Kim N. K., Park H. M., Lee J. K., Ku K. M., Lee C. H. J.Agric. Food Chem. 2015; 63:8631–8639.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Pueraria lobata on Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption
- The Effects of SCH-T2 Seaweed Extract
- Efficacy and Safety of Pueraria lobata Extract in Gray Hair Prevention: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
- Antitumor activity of spinasterol isolated from Pueraria roots
- A Study on the Tyrosinase Related to the Albinism