J Korean Surg Soc.
2013 Jul;85(1):1-6.
Experience of treatment of patients with granulomatous lobular mastitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. paojlus@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Surgery, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To present the author's experience with various treatment methods of granulomatous lobular mastitis (GLM) and to determine effective treatment methods of GLM.
METHODS
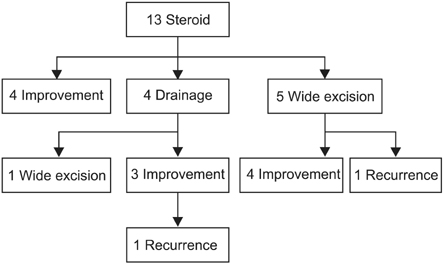
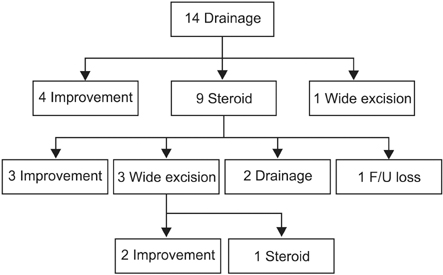
Fifty patients who were diagnosed with GLM were classified into five groups based on the initial treatment methods they underwent, which included observation (n = 8), antibiotics (n = 3), steroid (n = 13), drainage (n = 14), and surgical excision (n = 12). The treatment processes in each group were examined and their clinical characteristics, treatment processes, and results were analyzed respectively.
RESULTS
Success rates with each initial treatment were observation, 87.5%; antibiotics, 33.3%; steroids, 30.8%; drainage, 28.6%; and surgical excision, 91.7%. In most cases of observation, the lesions were small and the symptoms were mild. A total of 23 patients underwent surgical excision during treatment. Surgical excision showed particularly fast recovery, high success rate (90.3%) and low recurrence rate (8.7%).
CONCLUSION
The clinical course of GLM is complex and the outcome of each treatment type are variable. Surgery may play an important role when a lesion is determined to be mass-forming or appears localized as an abscess pocket during breast examination or imaging study.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Donn W, Rebbeck P, Wilson C, Gilks CB. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a report of three cases and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994. 118:822–825.2. Erhan Y, Veral A, Kara E, Ozdemir N, Kapkac M, Ozdedeli E, et al. A clinicopthologic study of a rare clinical entity mimicking breast carcinoma: idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Breast. 2000. 9:52–56.3. Akcan A, Akyildiz H, Deneme MA, Akgun H, Aritas Y. Granulomatous lobular mastitis: a complex diagnostic and therapeutic problem. World J Surg. 2006. 30:1403–1409.4. Lee JH, Oh KK, Kim EK, Kwack KS, Jung WH, Lee HK. Radiologic and clinical features of idiopathic granulomatous lobular mastitis mimicking advanced breast cancer. Yonsei Med J. 2006. 47:78–84.5. Kessler E, Wolloch Y. Granulomatous mastitis: a lesion clinically simulating carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972. 58:642–646.6. Kim J, Tymms KE, Buckingham JM. Methotrexate in the management of granulomatous mastitis. ANZ J Surg. 2003. 73:247–249.7. Tuncbilek N, Karakas HM, Okten OO. Imaging of granulomatous mastitis: assessment of three cases. Breast. 2004. 13:510–514.8. Imoto S, Kitaya T, Kodama T, Hasebe T, Mukai K. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: case report and review of the literature. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1997. 27:274–277.9. Fletcher A, Magrath IM, Riddell RH, Talbot IC. Granulomatous mastitis: a report of seven cases. J Clin Pathol. 1982. 35:941–945.10. Bani-Hani KE, Yaghan RJ, Matalka II, Shatnawi NJ. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: time to avoid unnecessary mastectomies. Breast J. 2004. 10:318–322.11. Diesing D, Axt-Fliedner R, Hornung D, Weiss JM, Diedrich K, Friedrich M. Granulomatous mastitis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2004. 269:233–236.12. Kim YJ, Choi YJ, Kim JY, Kim HJ, Park YS, Hong SW, et al. Clinicopathologic features of granulomatous mastitis. Korean J Pathol. 2005. 39:181–186.13. Going JJ, Anderson TJ, Wilkinson S, Chetty U. Granulomatous lobular mastitis. J Clin Pathol. 1987. 40:535–540.14. Heer R, Shrimankar J, Griffith CD. Granulomatous mastitis can mimic breast cancer on clinical, radiological or cytological examination: a cautionary tale. Breast. 2003. 12:283–286.15. Wilson JP, Massoll N, Marshall J, Foss RM, Copeland EM, Grobmyer SR. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: in search of a therapeutic paradigm. Am Surg. 2007. 73:798–802.16. Al-Khaffaf B, Knox F, Bundred NJ. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a 25-year experience. J Am Coll Surg. 2008. 206:269–273.17. Lai EC, Chan WC, Ma TK, Tang AP, Poon CS, Leong HT. The role of conservative treatment in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Breast J. 2005. 11:454–456.18. Tae SY, Lee SW, Han SU, Woo HD, Son DM, Kim SY, et al. Surgical treatment for idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 77:153–160.19. Asoglu O, Ozmen V, Karanlik H, Tunaci M, Cabioglu N, Igci A, et al. Feasibility of surgical management in patients with granulomatous mastitis. Breast J. 2005. 11:108–114.20. DeHertogh DA, Rossof AH, Harris AA, Economou SG. Prednisone management of granulomatous mastitis. N Engl J Med. 1980. 303:799–800.21. Hovanessian Larsen LJ, Peyvandi B, Klipfel N, Grant E, Iyengar G. Granulomatous lobular mastitis: imaging, diagnosis, and treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009. 193:574–581.22. Raj N, Macmillan RD, Ellis IO, Deighton CM. Rheumatologists and breasts: immunosuppressive therapy for granulomatous mastitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004. 43:1055–1056.23. Erozgen F, Ersoy YE, Akaydin M, Memmi N, Celik AS, Celebi F, et al. Corticosteroid treatment and timing of surgery in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis confusing with breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. 123:447–452.24. Jorgensen MB, Nielsen DM. Diagnosis and treatment of granulomatous mastitis. Am J Med. 1992. 93:97–101.25. Sato N, Yamashita H, Kozaki N, Watanabe Y, Ohtsuka T, Kuroki S, et al. Granulomatous mastitis diagnosed and followed up by fine-needle aspiration cytology, and successfully treated by corticosteroid therapy: report of a case. Surg Today. 1996. 26:730–733.26. Sakurai T, Oura S, Tanino H, Yoshimasu T, Kokawa Y, Kinoshita T, et al. A case of granulomatous mastitis mimicking breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer. 2002. 9:265–268.27. Katz U, Molad Y, Ablin J, Ben-David D, Paran D, Gutman M, et al. Chronic idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. 1108:603–608.