Korean J Urol.
2011 May;52(5):364-367.
Polyarteritis Nodosa Presenting with Bilateral Testicular Swelling and Complicated by Unilateral Facial Nerve Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Royal North Shore Hospital, Sydney, Australia. yuigiyuminaga@gmail.com
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Royal North Shore Hospital, Sydney, Australia.
- 3Department of Pathology, Royal North Shore Hospital, Sydney, Australia.
Abstract
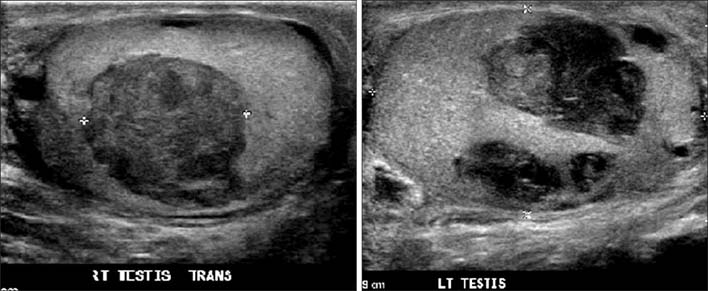
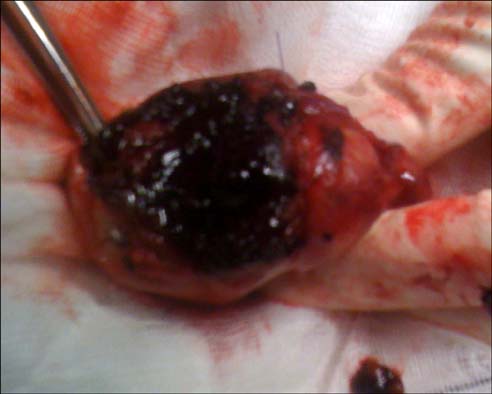
- Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing vasculitis that is generally restricted to medium-sized vessels. Here we describe the first case of a patient in which a bilateral testicular mass was a presenting symptom and the diagnosis was made on the basis of testicular histopathology. A 53-year-old Asian man presented with a history of constitutional symptoms and testicular swelling. Scrotal ultrasound revealed two avascular, bilateral, intratesticular lesions. The bilateral testicular abscess was treated without improvement. The patient developed left seventh cranial nerve palsy during his admission. The clinical changes made vasculitis or a related disorder more likely and the patient underwent a right testicular biopsy. Histopathology demonstrated features of transmural inflammation and fibrinoid necrosis of medium-sized vessel walls, consistent with PAN. This case illustrates the difficulty in diagnosing polyarteritis nodosa with isolated bilateral testicular swelling and the delay in the diagnosis. After 9 months of follow-up, no relapse had occurred and the patient's testosterone level was on the lower side of normal.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Watts RA, Lane SE, Scott DG, Koldingsnes W, Nossent H, Gonzalez-Gay MA, et al. Epidemiology of vasculitis in Europe. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. 60:1156–1157.2. Lightfoot RW Jr, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Hunder GG, Zvaifler NJ, McShane DJ, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990. 33:1088–1093.3. Shurbaji MS, Epstein JI. Testicular vasculitis: implications for systemic disease. Hum Pathol. 1988. 19:186–189.4. Travers RL, Allison DJ, Brettle RP, Hughes GR. Polyarteritis nodosa: a clinical and angiographic analysis of 17 cases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1979. 8:184–199.5. Gayraud M, Guillevin L, le Toumelin P, Cohen P, Lhote F, Casassus P, et al. Long-term followup of polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome: analysis of four prospective trials including 278 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:666–675.6. Eilber KS, Freedland SJ, Rajfer J. Polyarteritis nodosa presenting as hematuria and a testicular mass. J Urol. 2001. 166:624.7. Tanuma Y, Oda T, Yokoo A, Ito S, Takeuchi K. Recurrent polyarteritis nodosa limited to the testis. J Urol. 2003. 170:1953.8. Stroup SP, Herrera SR, Crain DS. Bilateral testicular infarction and orchiectomy as a complication of polyarteritis nodosa. Rev Urol. 2007. 9:235–238.9. Meeuwissen J, Maertens J, Verbeken E, Blockmans D. Case reports: testicular pain as a manifestation of polyarteritis nodosa. Clin Rheumatol. 2008. 27:1463–1466.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of polyarteritis nodosa complicated by bilateral renal hematomas and U.G.I. bleeding
- A Case of Polyarteritis Nodosa Presented as Myositis
- Bilateral Simultaneous Bell's Palsy-Two Case Studies
- A Case of Bilateral Bell's Palsy with Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus
- A case of polyarteritis nodosa with bilateral ureteral obstruction