Korean J Urol.
2009 Apr;50(4):380-386.
Analysis of the Learning Curve for Laparoscopic Renal Surgeries in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kskim2@amc.seoul.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
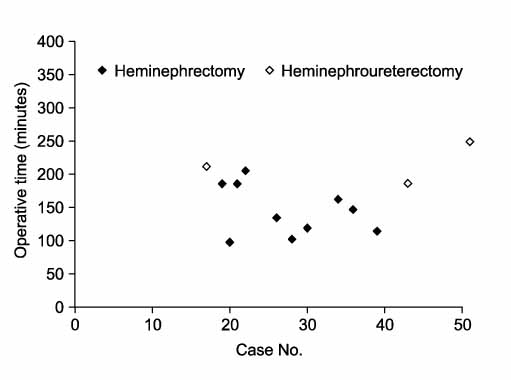
To guide pediatric urologists to start laparoscopic renal surgery in children, we analyze our experience with various laparoscopic renal surgeries to highlight the surgical outcomes and the degree of completion of specific laparoscopic skills. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively analyzed 51 children who underwent laparoscopic renal surgery by a single surgeon between March 2002 and July 2008 (25 nephrectomies, 12 nephroureterectomies, 10 heminephrectomies, 3 heminephroureterectomies, and 1 heminephrectomy in a horseshoe kidney). We compared the degree of completion of specific laparoscopic skills as well as operative parameters such as operative time, estimated blood loss, and complication rate. RESULTS: All laparoscopic renal surgeries were completed as planned without open conversions. In the nephrectomy group (nephrectomy+nephroureterectomy), the mean operative time decreased after 10 cases (239 minutes vs. 145 minutes, p<0.001). A decrease in mean estimated blood loss was also noted after 10 cases (119 vs. 32 ml, p<0.05). The complication rate decreased after 20 cases (30% vs. 4%, p<0.05). In all patients, the completion rates for specific laparoscopic skills were 98% for trocar insertion, 80% for removal of a pathological lesion, 82% for retroperitoneal insufflation, and 73% for refluxing ureterectomy and suturing. The overall completion rate increased after 18 cases (79% vs. 91%, p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: Operative time and blood loss in pediatric laparoscopic renal surgery are rapidly improved with experience. Improvement in the complication rate and specific laparoscopic skills require more time. We recommend that pediatric urologists beginning laparoscopic surgery try complex surgeries such as heminephrectomy or heminephroureterectomy after they have surmounted the learning curve of easy surgeries such as nephrectomy or nephroureterectomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Smaldone MC, Sweeney DD, Ost MC, Docimo SG. Laparoscopy in paediatric urology: present status. BJU Int. 2007. 100:143–150.2. Yucel S, Brown B, Bush NC, Ahmad N, Baker LA. What to anticipate with experience in pediatric laparoscopic ablative renal surgery. J Urol. 2008. 179:697–702.3. Lee A, Lim D, Oh SJ, Park MS, Choi H. Laparoscopic nephrectomy and heminephrectomy in pediatric patients. Korean J Urol. 1998. 39:698–703.4. Lee KS, Kim GN, Kim DY, Chung SK, Park YK, Kwon TG. Laparoscopic nephrectomy for ectopic dysplastic kidney. Korean J Urol. 2004. 45:88–90.5. You D, Kim KS. Selection of approach method during laparoscopic renal surgeries in pediatric patients. Korean J Urol. 2007. 48:276–282.6. Ehrlich RM, Gershman A, Mee S. Laparoscopic nephrectomy in a child: expanding horizons for laparoscopy in pediatric urology. J Endourol. 1992. 6:463–465.7. Jordan GH, Winslow BH. Laparoscopic upper pole partial nephrectomy with ureterectomy. J Urol. 1993. 150:940–943.8. Piaggio L, Franc-Guimond J, Figueroa TE, Barthold JS, González R. Comparison of laparoscopic and open partial nephrectomy for duplication anomalies in children. J Urol. 2006. 175:2269–2273.9. Robinson BC, Snow BW, Cartwright PC, De Vries CR, Hamilton BD, Anderson JB. Comparison of laparoscopic versus open partial nephrectomy in a pediatric series. J Urol. 2003. 169:638–640.10. Shay BF, Thomas R, Monga M. Urology practice patterns after residency training in laparoscopy. J Endourol. 2002. 16:251–256.11. Colegrove PM, Winfield HN, Donovan JF Jr, See WA. Laparoscopic practice patterns among North American urologists 5 years after formal training. J Urol. 1999. 161:881–886.12. Farhat W, Khoury A, Bagli D, McLorie G, El-Ghoneimi A. Mentored retroperitoneal laparoscopic renal surgery in children: a safe approach to learning. BJU Int. 2003. 92:617–620.13. Ku JH, Yeo WG, Kim HH, Choi H. Laparoscopic nephrectomy for renal diseases in children: Is there a learning curve? J Pediatr Surg. 2005. 40:1173–1176.14. Mushtaq I, Haleblian G. Laparoscopic heminephrectomy in infants and children: first 54 cases. J Pediatr Urol. 2007. 3:100–103.15. Valla JS, Breaud J, Carfagna L, Tursini S, Steyaert H. Treatment of ureterocele on duplex ureter: upper pole nephrectomy by retroperitoneoscopy in children based on a series of 24 cases. Eur Urol. 2003. 43:426–429.16. Passerotti CC, Nguyen HT, Retik AB, Peters CA. Patterns and predictors of laparoscopic complications in pediatric urology: the role of ongoing surgical volume and access techniques. J Urol. 2008. 180:681–685.17. Peters CA. Complications in pediatric urological laparoscopy: results of a survey. J Urol. 1996. 155:1070–1073.18. Esposito C, Lima M, Mattioli G, Mastroianni L, Centonze A, Monguzzi GL, et al. Complications of pediatric urological laparoscopy: mistakes and risks. J Urol. 2003. 169:1490–1492.19. Pareek G, Hedican SP, Gee JR, Bruskewitz RC, Nakada SY. Meta-analysis of the complications of laparoscopic renal surgery: comparison of procedures and techniques. J Urol. 2006. 175:1208–1213.20. Rosales A, Salvador DJ, Palou J, De Graeve N, Montlleó M, Huguet J, et al. 846 complications of laparoscopic renal surgery. Eur Urol. 2007. 6:Suppl 2. 234. abstract 846.21. Androulakakis PA, Stephanidis A, Antoniou A, Christophoridis C. Outcome of the distal ureteric stump after (hemi) nephrectomy and subtotal ureterectomy for reflux or obstruction. BJU Int. 2001. 88:586–589.22. El-Ghoneimi A, Abou-Hashim H, Bonnard A, Verkauskas G, Macher MA, Hout O, et al. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy in children: at last the gold standard? J Pediatr Urol. 2006. 2:357–363.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Learning Curve and Clinicopathologic Analysis in Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy; Performed by a Single Young Surgeon with No Experience of Open Adrenalectomy
- The Learning Curve of the Beginner Surgeon with Supervisor for Laparoscopic Totally Extraperitoneal Repair
- Laparoscopic Pediatric Surgery
- Learning Curve for a Laparoscopic Appendectomy by a Surgical Trainee
- Transition from Conventional to Reduced-Port Laparoscopic Gastrectomy to Treat Gastric Carcinoma: a Single Surgeon's Experience from a Small-Volume Center