Translation and Validation of the Korean Version of the 39-Item Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkinson@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Parkinson/Alzheimer Center, Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Neurology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Neurology, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2287567
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2013.9.1.26
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The importance of health-related quality of life (HrQoL) has been increasingly emphasized when assessing and providing treatment to patients with chronic, progressive, degenerative disorders. The 39-item Parkinson's disease questionnaire (PDQ-39) is the most widely used patient-reporting scale to assess HrQoL in Parkinson's disease (PD). This study evaluated the validity and reliability of the translated Korean version of the PDQ-39 (K-PDQ-39).
METHODS
One hundred and two participants with PD from 10 movement disorder clinics at university-affiliated hospitals in South Korea completed the K-PDQ-39. All of the participants were also tested using the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), Korean version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE), Korean version of the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Scale (K-MADS), Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) and non-motor symptoms scale (NMSS). Retests of the K-PDQ-39 were performed over time intervals from 10 to 14 days in order to assess test-retest reliability.
RESULTS
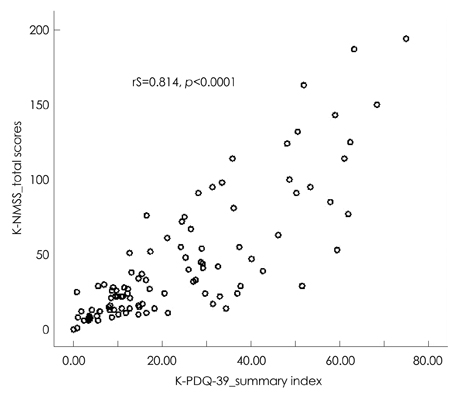
Each K-PDQ-39 domain showed correlations with the summary index scores (rS=0.559-0.793, p<0.001). Six out of eight domains met the acceptable standard of reliability (Cronbach's alpha coefficient > or =0.70). The Guttman split-half coefficient value of the K-PDQ-39 summary index, which is an indicator of test-retest reliability, was 0.919 (p<0.001). All of the clinical variables examined except for age, comprising disease duration, levodopa equivalent dose, modified Hoehn and Yahr stage (H&Y stage), UPDRS part I, II and III, mood status (K-MADS), cognition (K-MMSE), daytime sleepiness (ESS) and (NMSS) showed strong correlations with the K-PDQ-39 summary index (p<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
The K-PDQ-39 has been validated for use in the Korean-speaking PD population. The questionnaire is a valid and reliable assessment tool for assessing the HrQoL of Korean PD patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Validation of the Korean Version of the Scales for Outcomes in Parkinson's Disease-Sleep
Young-Hee Sung, Hee Jin Kim, Seong-Beom Koh, Joong-Seok Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Sang-Myung Cheon, Jin Whan Cho, Yoon-Joong Kim, Hyeo-Il Ma, Mee Young Park, Jong Sam Baik, Phil Hyu Lee, Sun Ju Chung, Jong-Min Kim, In-Uk Song, Han-Joon Kim, Ji-Young Kim, Do Young Kwon, Jae-Hyeok Lee, Jee-Young Lee, Ji Seon Kim, Ji Young Yun, Jin Yong Hong, Mi-Jung Kim, Jinyoung Youn, Ji Sun Kim, Eung Seok Oh, Hui-Jun Yang, Won Tae Yoon, Sooyeoun You, Kyum-Yil Kwon, Hyung-Eun Park, Su-Yun Lee, Younsoo Kim, Hee-Tae Kim, Tae-Beom Ahn
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(2):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e14.The KMDS-NATION Study: Korean Movement Disorders Society Multicenter Assessment of Non-Motor Symptoms and Quality of Life in Parkinson's Disease NATION Study Group
Do-Young Kwon, Seong-Beom Koh, Jae Hyeok Lee, Hee Kyung Park, Han-Joon Kim, Hae-Won Shin, Jinyoung Youn, Kun Woo Park, Sun-Ah Choi, Sang Jin Kim, Seong-Min Choi, Ji-Yun Park, Beom S. Jeon, Ji Young Kim, Sun Ju Chung, Chong Sik Lee, Jeong-Ho Park, Tae-Beom Ahn, Won Chan Kim, Hyun Sook Kim, Sang Myung Cheon, Hee-Tae Kim, Jee-Young Lee, Ji Sun Kim, Eun-Joo Kim, Jong-Min Kim, Kwang Soo Lee, Joong-Seok Kim, Min-Jeong Kim, Jong Sam Baik, Ki-Jong Park, Hee Jin Kim, Mee Young Park, Ji Hoon Kang, Sook Kun Song, Yong Duk Kim, Ji Young Yun, Ho-Won Lee, Hyung Geun Oh, Jinwhan Cho, In-Uk Song, Young H. Sohn, Phil Hyu Lee, Jae Woo Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(4):393-402. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.4.393.Subtypes of Sleep Disturbance in Parkinson's Disease Based on the Cross-Culturally Validated Korean Version of Parkinson's Disease Sleep Scale-2
Hui-Jun Yang, Han-Joon Kim, Seong-Beom Koh, Joong-Seok Kim, Tae-Beom Ahn, Sang-Myung Cheon, Jin Whan Cho, Yoon-Joong Kim, Hyeo-Il Ma, Mee Young Park, Jong Sam Baik, Phil Hyu Lee, Sun Ju Chung, Jong-Min Kim, In-Uk Song, Ji-Young Kim, Young-Hee Sung, Do Young Kwon, Jae-Hyeok Lee, Jee-Young Lee, Ji Seon Kim, Ji Young Yun, Hee Jin Kim, Jin Yong Hong, Mi-Jung Kim, Jinyoung Youn, Ji Sun Kim, Eung Seok Oh, Won Tae Yoon, Sooyeoun You, Kyum-Yil Kwon, Hyung-Eun Park, Su-Yun Lee, Younsoo Kim, Hee-Tae Kim, Sang Jin Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2020;16(1):66-74. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2020.16.1.66.
Reference
-
1. Saunders CD. Parkinson's Disease: A New Hope. 2000. Boston, MA: Harvard Health Publications.2. Marttila RJ, Rinne UK. Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease in Finland. Acta Neurol Scand. 1976. 53:81–102.
Article3. Den Oudsten BL, Van Heck GL, De Vries J. Quality of life and related concepts in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Mov Disord. 2007. 22:1528–1537.
Article4. Martinez-Martin P, Rodriguez-Blazquez C, Kurtis MM, Chaudhuri KR. NMSS Validation Group. The impact of non-motor symptoms on health-related quality of life of patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2011. 26:399–406.
Article5. Qin Z, Zhang L, Sun F, Fang X, Meng C, Tanner C, et al. Health related quality of life in early Parkinson's disease: impact of motor and non-motor symptoms, results from Chinese levodopa exposed cohort. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009. 15:767–771.
Article6. Uitti RJ. Treatment of Parkinson's disease: focus on quality of life issues. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012. 18:Suppl 1. S34–S36.
Article7. Jenkinson C, Fitzpatrick R, Peto V, Greenhall R, Hyman N. The Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39): development and validation of a Parkinson's disease summary index score. Age Ageing. 1997. 26:353–357.
Article8. Peto V, Jenkinson C, Fitzpatrick R, Greenhall R. The development and validation of a short measure of functioning and well being for individuals with Parkinson's disease. Qual Life Res. 1995. 4:241–248.
Article9. Bushnell DM, Martin ML. Quality of life and Parkinson's disease: translation and validation of the US Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39). Qual Life Res. 1999. 8:345–350.10. Martínez-Martín P, Frades Payo B. The Grupo Centro for Study of Movement Disorders. Quality of life in Parkinson's disease: validation study of the PDQ-39 Spanish version. J Neurol. 1998. 245:Suppl 1. S34–S38.
Article11. Tsang KL, Chi I, Ho SL, Lou VW, Lee TM, Chu LW. Translation and validation of the standard Chinese version of PDQ-39: a quality-of-life measure for patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2002. 17:1036–1040.
Article12. Katsarou Z, Bostantjopoulou S, Peto V, Alevriadou A, Kiosseoglou G. Quality of life in Parkinson's disease: Greek translation and validation of the Parkinson's disease questionnaire (PDQ-39). Qual Life Res. 2001. 10:159–163.13. Luo W, Gui XH, Wang B, Zhang WY, Ouyang ZY, Guo Y, et al. Validity and reliability testing of the Chinese (mainland) version of the 39-item Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39). J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010. 11:531–538.
Article14. Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Lees AJ. The clinical features of Parkinson's disease in 100 histologically proven cases. Adv Neurol. 1993. 60:595–599.15. Langston JW, Widner H, Goetz CG, Brooks D, Fahn S, Freeman T, et al. Core assessment program for intracerebral transplantations (CAPIT). Mov Disord. 1992. 7:2–13.
Article16. Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology. 1967. 17:427–442.
Article17. Movement Disorder Society Task Force on Rating Scales for Parkinson's Disease. The Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS): status and recommendations. Mov Disord. 2003. 18:738–750.18. Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997. 15:300–308.19. Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep. 1991. 14:540–545.
Article20. Chaudhuri KR, Martinez-Martin P, Brown RG, Sethi K, Stocchi F, Odin P, et al. The metric properties of a novel non-motor symptoms scale for Parkinson's disease: Results from an international pilot study. Mov Disord. 2007. 22:1901–1911.
Article21. Soh SE, Morris ME, McGinley JL. Determinants of health-related quality of life in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2011. 17:1–9.
Article22. Carod-Artal FJ, Martinez-Martin P, Vargas AP. Independent validation of SCOPA-psychosocial and metric properties of the PDQ-39 Brazilian version. Mov Disord. 2007. 22:91–98.
Article23. Chapuis S, Ouchchane L, Metz O, Gerbaud L, Durif F. Impact of the motor complications of Parkinson's disease on the quality of life. Mov Disord. 2005. 20:224–230.
Article24. Chrischilles EA, Rubenstein LM, Voelker MD, Wallace RB, Rodnitzky RL. Linking clinical variables to health-related quality of life in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2002. 8:199–209.
Article25. Gómez-Esteban JC, Zarranz JJ, Lezcano E, Tijero B, Luna A, Velasco F, et al. Influence of motor symptoms upon the quality of life of patients with Parkinson's disease. Eur Neurol. 2007. 57:161–165.
Article26. Cronbach LJ. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika. 1951. 16:297–334.
Article27. Schrag A, Jahanshahi M, Quinn N. What contributes to quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000. 69:308–312.
Article28. Schrag A, Selai C, Mathias C, Low P, Hobart J, Brady N, et al. Measuring health-related quality of life in MSA: the MSA-QoL. Mov Disord. 2007. 22:2332–2338.
Article29. Schrag A. Quality of life and depression in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2006. 248:151–157.
Article30. Muslimovic D, Post B, Speelman JD, Schmand B, de Haan RJ. CARPA Study Group. Determinants of disability and quality of life in mild to moderate Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2008. 70:2241–2247.
Article31. Qin Z, Zhang L, Sun F, Liu H, Fang X, Chan P, et al. Depressive symptoms impacting on health-related quality of life in early Parkinson's disease: results from Chinese L-dopa exposed cohort. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009. 111:733–737.
Article32. Rahman S, Griffin HJ, Quinn NP, Jahanshahi M. Quality of life in Parkinson's disease: the relative importance of the symptoms. Mov Disord. 2008. 23:1428–1434.
Article33. Winter Y, von Campenhausen S, Gasser J, Seppi K, Reese JP, Pfeiffer KP, et al. Social and clinical determinants of quality of life in Parkinson's disease in Austria: a cohort study. J Neurol. 2010. 257:638–645.
Article34. Hagell P, Whalley D, McKenna SP, Lindvall O. Health status measurement in Parkinson's disease: validity of the PDQ-39 and Nottingham Health Profile. Mov Disord. 2003. 18:773–783.
Article35. McHorney CA, Ware JE Jr, Lu JF, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): III. Tests of data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability across diverse patient groups. Med Care. 1994. 32:40–66.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Validation of the Korean version of the 39-Item Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39)
- Validation of the Thai Version of the Movement Disorder Society-Sponsored Revision of the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale
- Development of the Korean-translation of Androgen Deficiency in Aging Males (ADAM) Questionnaire
- Translation and Linguistic Validation of the Korean Version of the Wisconsin Stone Quality of Life Questionnaire
- Translation and linguistic validation of Korean version of short form of pelvic floor distress inventory-20, pelvic floor impact questionnaire-7