Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Apr;39(2):170-175. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.170.
Diagnostic Cutoff Value for Ultrasonography in the Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. idwom@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2273037
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.170
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine the diagnostic cutoff values of ultrasonographic measurements in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow (UNE).
METHODS
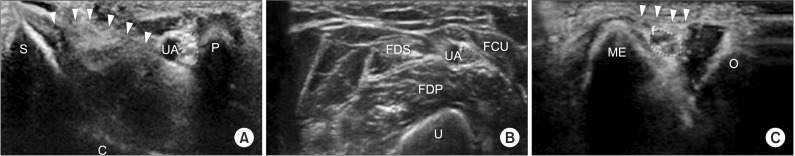
Twenty-five elbows of 23 patients (9 females, 16 males) diagnosed with UNE and 30 elbows of 30 healthy controls (15 females, 15 males) were included in our study. The ulnar nerve cross-sectional area (CSA) was measured at the Guyon canal, midforearm, and maximal swelling point (MS) around the elbow (the cubital tunnel inlet in healthy controls). CSA measurements of the ulnar nerve at each point, the Guyon canal-to-MS ulnar nerve area ratio (MS/G), and the midforearm-to-MS ulnar nerve ratio (MS/F) were calculated.
RESULTS
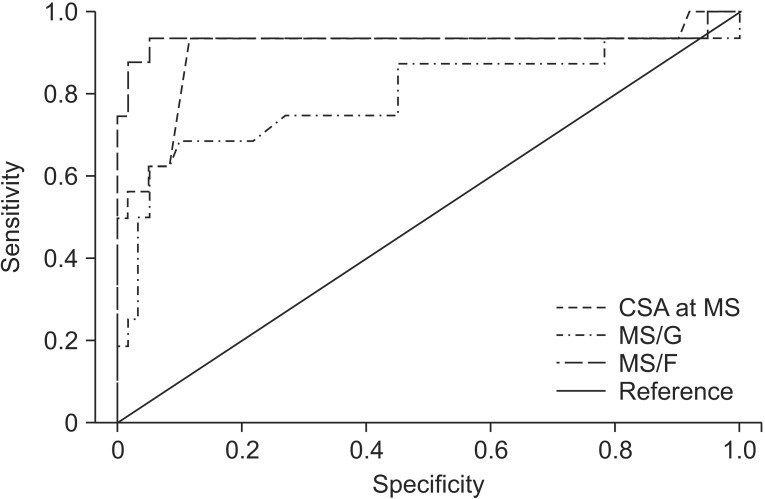
Among the variables, only CSA at MS, MS/G, and MS/F displayed significant differences between the control and patient groups. The cutoff value for diagnosing UNE was 8.95 mm2 for the CSA at MS (sensitivity 93.8%, specificity 88.3%), 1.99 for the MS/G (sensitivity 75.0%, specificity 73.3%), and 1.48 for the MS/F (sensitivity 93.8%, specificity 95.0%).
CONCLUSION
These findings may be helpful to diagnose UNE.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Cadaveric Study of Thread Cubital Tunnel Release with Newly Developed Threads
Minsuk Kang, Yong Seok Nam, In Jong Kim, Hae-Yeon Park, Jung Ryul Ham, Jae Min Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022;65(2):307-314. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2021.0135.
Reference
-
1. Chiou HJ, Chou YH, Cheng SP, Hsu CC, Chan RC, Tiu CM, et al. Cubital tunnel syndrome: diagnosis by high-resolution ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med. 1998; 17:643–648. PMID: 9771609.
Article2. Kitzinger HB, Aszmann OC, Moser VL, Frey M. Significance of electroneurographic parameters in the diagnosis of chronic neuropathy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2005; 37:276–281. PMID: 16149037.3. Wiesler ER, Chloros GD, Cartwright MS, Shin HW, Walker FO. Ultrasound in the diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy at the cubital tunnel. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:1088–1093. PMID: 16945708.
Article4. Beekman R, Schoemaker MC, Van Der Plas JP, Van Den Berg LH, Franssen H, Wokke JH, et al. Diagnostic value of high-resolution sonography in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Neurology. 2004; 62:767–773. PMID: 15007128.
Article5. Nakamichi K, Tachibana S. Ultrasonographic measurement of median nerve cross-sectional area in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: diagnostic accuracy. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 26:798–803. PMID: 12451604.
Article6. Yoon JS, Kim BJ, Kim SJ, Kim JM, Sim KH, Hong SJ, et al. Ultrasonographic measurements in cubital tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007; 36:853–855. PMID: 17879384.
Article7. Bayrak AO, Bayrak IK, Turker H, Elmali M, Nural MS. Ultrasonography in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: comparison of cross-sectional area and swelling ratio with electrophysiological severity. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 41:661–666. PMID: 19941341.
Article8. Yoon JS, Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Ultrasonographic swelling ratio in the diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 38:1231–1235. PMID: 18785184.
Article9. Mondelli M, Filippou G, Frediani B, Aretini A. Ultrasonography in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: relationships to clinical and electrophysiological findings. Neurophysiol Clin. 2008; 38:217–226. PMID: 18662618.
Article10. Gruber H, Glodny B, Peer S. The validity of ultrasonographic assessment in cubital tunnel syndrome: the value of a cubital-to-humeral nerve area ratio (CHR) combined with morphologic features. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010; 36:376–382. PMID: 20133042.
Article11. Ozturk E, Sonmez G, Colak A, Sildiroglu HO, Mutlu H, Senol MG, et al. Sonographic appearances of the normal ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel. J Clin Ultrasound. 2008; 36:325–329. PMID: 18446864.
Article12. Hobson-Webb LD, Massey JM, Juel VC, Sanders DB. The ultrasonographic wrist-to-forearm median nerve area ratio in carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008; 119:1353–1357. PMID: 18387336.
Article13. Jacob D, Creteur V, Courthaliac C, Bargoin R, Sassus B, Bacq C, et al. Sonoanatomy of the ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel: a multicentre study by the GEL. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:1770–1773. PMID: 15258824.
Article14. Volpe A, Rossato G, Bottanelli M, Marchetta A, Caramaschi P, Bambara LM, et al. Ultrasound evaluation of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: correlation with electrophysiological studies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48:1098–1101. PMID: 19567661.
Article15. American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. American Academy of Neurology. American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: summary statement. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22:408–411. PMID: 10086904.16. Contreras MG, Warner MA, Charboneau WJ, Cahill DR. Anatomy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow: potential relationship of acute ulnar neuropathy to gender differences. Clin Anat. 1998; 11:372–378. PMID: 9800916.
Article17. Kara M, Ozcakar L, De Muynck M, Tok F, Vanderstraeten G. Musculoskeletal ultrasound for peripheral nerve lesions. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2012; 48:665–674. PMID: 23183452.18. Polatsch DB, Melone CP Jr, Beldner S, Incorvaia A. Ulnar nerve anatomy. Hand Clin. 2007; 23:283–289. PMID: 17765580.
Article19. Yalcin E, Unlu E, Akyuz M, Karaahmet OZ. Ultrasound diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy: comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic nerve thickness. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014; 39:167–171. PMID: 23592536.
Article20. Won SJ, Kim BJ, Park KS, Yoon JS, Choi H. Reference values for nerve ultrasonography in the upper extremity. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 47:864–871. PMID: 23625758.
Article21. Cartwright MS, Passmore LV, Yoon JS, Brown ME, Caress JB, Walker FO. Cross-sectional area reference values for nerve ultrasonography. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 37:566–571. PMID: 18351581.
Article22. Cartwright MS, Shin HW, Passmore LV, Walker FO. Ultrasonographic findings of the normal ulnar nerve in adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:394–396. PMID: 17321837.
Article23. Landau ME, Barner KC, Campbell WW. Effect of body mass index on ulnar nerve conduction velocity, ulnar neuropathy at the elbow, and carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2005; 32:360–363. PMID: 15880630.
Article24. Park GY, Kim JM, Lee SM. The ultrasonographic and electrodiagnostic findings of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85:1000–1005. PMID: 15179657.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of Ulnar Neuropathy Caused by Intraneural Ganglion at Elbow with Ultrasound
- Tardy Ulnar Nerve Palsy by Neurofibroma
- Ultrasound Evaluation of Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow Caused by a Mass Lesion
- Ultrasonographic Findings and Usefulness in Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow
- Subclinical Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow in Diabetic Patients