Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Apr;39(2):163-169. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.163.
Accuracy of Needle Placement in Cadavers: Non-Guided Versus Ultrasound-Guided
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ljikyh@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2273036
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.163
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
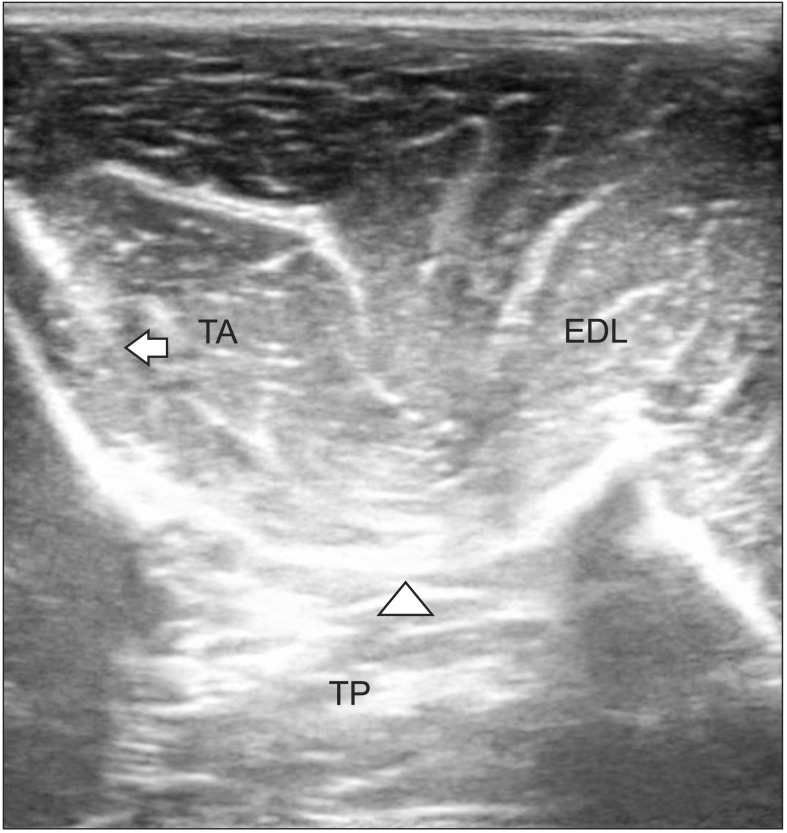
To compare the accuracy rates of non-guided vs. ultrasound-guided needle placement in four lower limb muscles (tibialis posterior, peroneus longus, and short and long heads of the biceps femoris).
METHODS
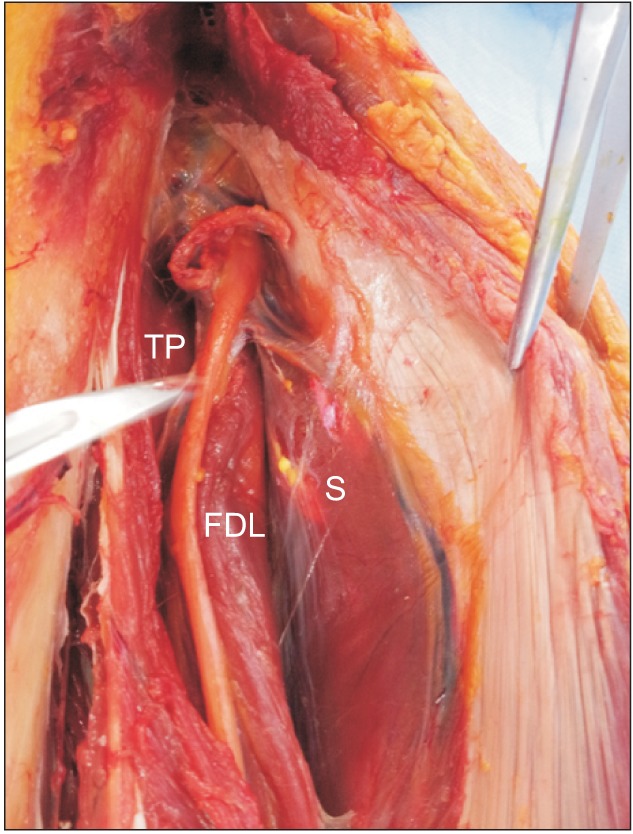
Two electromyographers examined the four muscles in each of eight lower limbs from four fresh frozen cadavers. Each electromyographer injected an assigned dye into each targeted muscle in a lower limb twice (once without guidance, another under ultrasound guidance). Therefore, four injections were done in each muscle of one lower limb. All injections were performed by two electromyographers using 18 gauge 1.5 inch or 24 gauge 2.4 inch needles to place 0.5 mL of colored acryl solution into the target muscles. The third person was blinded to the injection technique and dissected the lower limbs and determined injection accuracy.
RESULTS
A 71.9% accuracy rate was achieved by blind needle placement vs. 96.9% accuracy with ultrasound-guided needle placement (p=0.001). Blind needle placement accuracy ranged from 50% to 93.8%.
CONCLUSION
Ultrasound guidance produced superior accuracy compared with that of blind needle placement in most muscles. Clinicians should consider ultrasound guidance to optimize needle placement in these muscles, particularly the tibialis posterior.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Which Approach Is Most Optimal for Needle Electromyographic Examination of the Biceps Femoris Short Head: Medial or Lateral?
Jong Heon Park, Im Joo Rhyu, Ha Kyoung Lim, Jae Hyun Cha, Gi Jun Shin, Hye Chang Rhim, Dong Hwee Kim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2021;45(1):42-48. doi: 10.5535/arm.20092.
Reference
-
1. Boon AJ, Oney-Marlow TM, Murthy NS, Harper CM, McNamara TR, Smith J. Accuracy of electromyography needle placement in cadavers: non-guided vs. ultrasound guided. Muscle Nerve. 2011; 44:45–49. PMID: 21674520.
Article2. Haig AJ, Goodmurphy CW, Harris AR, Ruiz AP, Etemad J. The accuracy of needle placement in lower-limb muscles: a blinded study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 84:877–882. PMID: 12808542.3. Cho KH, Gee SJ, Lee HJ, Hwang SH. Comparision of blind technique and ultrasonography guided technique of subacromial subdeltoid bursa injection. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:209–213.4. Smith J, Hurdle MF, Locketz AJ, Wisniewski SJ. Ultrasound-guided piriformis injection: technique description and verification. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 87:1664–1667. PMID: 17141652.
Article5. Boon AJ, Alsharif KI, Harper CM, Smith J. Ultrasound-guided needle EMG of the diaphragm: technique description and case report. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 38:1623–1626. PMID: 19016552.
Article6. Perotto AO, Delagi EF. Anatomical guide for the electromyographer: the limbs and trunk. 4th ed. Springfield: Charles C Thomas;2005.7. Preston DC, Shapiro BE. Electromyography and neuromuscular disorders: clinical-electrophysiologic correlations. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Butterworth-Heinemann;2005.8. Schnitzler A, Roche N, Denormandie P, Lautridou C, Parratte B, Genet F. Manual needle placement: accuracy of botulinum toxin A injections. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 46:531–534. PMID: 22987693.
Article9. Rha DW, Im SH, Lee SC, Kim SK. Needle insertion into the tibialis posterior: ultrasonographic evaluation of an anterior approach. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 91:283–287. PMID: 20159135.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fine-Needle Biopsy: Should This Be the First Choice in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition?
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Direct Intervention for Solid Pancreatic Tumors
- Feasibility of Ultrasound Guided Atlanto-occipital Joint Injection
- How Can We Get the Best Results with Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration?
- Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided and Non-ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Toxin Injection Into Cadaver Salivary Glands