Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Apr;36(2):213-219. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.2.213.
Radiofrequency Sacral Rhizotomy for the Management of Intolerable Neurogenic Bladder in Spinal Cord Injured Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon 301-172, Korea. drlovingss@naver.com
- KMID: 2266759
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.2.213
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the effect of radiofrequency (RF) sacral rhizotomy of the intolerable neurogenic bladder in spinal cord injured patients. METHOD: Percutaneous RF sacral rhizotomy was performed on 12 spinal cord injured patients who had neurogenic bladder manifested with urinary incontinence resisted to an oral and intravesical anticholinergic instillation treatment. Various combinations of S2, S3, and S4 RF rhizotomies were performed. The urodynamic study (UDS) was performed 1 week before RF rhizotomy. The voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) and voiding diaries were compared 1 week before and 4 weeks after therapy. Total volume of daily urinary incontinence (ml/day) and clean intermittent catheterization (ml/time) volume of each time were also monitored.
RESULTS
After RF sacral rhizotomy, bladder capacity increased in 9 patients and the amount of daily urinary incontinence decreased in 11 patients. The mean maximal bladder capacity increased from 292.5 to 383.3 ml (p<0.05) and mean daily incontinent volume decreased from 255 to 65 ml (p<0.05). Bladder trabeculation and vesicoureteral reflux findings did not change 4 weeks after therapy.
CONCLUSION
This study revealed that RF sacral rhizotomy was an effective method for neurogenic bladder with uncontrolled incontinence using conventional therapy among spinal cord injured patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
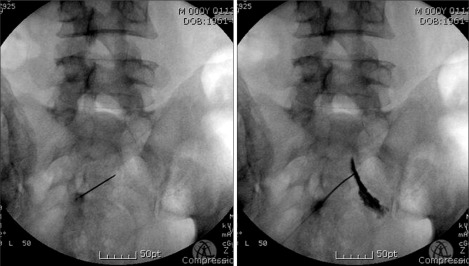
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Short-Term Effect of Percutaneous Bipolar Continuous Radiofrequency on Sacral Nerves in Patients Treated for Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity After Spinal Cord Injury: A Randomized Controlled Feasibility Study
Jin Hyun Kim, Sang Ho Ahn, Yun Woo Cho, Sang Gyu Kwak, Hyo Sung Kim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(5):718-725. doi: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.5.718.
Reference
-
1. Noronha-Blob L, Lowe VC, Peterson JS, Hanson RC. The anticholinergic activity of agents indicated for urinary incontinence is an important property for effective control do bladder dysfunction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989; 251:586–593. PMID: 2810112.2. Buyse G, Waldeck K, Verpoorten C, Bjork H, Casaer P, Andersson KE. Intravesical oxybutynin for neurogenic bladder dysfunction: less systemic side effects due to reduced first pass metabolism. J Urol. 1998; 160:892–896. PMID: 9720583.
Article3. Schurch B, de Seze M, Denys P, Chartier-Kastler E, Haab F, Everaert K, Plante P, Perrouin-Verbe B, Kumar C, Fraczek S, et al. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: results of a single treatment, randomized, placebo controlled 6-month study. J Urol. 2005; 174:196–200. PMID: 15947626.
Article4. Ekstrom B, Andersson KE, Mattiason A. Urodynamic effects of intravesical instillation of atropine and phentolamine in patients with detrusor hyperactivity. J Urol. 1993; 149:155–158. PMID: 8417203.5. Brindley GS. The first 500 patients with sacral anterior root stimulator implants: general description. Paraplegia. 1994; 32:795–805. PMID: 7708419.
Article7. Kapural L, Mekhail N. Radiofrequency ablation for chronic pain control. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2001; 5:517–525. PMID: 11676886.
Article8. Mulcahy JJ, Young AB. Percutaneous radiofrequency sacral rhizotomy in the treatment of the hyperreflexic bladder. J Urol. 1978; 120:557–558. PMID: 712897.
Article9. Mulcahy JJ, Young AB. Long-term follow-up of percutaneous radiofrequency sacral rhizotomy. Urol. 1990; 35:76–77. PMID: 2296824.10. Weibing S, Dongwen W. Relationship between the bladder trabeculation grades and pressure of detrusor in benign prostatic hyperplasia. China J Mod Med. 2010; 20:723–725.11. Arnold EP, Fukui J, Anthony A, Utley WL. Bladder function following spinal cord injury: a urodynamic analysis of the outcome. Br J Urol. 1984; 56:172–177. PMID: 6498436.
Article12. Kim DY, Chancellor MB. Intravesical neuromodulatory drugs: capsaicin and resiniferatoxin to treat the overactive bladder. J Endourol. 2000; 14:97–103. PMID: 10735579.
Article13. de Seze M, Wiart L, de Seze MP, Soyeur L, Dosque JP, Blajezewski S, Moore N, Brochet B, Mazaux JM, Barat M, et al. Intravesical capsaicin versus resiniferatoxin for the treatment of detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured patients: a double-blind, randomized, controlled study. J Urol. 2004; 171:251–255. PMID: 14665887.14. Shin JC, Park CI, Kim YW, Park SY, Rha DW, Kim JE. Stretching therapy of neurogenic bladder in patients with spinal cord injury. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2003; 27:344–348.15. Helmstein K. Treatment of bladder carcinoma by a hydrostatic pressure technique. Br J Urol. 1972; 44:434–450. PMID: 5070147.16. Dunn M, Ramsden PD, Roberts JB, Smith JC, Smith PJ. Interstitial cyctitis, treated by prolonged bladder distension. Br J Urol. 1977; 49:641–645. PMID: 597701.17. Sluijter M, Racz G. Technical aspects of radiofrequency. Pain Pract. 2002; 2:195–200. PMID: 17147730.
Article18. Blaivas JG. Pathophysiology of lower urinary tract dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 1985; 12:215–224. PMID: 4039484.
Article19. Ferreira RS, Levi d'Ancona CA, Dantas-Filho VP, Rodrigues Netto, Miyaoka R. Percutaneous radiofrequency sacral rhizotomy in the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injured patients. Actas Urol Esp. 2011; 35:325–330. PMID: 21477886.
Article20. Shin JC, Park CI, Kim YR, Bang IK, Kim JE. Clinical effectiveness of intravesical oxybutynin instillation in spinal cord injured patients with hyperreflexic or hypertonic neurogenic bladder. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2000; 24:28–34.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation (II): Management of Neurogenic Bladder
- Urethral Stent as a Part of Management of the Neurogenic Bladder in Spinal Cord Injury: Two cases report
- Postdischarge Change of Neurogenic Bladder Management Methods in Spinal Cord Injured Patients
- Treatment of Malignant Sacral Pain by Radiofrequency Lesion Generator
- Risk Factors for Urinary Tract Infection in Chronic Spinal Cord Injured Patients