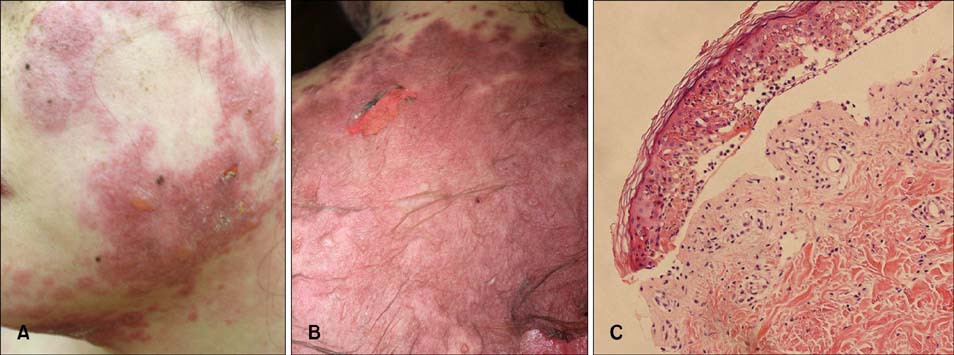
Ann Dermatol.
2014 Oct;26(5):645-646. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.645.
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in a Patient with HLA-B*5901 Haplotype Caused by Topical and Oral Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jwkim52@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2265508
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.645
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Harr T, French LE. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2012; 97:149–166.
Article2. Mincione F, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT. The development of topically acting carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as antiglaucoma agents. Curr Pharm Des. 2008; 14:649–654.
Article3. Kim SH, Kim M, Lee KW, Kim SH, Kang HR, Park HW, et al. HLA-B*5901 is strongly associated with methazolamide-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Pharmacogenomics. 2010; 11:879–884.
Article4. Chun JS, Yun SJ, Lee JB, Kim SJ, Won YH, Lee SC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by the topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors brinzolamide and dorzolamide. Ann Dermatol. 2008; 20:260–262.
Article5. Lee KW, Oh DH, Lee C, Yang SY. Allelic and haplotypic diversity of HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, and -DQB1 genes in the Korean population. Tissue Antigens. 2005; 65:437–447.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Induced by the Topical Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Brinzolamide and Dorzolamide
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Caused by Topical Ophthalmic Use of Dorzolamide
- Two Cases of HLA-B59(+) Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)-Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) Associated with Methazolamide Treatment
- The Effects of Topical Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors on Nitric Oxide Production in Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Epidermal Necrolysis due to Methazolamide Treatment in Glaucomatous Patients