Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2013 Mar;1(1):84-89. 10.4168/aard.2013.1.1.84.
The clinical characteristics in infantile bronchiolitis and pneumonia according to respiratory syncytial virus subgroups: experience of single tertiary medical center from 2010 to 2012
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. kimyhped@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2263065
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2013.1.1.84
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The most common cause of bronchiolitis and pneumonia in infants is respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). We evaluated the clinical characteristics according to RSV subgroup in infantile bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
METHODS
This study enrolled infants with bronchiolitis or pneumonia infected by single virus. Virus infection was confirmed by respiratory virus reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction in two consecutive seasons (2010-2011, 2011-2012). They were divided into 3 groups: group 1 with RSV A, group 2 with RSV B, and group 3 with other virus. We retrospectively reviewed the medical charts to collect data on the hospitalized patients.
RESULTS
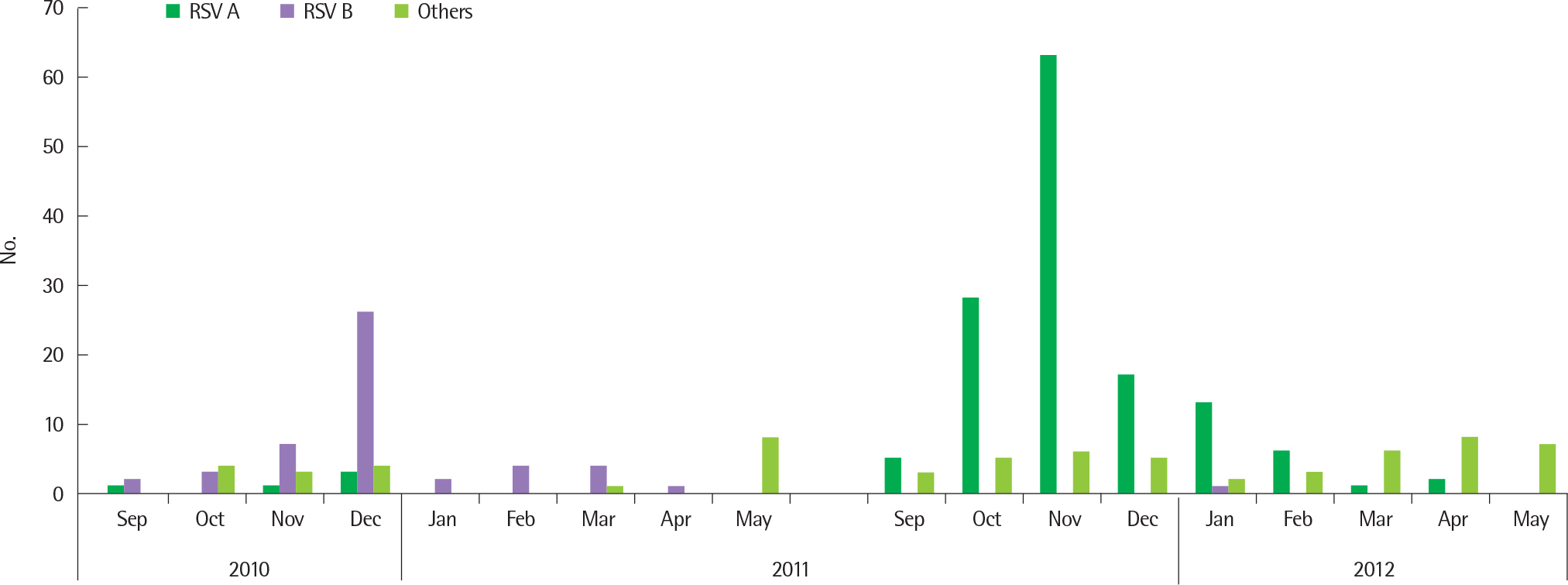
Seventy four and 181 infants were included in the two seasons, respectively. The most common virus was RSV B in 2010-2011 and RSV A in 2011.2012. Among 255 infants, 55% (141/255) were group 1, 20% (49/255) group 2, 25% (65/255) group 3. Infants younger than 3 months were 55%. There were no significant age differences between groups. In comparison to group 3, group 1 and 2 showed frequent abnormal chest auscultation, high symptom severity score and need for systemic corticosteroid (P<0.05). In comparison to group 1 and 3, group 2 had longer hospitalization and time to need for normalization of lung sound (P<0.05). The recurrence rates within 6 months showed no significant differences between groups.
CONCLUSION
The RSV subgroup changed from one year to another. Patients' clinical manifestations and symptom severity may vary according to infected virus subgroup.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Characteristics of Respiratory Syncytial Virus isolated from Acute Respiratory Infectious Disease in Busan
Su-Jeong Hwang, Dong-Ju Park, Pyeung-Tae Gu, Hee-Soo Koo, Mi-Ok Lee
J Bacteriol Virol. 2016;46(3):173-180. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2016.46.3.173.
Reference
-
1. Holberg CJ, Wright AL, Martinez FD, Ray CG, Taussig LM, Lebowitz MD. Risk factors for respiratory syncytial virus-associated lower respiratory illnesses in the first year of life. Am J Epidemiol. 1991; 133:1135–51.
Article2. Henrickson KJ, Hoover S, Kehl KS, Hua W. National disease burden of respiratory viruses detected in children by polymerase chain reaction. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004; 23(1 Suppl):S11–8.
Article3. Hall CB, Weinberg GA, Iwane MK, Blumkin AK, Edwards KM, Staat MA, et al. The burden of respiratory syncytial virus infection in young children. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:588–98.
Article4. Lim JS, Woo SI, Kwon HI, Baek YH, Choi YK, Hahn YS. Clinical characteristics of acute lower respiratory tract infections due to 13 respiratory viruses detected by multiplex PCR in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2010; 53:373–9.
Article5. Kim KH, Lee JH, Sun DS, Kim YB, Choi YJ, Park JS, et al. Detection and clinical manifestations of twelve respiratory viruses in hospitalized children with acute lower respiratory tract infections: Focus on human metapneumovirus, human rhinovirus and human coronavirus. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:834–41.6. Kim HJ, Kim JH, Kang IJ. Association of respiratory viral infection and atopy with severity of acute bronchiolitis in infants. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:302–12.
Article7. Zhang ZY, Du LN, Chen X, Zhao Y, Liu EM, Yang XQ, et al. Genetic variability of respiratory syncytial viruses (RSV) prevalent in Southwest-ern China from 2006 to 2009: emergence of subgroup B and A RSV as dominant strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:1201–7.
Article8. Parveen S, Sullender WM, Fowler K, Lefkowitz EJ, Kapoor SK, Broor S. Genetic variability in the G protein gene of group A and B respiratory syncytial viruses from India. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:3055–64.
Article9. Denny FW, Clyde WA Jr. Acute lower respiratory tract infections in non-hospitalized children. J Pediatr. 1986; 108(5 Pt 1):635–46.
Article10. British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Committee. British Thoracic Society Guidelines for the Management of Community Acquired Pneumonia in Childhood. Thorax. 2002; 57(Suppl 1):i1–24.11. Tal A, Bavilski C, Yohai D, Bearman JE, Gorodischer R, Moses SW. Dexamethasone and salbutamol in the treatment of acute wheezing in infants. Pediatrics. 1983; 71:13–8.
Article12. Gilca R, De Serres G, Tremblay M, Vachon ML, Leblanc E, Bergeron MG, et al. Distribution and clinical impact of human respiratory syncytial virus genotypes in hospitalized children over 2 winter seasons. J Infect Dis. 2006; 193:54–8.
Article13. Hornsleth A, Klug B, Nir M, Johansen J, Hansen KS, Christensen LS, et al. Severity of respiratory syncytial virus disease related to type and geno-type of virus and to cytokine values in nasopharyngeal secretions. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998; 17:1114–21.
Article14. Martinello RA, Chen MD, Weibel C, Kahn JS. Correlation between respiratory syncytial virus genotype and severity of illness. J Infect Dis. 2002; 186:839–42.
Article15. Mentel R, Ilgert U, Wegner U, Zimmerman K, Bruns R, Gurtler L. Molecular and clinical characteristics of respiratory syncytial virus infections in hospitalized children. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2005; 194:67–71.
Article16. Papadopoulos NG, Moustaki M, Tsolia M, Bossios A, Astra E, Prezerak-ou A, et al. Association of rhinovirus infection with increased disease severity in acute bronchiolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 165:1285–9.
Article17. Greensill J, McNamara PS, Dove W, Flanagan B, Smyth RL, Hart CA. Human metapneumovirus in severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003; 9:372–5.
Article18. Zhang RF, Jin Y, Xie ZP, Liu N, Yan KL, Gao HC, et al. Human respiratory syncytial virus in children with acute respiratory tract infections in China. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:4193–9.
Article19. Coggins WB, Lefkowitz EJ, Sullender WM. Genetic variability among group A and group B respiratory syncytial viruses in a children's hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:3552–7.
Article20. Scott PD, Ochola R, Ngama M, Okiro EA, Nokes DJ, Medley GF, et al. Molecular epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus in Kilifi district, Kenya. J Med Virol. 2004; 74:344–54.
Article21. Shobugawa Y, Saito R, Sano Y, Zaraket H, Suzuki Y, Kumaki A, et al. Emerging genotypes of human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup A among patients in Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:2475–82.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical and epidemiologic features of respiratory sybcytial virus infection
- A Case of Respiratory Syncytial Virus(RSV) Infection in the Prematurity with Respiratory Failure and accompanied by Apnea
- The Role of Vascular Endithelial Growth Factor in Pathogenesis of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis
- Immunological Responses in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis and Childhood Asthma