Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2010 Jan;2(1):14-19. 10.4168/aair.2010.2.1.14.
Pharmacogenetics of asthma in children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Graduate School of Medicine, Gifu University, Gifu, Japan. nkondo@gifu-u.ac.jp
- KMID: 2260414
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2010.2.1.14
Abstract
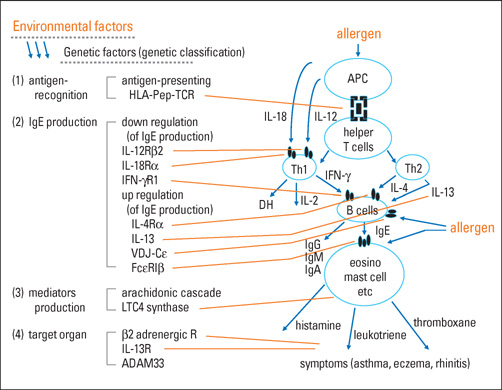
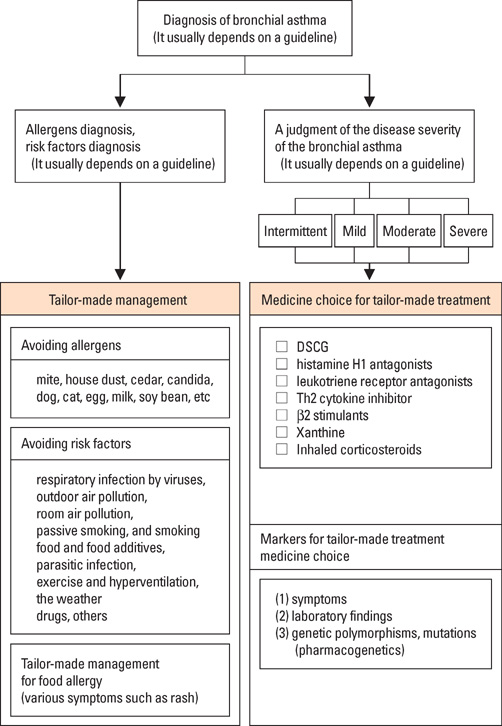
- Allergic diseases such as bronchial asthma and atopic dermatitis develop by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Several candidate causative genes of asthma and atopy have been reported as the genetic factors. The clinical features of patients and causes of diseases vary. Therefore, personalized medicine (tailor-made medicine) is necessary for the improvement of quality of life (QOL) and for asthma cure. Pharmacogenetics is very important for personalized medicine. Here, we present the genetics and pharmacogenetics of asthma in children. Finally, we show the guideline for personalized medicine for asthma, particularly in childhood, including the pharmacogenetics of anti-asthmatic drugs, preliminarily produced by the authors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Association of house dust mite-specific IgE with asthma control, medications and household pets
Pia Marie Albano, John Donnie A. Ramos
Asia Pac Allergy. 2011;1(3):145-151. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.3.145.
Reference
-
1. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA): Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2006. Available from: http://www.ginasthma.org.2. Ober C, Hoffjan S. Asthma genetics 2006: the long and winding road to gene discovery. Genes and Immunity. 2006. 7:95–100.3. Juhn YJ, Kita H, Lee LA, Smith RW, Bagniewski SM, Weaver AL, Pankratz VS, Jocobson RM, Poland GA. Childhood asthma and human leukocyte antigen type. Tissue Antigens. 2007. 69:38–46.4. Juhn YJ, Kita H, Bagniewski SM, Weaver AL, Pankratz VS, Jocobson RM, Poland GA. Severity of childhood asthma and human leukocyte antigens type. J Asthma. 2007. 44:163–168.5. Kondo N, Matsui E, Kaneko H, Fukao T, Teramoto T, Kato Z, Onishi H, Nishimura A. Pawankar R, Holgate ST, Rosenwasser LJ, editors. Genetics of pediatric asthma. Allergy frontiers volume 1 allergy frontiers: epigenetics, allergens and risk factors. 2009. Heidelberg: Springer;189–203.6. Cookson WO, Sharp PA, Faux JA, Hopkin JM. Linkage between immunoglobulin E responses underlying asthma and rhinitis and chromosome 11q. Lancet. 1989. 1:1292–1295.7. Shirakawa T, Li A, Dubowitz M, Dekker JW, Shaw AE, Faux JA, Ra C, Cookson WO, Hopkin JM. Association between atopy and variants of the beta subunit of the high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor. Nat Genet. 1994. 7:125–130.8. Mitsuyasu H, Izuhara K, Mao XQ, Gao PS, Arinobu Y, Enomoto T, Kawai M, Sasaki S, Dake Y, Hamasaki N, Shirakawa T, Hopkin JM. Ile50Val variant of IL4R alpha upregulates IgE synthesis and associates with atopic asthma. Nat Genet. 1998. 19:119–120.9. Shirakawa T, Deichmann KA, Izuhara I, Mao I, Adra CN, Hopkin JM. Atopy and asthma: genetic variants of IL-4 and IL-13 signalling. Immunol Today. 2000. 21:60–64.10. Matsui E, Kaneko H, Fukao T, Teramoto T, Inoue R, Watanabe M, Kasahara K, Kondo N. Mutations of the IL-12 receptor β2 chain gene in atopic subjects. Biochem Biophy Res Commun. 1999. 266:551–555.11. Watanabe M, Kaneko H, Shikano H, Aoki M, Sakaguchi H, Matsui E, Inoue R, Kato Z, Kasahara K, Fukutomi O, Kondo T, Kondo N. Predominant expression of 950delCAG of IL-18R alpha chain cDNA is associated with reduced IFN-gamma production and high serum IgE levels in atopic Japanese children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 109:669–675.12. Aoki M, Matsui E, Kaneko H, Inoue R, Fukao T, Watanabe M, Teramoto T, Kato Z, Suzuki K, Suzuki Y, Kasahara K, Kondo N. A novel single-nucleotide substitution, Leu 467 Pro, in the interferon-gamma receptor 1 gene associated with allergic diseases. Int J Mol Med. 2003. 12:185–191.13. Henderson WR Jr. The role of leukotrienes in inflammation. Ann Intern Med. 1994. 121:684–697.14. Sanak M, Hu S, Szczeklik A. Leukotriene C4 synthase promoter polymorphism and risk of aspirin-induced asthma. Lancet. 1997. 29:1599–1600.15. Kim SH, Hur GY, Choi JH, Park HS. Pharmacogenetics of aspirin-intolerant asthma. Pharmacogenomics. 2008. 9:85–91.16. Van Sambeek R, Stevenson DD, Baldasaro M, Lam BK, Zhao J, Yoshida S, Yandora C, Drazen JM, Penrose JF. 5'flanking region polymorphism of the gene encoding leukotriene C4 synthase does not correlate with the aspirin-intolerant asthma phenotype in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 106:72–76.17. Yoshikawa K, Matsui E, Kaneko H, Fukao T, Inoue R, Teramoto T, Shinoda S, Fukutomi O, Aoki M, Kasahara K, Kondo N. A novel single-nucleotide substitution, Glu 4 Lys, in the leukotriene C4 synthase gene associated with allergic diseases. Int J Mol Med. 2005. 16:827–831.18. Gao PS, Kawada H, Kasamatsu T, Mao XQ, Roberts MH, Miyamoto Y, Yoshimura M, Saitoh Y, Yasue H, Nakao K, Adra CN, Kun JF, Moro-oka S, Inoko H, Ho LP, Shirakawa T, Hopkin JM. Variants of NOS1, NOS2, and NOS3 genes in asthmatics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. 267:761–763.19. Reihsaus EM, Innis M, MacIntyre N, Liggett SB. Mutations in the gene encoding for the beta 2-adrenergic receptor in normal and asthmatic subjects. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993. 8:334–339.20. Turki J, Pak J, Green SA, Martin RJ, Liggett SB. Genetic polymorphisms of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor in nocturnal and non-nocturnal asthma. Evidence that Gly16 correlates with the nocturnal phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1995. 95:1635–1641.21. Van Eerdewegh P, Little RD, Dupuis J, Mastro RGD, Falls K, Simon J, Torrey D, Pandit S, McKenny J, Braunschweiger K, Walsh A, Liu Z, Hayward B, Folz C, Manning SP, Bawa A, Saracino L, Thackston M, Benchekroun Y, Capparell N, Wang M, Adair R, Feng Y, Dubois J, FitzGerald MG, Huang H, Gibson R, Allen KM, Pedan A, Danzig MR, Umland SP, Egan RW, Cuss FM, Rorke S, Clough JB, Holloway JW, Holgate ST, Keith TP. Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Nature. 2002. 418:426–430.22. Kondo N, Matsui E, Kaneko H, Kato Z, Fukao T, Teramoto T, Shikano H, Aoki M, Onishi H, Tatebayashi K, Omoya K, Kondo M, Matsukuma E, Kasahara K, Morimoto N. Genetic defects in downregulation of IgE production and a new genetic classification of atopy. Allergology International. 2004. 53:77–85.23. Hall IP. Pharmacogenetics of asthma. Chest. 2006. 130:1873–1878.24. Israel E, Drazen JM, Liggett SB, Boushey HA, Cherniack RM, Chinchilli VM, Cooper DM, Fahy JV, Fish JE, Ford JG, Kraft M, Kunselman S, Lazarus SC, Lemanske RF, Martin RJ, McLean DE, Peters SP, Silverman EK, Sorkness CA, Szefler SJ, Weiss ST, Yandava CN. The effect of polymorphisms of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor on the response to regular use of albuterol in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:75–80.25. Israel E, Chinchilli VM, Ford JG, Boushey HA, Cherniack R, Craig TJ, Deykin A, Fagan JK, Fahy JV, Fish J, Kraft M, Kunselman SJ, Lazarus SC, Lemanske RF Jr, Liggett SB, Martin RJ, Mitra N, Peters SP, Silverman E, Sorkness CA, Szefler SJ, Wechsler ME, Weiss ST, Drazen JM; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Asthma Clinical Research Network. Use of regularly scheduled albuterol treatment in asthma: genotype-stratified, randomised, placebo-controlled cross-over trial. Lancet. 2004. 364:1505–1512.26. Wechsler ME, Lehman E, Lazarus SC, Lemanske RF Jr, Boushey HA, Deykin A, Fahy JV, Sorkness CA, Chinchilli VM, Craig TJ, DiMango E, Kraft M, Leone F, Martin RJ, Peters SP, Szefler SJ, Liu W, Israel E; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Asthma Clinical Research Network. beta-Adrenergic receptor polymorphisms and response to salmeterol. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. 173:519–526.27. Palmer LJ, Silverman ES, Weiss ST, Drazen JM. Pharmacogenetics of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 165:861–866.28. Sampson AP, Siddiqui S, Buchanan D, Howarth PH, Holgate ST, Holloway JW, Sayers I. Variant LTC(4) synthase allele modifies cysteinyl leukotriene synthesis in eosinophils and predicts clinical response to zafirlukast. Thorax. 2000. 55:Suppl 2. S28–S31.29. Asano K, Shiomi T, Hasegawa N, Nakamura H, Kudo H, Matsuzaki T, Hakuno H, Fukunaga K, Suzuki Y, Kanazawa M, Yamaguchi K. Leukotriene C4 synthase gene A(-444)C polymorphism and clinical response to a CYS-LT(1) antagonist, pranlukast, in Japanese patients with moderate asthma. Pharmacogenetics. 2002. 12:565–570.30. Tamaoki J, Kondo M, Sakai N, Aoshiba K, Tagaya E, Nakata J, Isono K, Nagai A. Effect of suplatast tosilate, a Th2 cytokine inhibitor, on steroid-dependent asthma: a double-blind randomised study. Lancet. 2000. 356:273–278.31. Leung DY, Bloom JW. Update on glucocorticoid action and resistance. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:3–22.32. Tantisira KG, Weiss ST. The pharmacogenetics of asthma: an update. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2005. 7:209–217.33. Szalai C, Ungvári I, Pelyhe L, Tölgyesi G, Falus A. Asthma from a pharmacogenomic point of view. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. 153:1602–1614.34. Tantisira KG, Hwang ES, Raby BA, Silverman ES, Lake SL, Richter BG, Peng SL, Drazen JM, Glimcher LH, Weiss ST. TBX21: a functional variant predicts improvement in asthma with the use of inhaled corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004. 101:18099–18104.