Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2013 Jul;5(4):242-244. 10.4168/aair.2013.5.4.242.
Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia Leading to Acute Respiratory Failure in a Current Systemic Corticosteroid User
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology & Pain Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Chest Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jykimmd@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2260319
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.4.242
Abstract
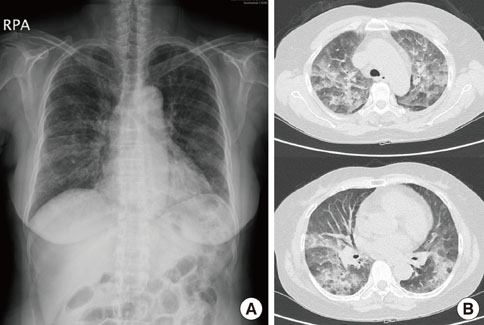
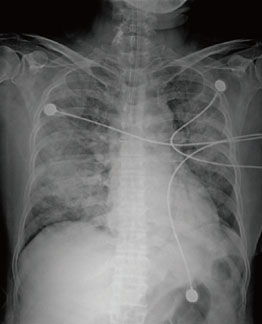
- A 69-year-old female patient visited the emergency room with fever (38.3degrees C) and dyspnea. She had been taking prednisolone (5 mg once per day) and methotrexate (2.5 mg once per week) for rheumatoid arthritis for 2 years. Chest computed tomography (CT) showed bilateral, multifocal ground glass opacity with interlobular septal thickening. Peripheral blood leukocyte count was 6,520/mm3 (neutrophils, 77.4%; eosinophils, 12.1%). During the night, mechanical ventilation was initiated due to the development of severe hypoxemia. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid showed a high proportion of eosinophils (49%). Her symptoms improved dramatically after commencement of intravenous methylprednisolone therapy. This is the first report of idiopathic acute eosinophilic pneumonia developing in a current user of systemic corticosteroids.
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Anoxia
Arthritis, Rheumatoid
Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid
Dyspnea
Emergencies
Eosinophils
Female
Fever
Glass
Humans
Leukocyte Count
Methotrexate
Methylprednisolone
Prednisolone
Pulmonary Eosinophilia
Respiration, Artificial
Respiratory Insufficiency
Thorax
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Methotrexate
Methylprednisolone
Prednisolone
Figure
Reference
-
1. Badesch DB, King TE Jr, Schwarz MI. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia: a hypersensitivity phenomenon? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989; 139:249–252.2. Allen JN, Pacht ER, Gadek JE, Davis WB. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia as a reversible cause of noninfectious respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 1989; 321:569–574.3. Philit F, Etienne-Mastroïanni B, Parrot A, Guérin C, Robert D, Cordier JF. Idiopathic acute eosinophilic pneumonia: a study of 22 patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:1235–1239.4. Jantz MA, Sahn SA. Corticosteroids in acute respiratory failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 160:1079–1100.5. Watanabe K, Fujimura M, Kasahara K, Yasui M, Myou S, Kita T, Watanabe A, Nakao S. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia following cigarette smoking: a case report including cigarette-smoking challenge test. Intern Med. 2002; 41:1016–1020.6. Bok GH, Kim YK, Lee YM, Kim KU, Uh ST, Hwang JH, Kim DW. Cigarette smoking-induced acute eosinophilic pneumonia: a case report including a provocation test. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:134–137.7. Rom WN, Weiden M, Garcia R, Yie TA, Vathesatogkit P, Tse DB, McGuinness G, Roggli V, Prezant D. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia in a New York City firefighter exposed to World Trade Center dust. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:797–800.8. Buchheit J, Eid N, Rodgers G Jr, Feger T, Yakoub O. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia with respiratory failure: a new syndrome? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992; 145:716–718.9. Yamaguchi S, Okubo Y, Hossain M, Fujimoto K, Honda T, Kubo K, Sekiguchi M, Takatsu K. IL-5 predominant in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood in a patient with acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Intern Med. 1995; 34:65–68.10. Lee JE, Rhee CK, Lim JH, Lee SM, Shim YS, Lee CT, Lee SW. Fraction of exhaled nitric oxide in patients with acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Chest. 2012; 141:1267–1272.11. Miki K, Miki M, Nakamura Y, Suzuki Y, Okano Y, Ogushi F, Ohtsuki Y, Nakayama T. Early-phase neutrophilia in cigarette smoke-induced acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Intern Med. 2003; 42:839–845.