Korean J Neurotrauma.
2014 Oct;10(2):130-133. 10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.130.
Short-Term Clinical and Angiographic Outcome in Child with Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm in A2 Segment of Anterior Cerebral Artery after Endovascular Treatment: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. ns4793@hanmail.net
- 2Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2256247
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.130
Abstract
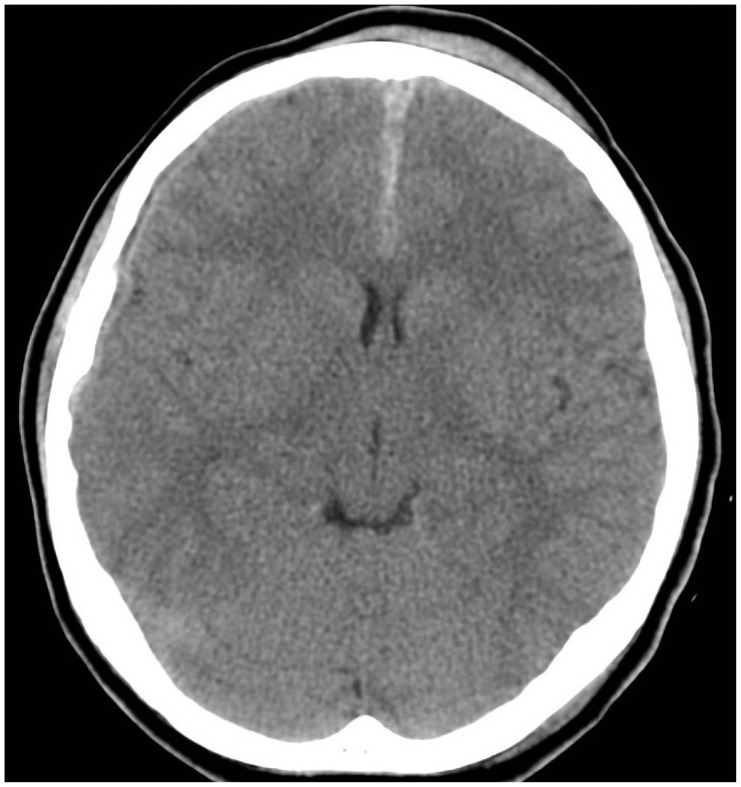
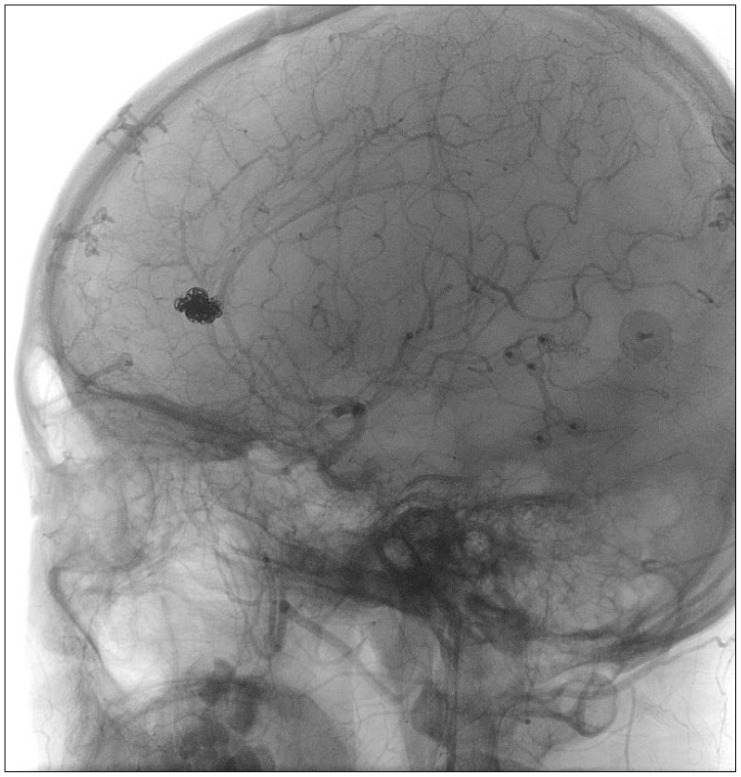
- Intracranial traumatic pseudoaneurysms are rare, and their vessel structures are immature and easy to disrupt, especially in children. Furthermore, it is difficult to diagnose and treat, which is a characteristic of traumatic pseudoaneurysm. In this study, the authors described a traumatic pseudoaneurysm in A2 segment of anterior cerebral artery, and the treatment with stent for structural stability of vessel.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aarabi B. Management of traumatic aneurysms caused by high-velocity missile head wounds. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1995; 6:775–797. PMID: 8527918.
Article2. Amirjamshidi A, Rahmat H, Abbassioun K. Traumatic aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas of intracranial vessels associated with penetrating head injuries occurring during war: principles and pitfalls in diagnosis and management. A survey of 31 cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1996; 84:769–780. PMID: 8622150.3. Britz GW, Mayberg MR. Pathology of cerebral aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage. In : Welch KMA, Caplan LR, Reis DJ, Siesjö BK, Weir B, editors. Primer on cerebrovascular diseases. San Diego, CA: Academic Press;1997. p. 498–502.4. Ciceri EF, Regna-Gladin C, Erbetta A, Chiapparini L, Nappini S, Savoiardo M, et al. Iatrogenic intracranial pseudoaneurysms: neuroradiological and therapeutical considerations, including endovascular options. Neurol Sci. 2006; 27:317–322. PMID: 17122940.
Article5. Dunn IF, Woodworth GF, Siddiqui AH, Smith ER, Vates GE, Day AL, et al. Traumatic pericallosal artery aneurysm: a rare complication of transcallosal surgery. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2007; 106(2 Suppl):153–157. PMID: 17330545.6. Golshani K, Britz GW, Yoo A, West GA. Traumatic cerebral aneurysms secondary to penetrating intracranial injuries. In : Winn HR, editor. Youmans neurological surgery. ed 6. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders;2011. p. 4000–4003.7. Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Goto K, Norman D, Newton TH. Dural fistulas involving the transverse and sigmoid sinuses: results of treatment in 28 patients. Radiology. 1987; 163:443–447. PMID: 3562824.
Article8. Hart RG, Easton JD. Dissections of cervical and cerebral arteries. Neurol Clin. 1983; 1:155–182. PMID: 6680158.
Article9. Kieck CF, de Villiers JC. Vascular lesions due to transcranial stab wounds. J Neurosurg. 1984; 60:42–46. PMID: 6689727.
Article10. Lee M, Kim MS, Yoon SW. Interhemispheric subdural hematoma presenting with falx syndrome after trauma. J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc. 2010; 6:158–161.
Article11. Lempert TE, Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, Urwin RW, Balousek PA, et al. Endovascular treatment of pseudoaneurysms with electrolytically detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:907–911. PMID: 9613510.12. Rayes M, Bahgat DA, Kupsky WJ, Mittal S. Middle cerebral artery pseudoaneurysm formation following stereotactic biopsy. Can J Neurol Sci. 2008; 35:664–668. PMID: 19235456.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the External and Internal Carotid Artery Presenting as Epistaxis: Case Report
- A2 Anomaly Associated with Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm
- Traumatic Intracranial Aneurysm: A Case Report
- Endovascular Thrombin Injection for a Pulmonary Artery Pseudoaneurysm: Case Report
- Clinical Analysis of Traumatic Cerebral Pseudoaneurysms