Korean Circ J.
2012 Nov;42(11):792-795. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.11.792.
Congenital Giant Right Coronary Artery Aneurysm With Fistula to the Coronary Sinus and Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava in an Old Woman
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. nadroj@chol.com
- KMID: 2224983
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.11.792
Abstract
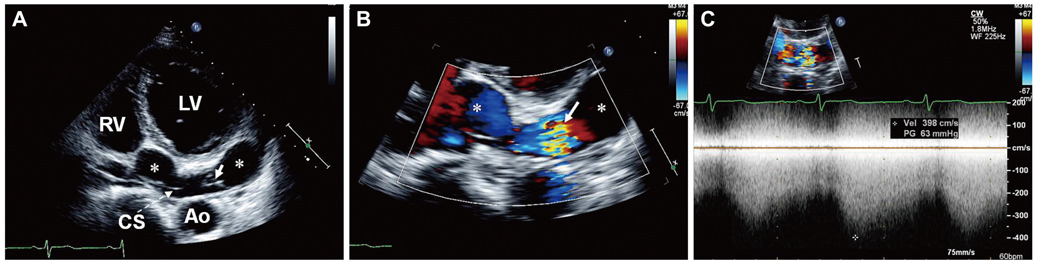
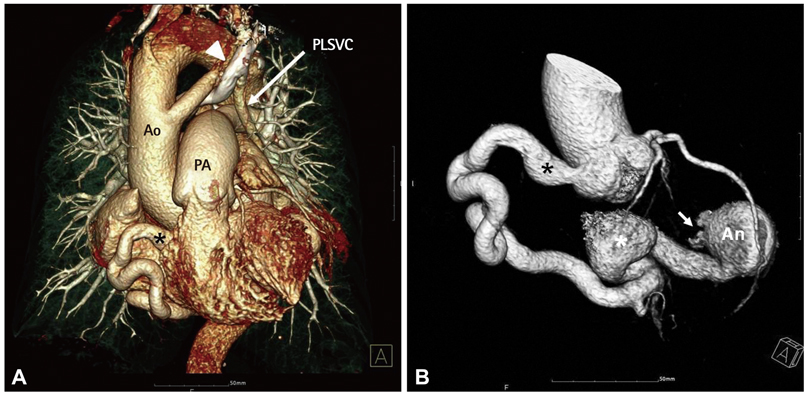
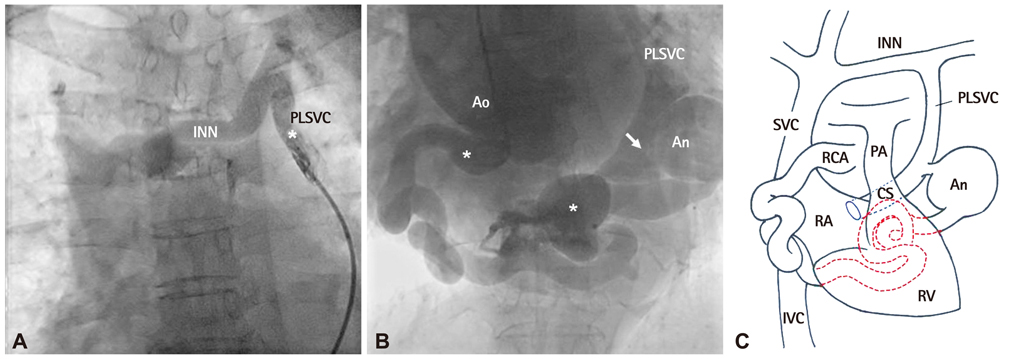
- The combination of coronary arteriovenous fistula to the coronary sinus (CS), dilatation of the entire length of coronary artery, coronary aneurysm and persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) is very rare. We present the case of a 63-year-old female admitted for dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea, and facial edema. Echocardiography detected a giant coronary artery with shunt flow, dilated CS and PLSVC and a coronary angiography reaffirmed these findings. The calculated ratio of pulmonary blood flow to systemic blood flow by cardiac catheterization was 1.53. After multidisciplinary review considering old age, hypoactivity due to underlying Parkinsonism and relatively small amount of shunt flow, medical therapy was chosen. The patient remained asymptomatic for 10 months after discharge without intervention.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haller JA Jr, Little JA. Diagnosis and surgical correction of congenital coronary artery-coronary sinus fistula. Circulation. 1963. 27:939–942.2. Tirilomis T, Aleksic I, Busch T, Zenker D, Ruschewski W, Dalichau H. Congenital coronary artery fistulas in adults: surgical treatment and outcome. Int J Cardiol. 2005. 98:57–59.3. Ozler A, Tarhan IA, Kehlibar T, et al. Resection of a right coronary artery aneurysm with fistula to the coronary sinus. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008. 85:649–651.4. Komoda S, Komoda T, Ivanitskaia-Kuehn E, Dreysse S, Pasic M, Hetzer R. Giant aneurysm of the right coronary artery and fistula to the coronary sinus. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010. 58:78–81.5. El Watidy AM, Ismail HH, Calafiore AM. Surgical management of right coronary artery-coronary sinus fistula causing severe mitral and tricuspid regurgitation. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010. 10:110–112.6. Yu L, Shi E, Gu T. Aneurysmal right coronary with fistula to the coronary sinus combined with severe stenosis of the left anterior descending artery: a snake on the heart. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011. 142:937–939.7. Wilkinson JL. Haemodynamic calculations in the catheter laboratory. Heart. 2001. 85:113–120.8. Gowda RM, Vasavada BC, Khan IA. Coronary artery fistulas: clinical and therapeutic considerations. Int J Cardiol. 2006. 107:7–10.9. Yamanaka O, Hobbs RE. Coronary artery anomalies in 126,595 patients undergoing coronary arteriography. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1990. 21:28–40.10. Liberthson RR, Sagar K, Berkoben JP, Weintraub RM, Levine FH. Congenital coronary arteriovenous fistula: report of 13 patients, review of the literature and delineation of management. Circulation. 1979. 59:849–854.11. Yilmaz R, Demirbag R, Gur M. Echocardiographic diagnosis of a right coronary artery-coronary sinus fistula. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2005. 21:649–654.12. Bittencourt MS, Seltman M, Achenbach S, Rost C, Ropers D. Right coronary artery fistula to the coronary sinus and right atrium associated with giant right coronary enlargement detected by transthoracic echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2011. 12:E22.13. Tekbas G, Onder H, Tekbas E, Yavuz C, Bilici A. Giant right coronary artery and coronary sinus aneurysm due to fistula. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011. 38:314–315.14. Mitropoulos F, Samanidis G, Kalogris P, Michalis A. Tortuous right coronary artery to coronary sinus fistula. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011. 13:672–674.15. Hamada M, Kubo H, Matsuoka H, Kokubu T, Oosuga Y, Joh T. Myocardial infarction complicating surgical repair of left coronary-right ventricular fistula in an adult. Am J Cardiol. 1986. 57:372–374.16. Loo B, Cox ID, Morgan-Hughes GJ, Marchbank AJ. Thrombotic occlusion of giant circumflex artery aneurysm after ligation of arteriovenous fistula. Circulation. 2010. 122:e447–e448.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Rare Combination of the Left Circumflex Coronary Artery Fistula Connecting a Dilated Coronary Sinus with Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava and Multiple Arteriovenous Fistulae
- A Case of Coronary Arteriovenous Fistula Associated with Giant Coronary Artery Aneurysm
- Giant Coronary Sinus Caused by Absent Right and Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava and Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation
- Unroofed Coronary Sinus Associated with Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava : Detection by Agitated Saline Contrast Echocardiography
- A Case of Persistent Left SVC Associated with Tricuspid Regurgitation