Clin Endosc.
2015 Jan;48(1):52-58. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.1.52.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection with Circumferential Incision for the Treatment of Large Sessile Polyps and Laterally Spreading Tumors of the Colorectum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine and Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. mdkhwook@gmail.com
- KMID: 2221759
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.1.52
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
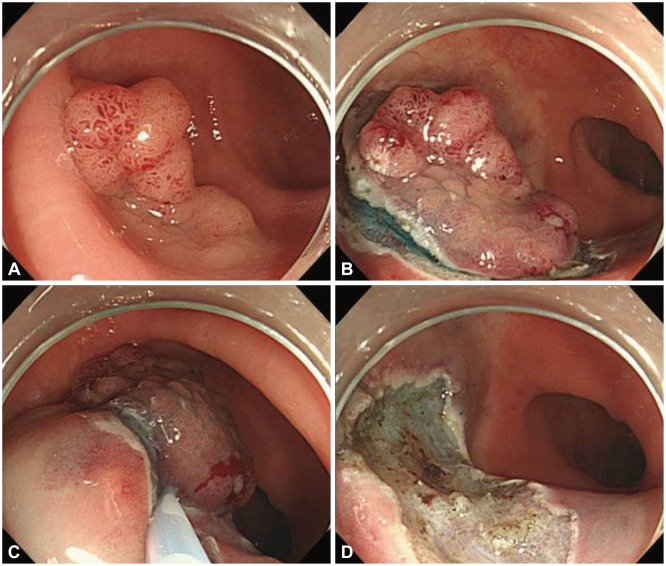
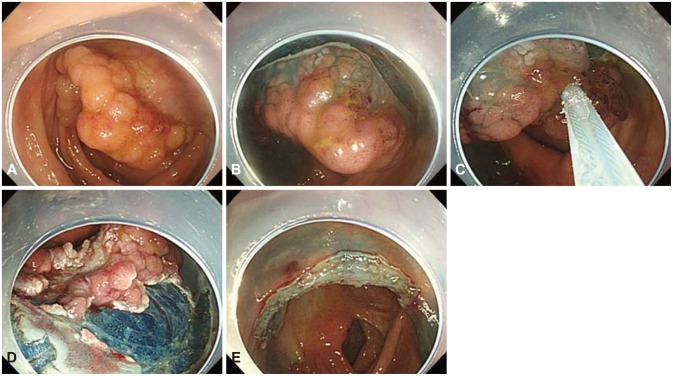
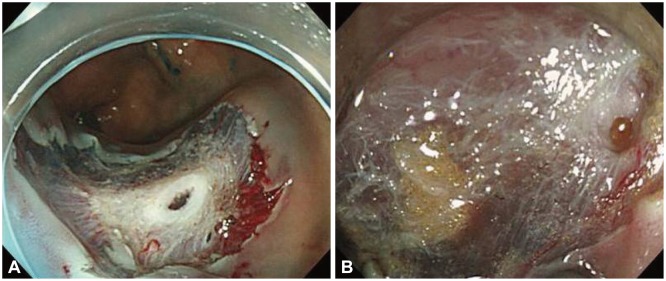
Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is the standard treatment for colorectal polyps such as adenomas and early cancers with no risk of lymph node metastasis. However, endoscopic resection of large colorectal polyps (> or =20 mm diameter) is difficult to perform. We evaluated the clinical outcomes of EMR with circumferential incision (EMR-CI) for the resection of large sessile polyps (Is) and laterally spreading tumors (LSTs) in the colorectum.
METHODS
Between February 2009 and March 2011, we resected 80 large colorectal polyps by EMR-CI. We retrospectively investigated the en bloc resection rate, histologic complete resection rate, recurrence rate, and complications.
RESULTS
The median polyp size was approximately 25 mm (range, 20 to 50), and the morphologic types included Is (13 cases), LST-granular (37 cases), and LST-nongranular (30 cases). The en bloc and complete histologic resection rates were 66.3% and 45.0%, respectively. The recurrence rate was 0% (median follow-up duration, 23 months), and perforation occurred in five cases (6.3%).
CONCLUSIONS
EMR-CI is an effective treatment modality for 20 to 30 mm-sized colorectal polyps, and may be considered as a second line therapeutic option if ESD is difficult.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection with Circumferential Mucosal Incision for Colorectal Neoplasms: Comparison with Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection and between Two Endoscopists with Different Experiences
Dong-Hoon Yang, Min-Seob Kwak, Sang Hyoung Park, Byong Duk Ye, Jeong-Sik Byeon, Seung-Jae Myung, Suk-Kyun Yang, Hyun Gun Kim, Shai Friedland
Clin Endosc. 2017;50(4):379-387. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.058.Many Options to Manage Laterally Spreading Tumors
Dong Kyung Chang
Clin Endosc. 2015;48(1):4-5. doi: 10.5946/ce.2015.48.1.4.
Reference
-
1. Van Gossum A, Cozzoli A, Adler M, Taton G, Cremer M. Colonoscopic snare polypectomy: analysis of 1485 resections comparing two types of current. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38:472–475. PMID: 1511824.
Article2. Kudo S. Endoscopic mucosal resection of flat and depressed types of early colorectal cancer. Endoscopy. 1993; 25:455–461. PMID: 8261988.
Article3. Saito Y, Fujii T, Kondo H, et al. Endoscopic treatment for laterally spreading tumors in the colon. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:682–686. PMID: 11490384.
Article4. Ahmad NA, Kochman ML, Long WB, Furth EE, Ginsberg GG. Efficacy, safety, and clinical outcomes of endoscopic mucosal resection: a study of 101 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:390–396. PMID: 11868015.
Article5. Hurlstone DP, Sanders DS, Cross SS, et al. Colonoscopic resection of lateral spreading tumours: a prospective analysis of endoscopic mucosal resection. Gut. 2004; 53:1334–1339. PMID: 15306595.
Article6. Kiesslich R, Neurath MF. Endoscopic mucosal resection: an evolving therapeutic strategy for non-polypoid colorectal neoplasia. Gut. 2004; 53:1222–1224. PMID: 15306573.
Article7. Puli SR, Kakugawa Y, Gotoda T, Antillon D, Saito Y, Antillon MR. Meta-analysis and systematic review of colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:4273–4277. PMID: 19750569.
Article8. Soetikno RM, Inoue H, Chang KJ. Endoscopic mucosal resection. Current concepts. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2000; 10:595–617. PMID: 11036535.
Article9. Tanaka S, Haruma K, Oka S, et al. Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:62–66. PMID: 11427843.
Article10. Tamura S, Nakajo K, Yokoyama Y, et al. Evaluation of endoscopic mucosal resection for laterally spreading rectal tumors. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:306–312. PMID: 15057679.
Article11. Walsh RM, Ackroyd FW, Shellito PC. Endoscopic resection of large sessile colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38:303–309. PMID: 1607080.12. Conio M, Repici A, Demarquay JF, Blanchi S, Dumas R, Filiberti R. EMR of large sessile colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:234–241. PMID: 15278051.
Article13. Salama M, Ormonde D, Quach T, Ee H, Yusoff I. Outcomes of endoscopic resection of large colorectal neoplasms: an Australian experience. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:84–89. PMID: 19793173.
Article14. Tanaka S, Oka S, Kaneko I, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:100–107. PMID: 17591481.
Article15. Uraoka T, Kato J, Ishikawa S, et al. Thin endoscope-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection for large colorectal tumors (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:836–839. PMID: 17905031.
Article16. Sakamoto N, Osada T, Shibuya T, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of large colorectal tumors by using a novel spring-action S-O clip for traction (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:1370–1374. PMID: 19403131.
Article17. Repici A, Conio M, De Angelis C, et al. Insulated-tip knife endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal polyps unsuitable for standard polypectomy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1617–1623. PMID: 17403075.
Article18. Hirao M, Masuda K, Nakamura M. Endoscopic resection with local injection of HSE (ERHSE) in early gastric carcinomas. Gan No Rinsho. 1986; 32:1180–1184. PMID: 3491227.19. Sakamoto T, Matsuda T, Nakajima T, Saito Y. Efficacy of endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential incision for patients with large colorectal tumors. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:22–26. PMID: 22016034.
Article20. Lee EJ, Lee JB, Lee SH, Youk EG. Endoscopic treatment of large colorectal tumors: comparison of endoscopic mucosal resection, endoscopic mucosal resection-precutting, and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:2220–2230. PMID: 22278105.
Article21. Participants in the Paris Workshop. The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, 2002. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58(6 Suppl):S3–S43. PMID: 14652541.22. Ah Soune P, Menard C, Salah E, Desjeux A, Grimaud JC, Barthet M. Large endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal tumors exceeding 4 cm. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:588–595. PMID: 20128027.
Article23. Brooker JC, Saunders BP, Shah SG, Williams CB. Endoscopic resection of large sessile colonic polyps by specialist and non-specialist endoscopists. Br J Surg. 2002; 89:1020–1024. PMID: 12153628.
Article24. Iishi H, Tatsuta M, Iseki K, et al. Endoscopic piecemeal resection with submucosal saline injection of large sessile colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51:697–700. PMID: 10840302.
Article25. Saito Y, Fukuzawa M, Matsuda T, et al. Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal tumors as determined by curative resection. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:343–352. PMID: 19517168.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Indications for and Technical Aspects of Colorectal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- A Case of Synchronous Colonic Laterally Spreading Tumors Treated by Sequential Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Performed on Two Consecutive Days
- Is the Double Channel Gastroscope Useful in Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Large Sessile Colon Polyps?
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection with Band Ligation for Two Cases of Gastric Flat Adenoma
- History and Development of Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection