J Pathol Transl Med.
2016 Jan;50(1):26-36. 10.4132/jptm.2015.11.09.
Overview of IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Its Mimickers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jeong10@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2211398
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.11.09
Abstract
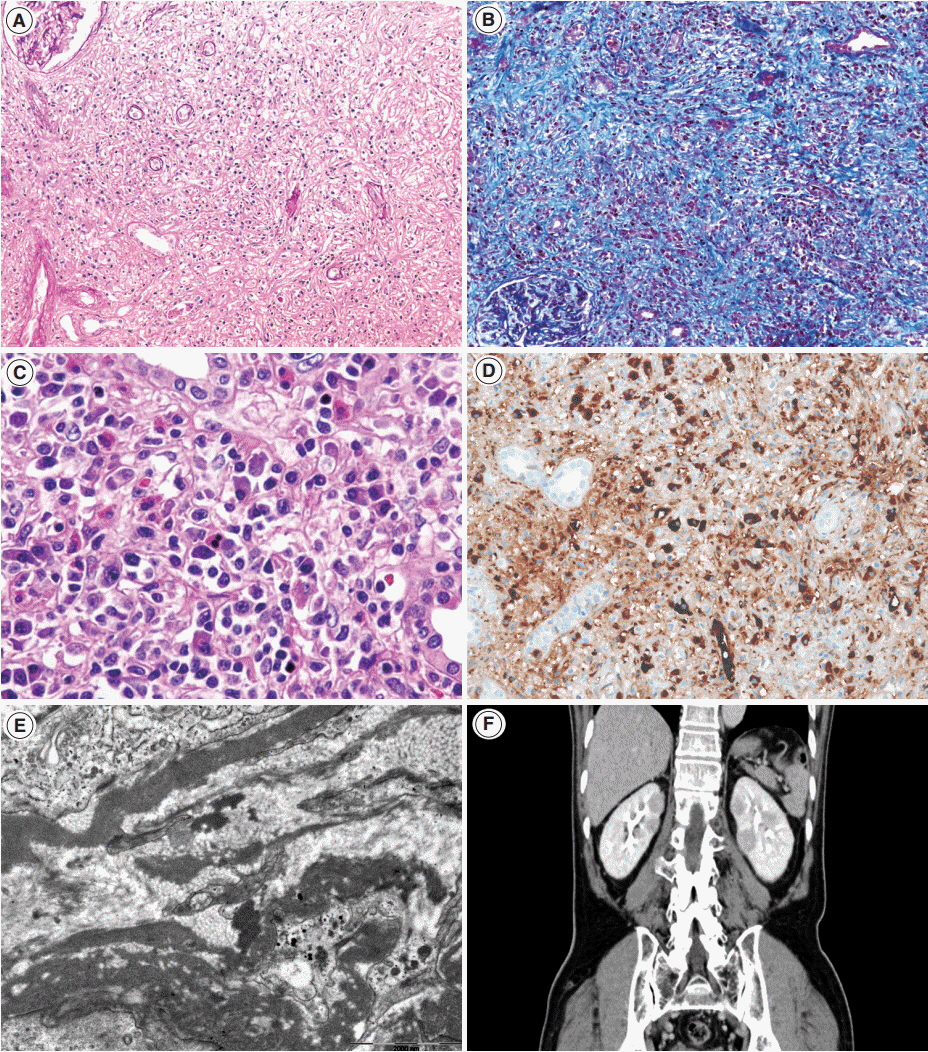
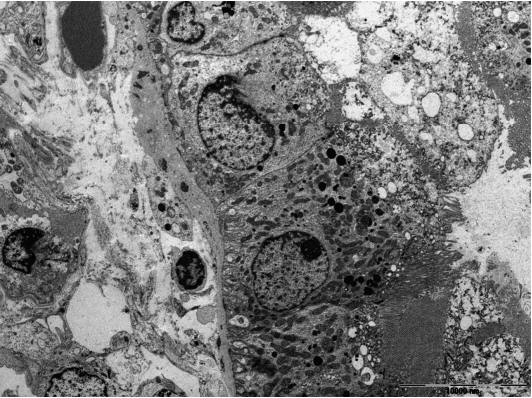
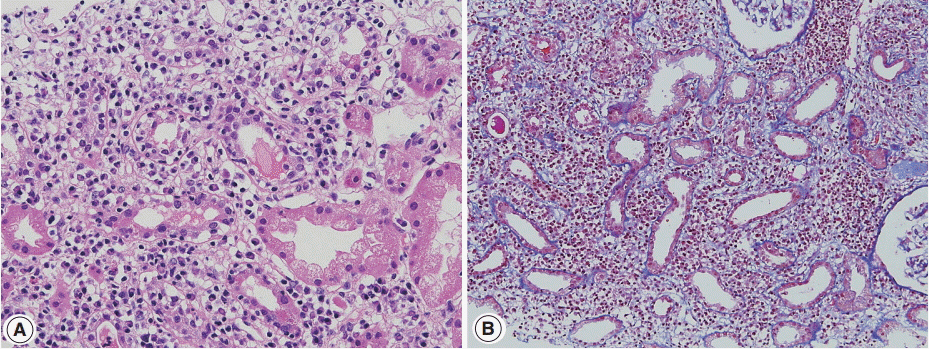
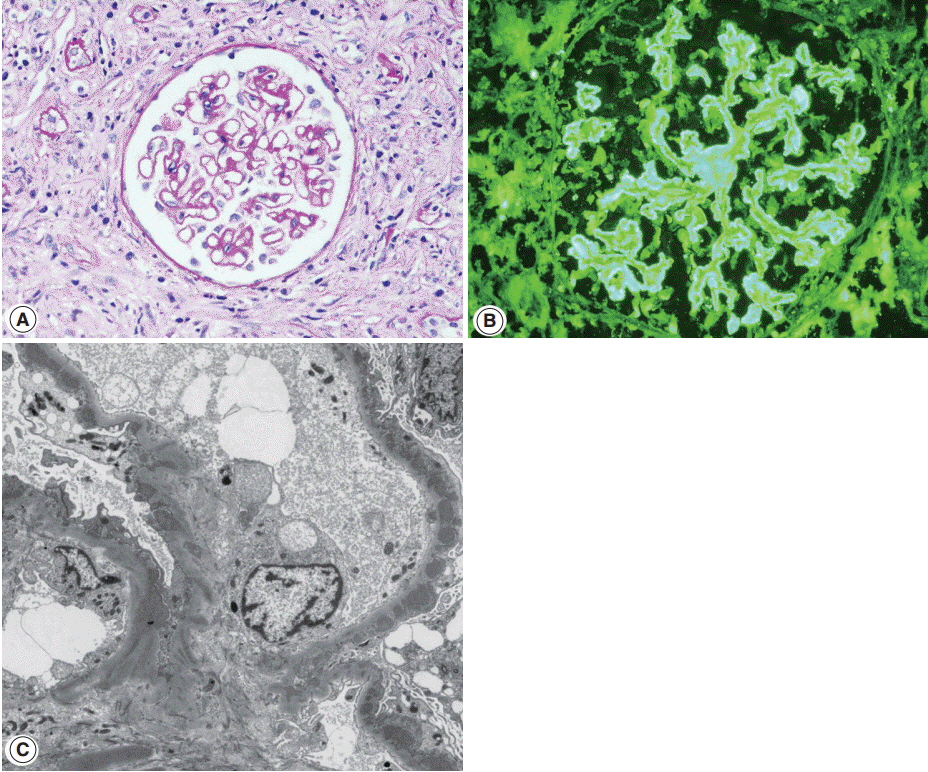
- Tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) is the most common form of renal involvement in IgG4-related disease. It is characterized by a dominant infiltrate of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the interstitium and storiform fibrosis. Demonstration of IgG4-positive plasma cells is essential for diagnosis, but the number of IgG4-positive cells and the ratio of IgG4-positive/IgG-positive plasma cells may vary from case to case and depending on the methods of tissue sampling even in the same case. IgG4-positive plasma cells can be seen in TIN associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren syndrome, or anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis, which further add diagnostic confusion and difficulties. To have a more clear view of IgG4-TIN and to delineate differential points from other TIN with IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltrates, clinical and histological features of IgG4-TIN and its mimickers were reviewed. In the rear part, cases suggesting overlap of IgG4-TIN and its mimickers and glomerulonephritis associated with IgG4-TIN were briefly described.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Utilizing Immunoglobulin G4 Immunohistochemistry for Risk Stratification in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Associated with Hashimoto Thyroiditis
Faridul Haq, Gyeongsin Park, Sora Jeon, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(3):468-478. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.1923.
Reference
-
1. Saeki T, Kawano M. IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014; 85:251–7.
Article2. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–51.
Article3. Divatia M, Kim SA, Ro JY. IgG4-related sclerosing disease, an emerging entity: a review of a multi-system disease. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:15–34.
Article4. Kambham N, Markowitz GS, Tanji N, Mansukhani MM, Orazi A, D’Agati VD. Idiopathic hypocomplementemic interstitial nephritis with extensive tubulointerstitial deposits. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001; 37:388–99.
Article5. Uchiyama-Tanaka Y, Mori Y, Kimura T, et al. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune-related pancreatitis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004; 43:e18–25.
Article6. Takeda S, Haratake J, Kasai T, Takaeda C, Takazakura E. IgG4-associated idiopathic tubulointerstitial nephritis complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004; 19:474–6.
Article7. Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010; 78:1016–23.
Article8. Raissian Y, Nasr SH, Larsen CP, et al. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011; 22:1343–52.
Article9. Houghton DC, Troxell ML. An abundance of IgG4+ plasma cells is not specific for IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Mod Pathol. 2011; 24:1480–7.
Article10. Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011; 15:615–26.
Article11. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181–92.12. Deng C, Li W, Chen S, et al. Histopathological diagnostic value of the IgG4+/IgG+ ratio of plasmacytic infiltration for IgG4-related diseases: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e579.13. Yamaguchi Y, Kanetsuna Y, Honda K, et al. Characteristic tubulointerstitial nephritis in IgG4-related disease. Hum Pathol. 2012; 43:536–49.
Article14. Yoshita K, Kawano M, Mizushima I, et al. Light-microscopic characteristics of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis: distinction from non-IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012; 27:2755–61.
Article15. Alexander MP, Larsen CP, Gibson IW, et al. Membranous glomerulonephritis is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Kidney Int. 2013; 83:455–62.
Article16. Sharma SG, Vlase HL, D’Agati VD. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis with plasma cell-rich renal arteritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013; 61:638–43.
Article17. Nagamachi S, Ohsawa I, Sato N, et al. Immune complex-mediated complement activation in a patient with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Case Rep Nephrol Urol. 2011; 1:7–14.
Article18. Cornell LD, Chicano SL, Deshpande V, et al. Pseudotumors due to IgG4 immune-complex tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune pancreatocentric disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:1586–97.
Article19. Nishi S, Imai N, Yoshida K, Ito Y, Saeki T. Clinicopathological findings of immunoglobulin G4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011; 15:810–9.
Article20. Koizumi S, Kamisawa T, Kuruma S, et al. Organ correlation in IgG4-related diseases. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:743–8.
Article21. Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010; 34:1812–9.22. Inoue D, Yoshida K, Yoneda N, et al. IgG4-related disease: dataset of 235 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e680.23. Vlachou PA, Khalili K, Jang HJ, Fischer S, Hirschfield GM, Kim TK. IgG4-related sclerosing disease: autoimmune pancreatitis and extrapancreatic manifestations. Radiographics. 2011; 31:1379–402.
Article24. Mavragani CP, Fragoulis GE, Rontogianni D, Kanariou M, Moutsopoulos HM. Elevated IgG4 serum levels among primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients: do they unmask underlying IgG4-related disease? Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014; 66:773–7.25. Goh TL, Cicovic A, Sapsford T, Semple D. A case of immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) tubulointerstitial nephritis with delayed elevation of serum IgG4 levels. Intern Med J. 2015; 45:788–90.
Article26. Watson SJ, Jenkins DA, Bellamy CO. Nephropathy in IgG4-related systemic disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006; 30:1472–7.
Article27. Yoneda K, Murata K, Katayama K, et al. Tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with IgG4-related autoimmune disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007; 50:455–62.
Article28. Kawano M, Mizushima I, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Immunohistochemical characteristics of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis: detailed analysis of 20 Japanese cases. Int J Rheumatol. 2012; 2012:609795.
Article29. Arai H, Hayashi H, Takahashi K, et al. Tubulointerstitial fibrosis in patients with IgG4-related kidney disease: pathological findings on repeat renal biopsy. Rheumatol Int. 2015; 35:1093–101.
Article30. Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, et al. IgG4-related disease: clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67:2466–75.
Article31. Cunningham E, Provost T, Brentjens J, Reichlin M, Venuto RC. Acute renal failure secondary to interstitial lupus nephritis. Arch Intern Med. 1978; 138:1560–1.
Article32. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercise. Case 53-1976. N Engl J Med. 1976; 295:1526–32.33. Gur H, Kopolovic Y, Gross DJ. Chronic predominant interstitial nephritis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a follow up of three years and review of the literature. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987; 46:617–23.
Article34. Tron F, Ganeval D, Droz D. Immunologically-mediated acute renal failure of nonglomerular origin in the course of systemic lupus erythematosus [SLE]: report of two cases. Am J Med. 1979; 67:529–32.35. Mori Y, Kishimoto N, Yamahara H, et al. Predominant tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with systemic lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2005; 9:79–84.
Article36. Omokawa A, Wakui H, Okuyama S, et al. Predominant tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: phenotype of infiltrating cells. Clin Nephrol. 2008; 69:436–44.
Article37. Singh AK, Ucci A, Madias NE. Predominant tubulointerstitial lupus nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996; 27:273–8.
Article38. Alpers CE, Hopper J Jr, Bernstein MJ, Biava CG. Late development of systemic lupus erythematosus in patients with glomerular “fingerprint” deposits. Ann Intern Med. 1984; 100:66–8.
Article39. Okada H, Takahira S, Sugahara S, Nakamoto H, Suzuki H. Retroperitoneal fibrosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999; 14:1300–2.40. Kiyama K, Yoshifuji H, Kandou T, et al. Screening for IgG4-type anti-nuclear antibodies in IgG4-related disease. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:129.
Article41. Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Seror R, et al. Characterization of systemic disease in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: EULAR-SS Task Force recommendations for articular, cutaneous, pulmonary and renal involvements. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015; 54:2230–8.42. Kidder D, Rutherford E, Kipgen D, Fleming S, Geddes C, Stewart GA. Kidney biopsy findings in primary Sjögren syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015; 30:1363–9.
Article43. Pijpe J, Vissink A, Van der Wal JE, Kallenberg CG. Interstitial nephritis with infiltration of IgG-kappa positive plasma cells in a patient with Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004; 43:108–10.44. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:1–14.
Article45. Kawano M, Suzuki Y, Yamada K, et al. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome with chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis and lymphadenopathy mimicking IgG4-related disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2015; 25:637–41.
Article46. Yukawa N, Tsuboi N, Yukawa S, et al. Marked hypocomplementemia and tubulointerstitial nephritis in a male patient with Sjögren’s syndrome. Mod Rheumatol. 2004; 14:164–8.
Article47. Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Shinomura Y. Are Sjögren’s syndrome and IgG4-related disease able to coexist? Mod Rheumatol. 2015; 25:970–1.
Article48. Kronbichler A, Gut N, Zwerina J, Neuwirt H, Rudnicki M, Mayer G. Extending the spectrum of a chameleon: IgG4-related disease appearing as interstitial nephritis and mimicking anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015; 54:1936–8.49. Perez Alamino R, Martínez C, Espinoza LR. IgG4-associated vasculitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013; 15:348.
Article50. Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Suzuki C, et al. Analysis of serum IgG subclasses in Churg-Strauss syndrome: the meaning of elevated serum levels of IgG4. Intern Med. 2010; 49:1365–70.
Article51. Vaglio A, Strehl JD, Manger B, et al. IgG4 immune response in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:390–3.
Article52. Chang SY, Keogh KA, Lewis JE, et al. IgG4-positive plasma cells in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study on 43 granulomatosis with polyangiitis and 20 control cases. Hum Pathol. 2013; 44:2432–7.
Article53. Ayuzawa N, Ubara Y, Keiichi S, et al. Churg-Strauss syndrome with a clinical condition similar to IgG4-related kidney disease: a case report. Intern Med. 2012; 51:1233–8.
Article54. Zaarour M, Weerasinghe C, Eter A, El-Sayegh S, El-Charabaty E. An overlapping case of lupus nephritis and IgG4-related kidney disease. J Clin Med Res. 2015; 7:575–81.
Article55. Sugimoto T, Tanaka Y, Morita Y, Kume S, Uzu T, Kashiwagi A. Is tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome associated with IgG4-related systemic disease? Nephrology (Carlton). 2008; 13:89.
Article56. Houghton D, Troxell M, Fox E, Rosenbaum J. TINU (tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis) syndrome is not usually associated with IgG4 sclerosing disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012; 59:583–4.
Article57. Sakairi T, Okabe S, Hiromura K, et al. A case of ANCA-negative renal small-vessel vasculitis with tubulointerstitial infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells. Mod Rheumatol. 2014; May. 20. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2014.915510.
Article58. Hara S, Kawano M, Mizushima I, et al. A condition closely mimicking IgG4-related disease despite the absence of serum IgG4 elevation and IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration. Mod Rheumatol. 2014; Jun. 2. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2014.916836.
Article59. Malone AF, Sparks MA, Howell DN, Middleton JP, Smith SR, Lehrich RW. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Nephrol. 2013; 26:1195–8.
Article60. Nishikawa K, Takeda A, Masui S, et al. A case of IgG4-positive plasma cell-rich tubulointerstitial nephritis in a kidney allograft mimicking IgG4-related kidney disease. Nephrology (Carlton). 2014; 19 Suppl 3:52–6.
Article61. Rekvig OP, Van der Vlag J. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus: still not resolved. Semin Immunopathol. 2014; 36:301–11.
Article62. Soliotis F, Mavragani CP, Plastiras SC, Rontogianni D, Skopouli FN, Moutsopoulos HM. IgG4-related disease: a rheumatologist’s perspective. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014; 32:724–7.63. Cravedi P, Abbate M, Gagliardini E, et al. Membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011; 58:272–5.
Article64. Fervenza FC, Downer G, Beck LH Jr, Sethi S. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis with membranous nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011; 58:320–4.
Article65. Jindal N, Yadav D, Passero C, et al. Membranous nephropathy: a rare renal manifestation of IgG4-related systemic disease. Clin Nephrol. 2012; 77:321–8.
Article66. Li XL, Yan TK, Li HF, et al. IgG4-related membranous nephropathy with high blood and low urine IgG4/IgG ratio: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol. 2014; 33:145–8.
Article67. Palmisano A, Corradi D, Carnevali ML, et al. Chronic periaortitis associated with membranous nephropathy: clues to common pathogenetic mechanisms. Clin Nephrol. 2010; 74:485–90.
Article68. Saeki T, Imai N, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Nishi S. Membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related systemic disease and without autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin Nephrol. 2009; 71:173–8.
Article69. Stylianou K, Maragkaki E, Tzanakakis M, Stratakis S, Gakiopoulou H, Daphnis E. Acute interstitial nephritis and membranous nephropathy in the context of IgG4-related disease. Case Rep Nephrol Dial. 2015; 5:44–8.
Article70. Jennette JC, Iskandar SS, Dalldorf FG. Pathologic differentiation between lupus and nonlupus membranous glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 1983; 24:377–85.
Article71. Haas M. IgG subclass deposits in glomeruli of lupus and nonlupus membranous nephropathies. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994; 23:358–64.
Article72. Omokawa A, Komatsuda A, Nara M, et al. Distribution of glomerular IgG subclass deposits in patients with membranous nephropathy and anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein antibody. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012; 27:1937–41.
Article73. Tamai R, Hasegawa Y, Hisano S, Miyake K, Nakashima H, Saito T. A case of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis concurrent with Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2011; 7:5.
Article74. Ito K, Yamada K, Mizushima I, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis in a patient with IgG4-related disease: a possible association. Clin Nephrol. 2013; 79:246–52.
Article75. Yang H, Choi SK, Kim B, et al. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis accompanied by Henoch-Schonlein purpura. Korean J Med. 2014; 87:96–100.76. Morimoto J, Hasegawa Y, Fukushima H, et al. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis-like glomerular disease and concurrent tubulointerstitial nephritis complicating IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern Med. 2009; 48:157–62.
Article77. Katano K, Hayatsu Y, Matsuda T, et al. Endocapillary proliferative glomerulonephritis with crescent formation and concurrent tubulointerstitial nephritis complicating retroperitoneal fibrosis with a high serum level of IgG4. Clin Nephrol. 2007; 68:308–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis Accompanied by Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- Autoimmune Pancreatitis Accompanied by Tubulointerstitial Nephritis
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Pictorial Review of the Imaging Spectrum, Mimickers, and Clinicopathological Characteristics
- A Case of Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Uveitis
- Classification and Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis