J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Nov;58(5):448-453. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.448.
Survival-Related Factors of Spinal Metastasis with Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Current Surgical Treatment Modalities : A Single Institute Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Spine Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sobotta72@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Spine Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2191410
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.448
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Recently, the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been prolonged with improvements in various diagnostic tools and medical treatment modalities. Consequently, spine metastases from HCC are being diagnosed more frequently. The accurate prediction of prognosis plays a critical role in determining a patient's treatment plan, including surgery for patients with spinal metastases of HCC. We investigated the clinical features, surgical outcomes, and prognostic factors of HCC presenting with spine metastases, in patients who underwent surgery.
METHODS
A retrospective review was conducted on 33 HCC patients who underwent 36 operations (three patients underwent surgical treatment twice) from February 2006 to December 2013. The median age of the patients was 56 years old (range, 28 to 71; male : female=30 : 3).
RESULTS
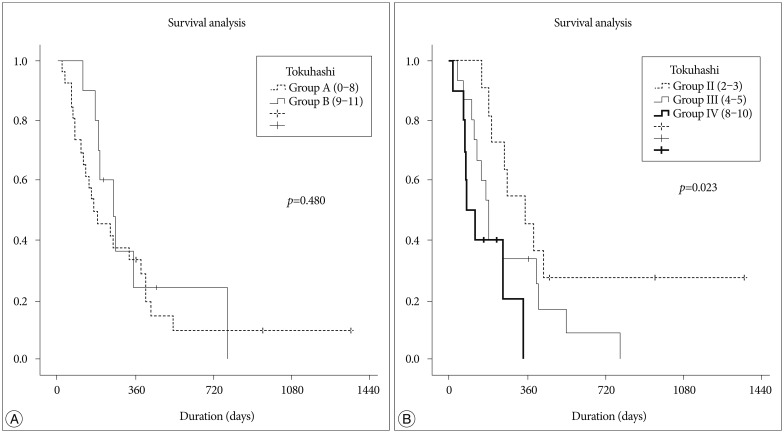
Overall survival was not correlated with age, sex, level of metastases, preoperative Child-Pugh classification, preoperative ambulatory function, preoperative radiotherapy, type of operation, administration of Sorafenib, or the Tokuhashi scoring system. Only the Tomita scoring system was shown to be an independent prognostic factor for overall survival. Comparing the Child-Pugh classification and ambulatory ability, there were no statistically differences between patients pre- and post-operatively.
CONCLUSION
The Tomita scoring system represents a practicable and highly predictive prognostic tool. Even though surgical intervention may not restore ambulatory function, it should be considered to prevent deterioration of the patient's overall condition. Additionally, aggressive management may be needed if there is any ambulatory ability remaining.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Effect of Perioperative Radiation Therapy on Spinal Bone Fusion Following Spine Tumor Surgery
Tae-Kyum Kim, Wonik Cho, Sang Min Youn, Ung-Kyu Chang
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016;59(6):597-603. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.6.597.
Reference
-
1. Abrahm JL, Banffy MB, Harris MB. Spinal cord compression in patients with advanced metastatic cancer : "all I care about is walking and living my life". JAMA. 2008; 299:937–946. PMID: 18314436.
Article2. Bilsky MH, Laufer I, Burch S. Shifting paradigms in the treatment of metastatic spine disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(22 Suppl):S101–S107. PMID: 19829269.
Article3. Chang EL, Shiu AS, Mendel E, Mathews LA, Mahajan A, Allen PK, et al. Phase I/II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastasis and its pattern of failure. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 7:151–160. PMID: 17688054.
Article4. Chang UK, Kim MS, Han CJ, Lee DH. Clinical result of stereotactic radiosurgery for spinal metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma : comparison with conventional radiation therapy. J Neurooncol. 2014; 119:141–148. PMID: 24803002.
Article5. Chao ST, Koyfman SA, Woody N, Angelov L, Soeder SL, Reddy CA, et al. Recursive partitioning analysis index is predictive for overall survival in patients undergoing spine stereotactic body radiation therapy for spinal metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 82:1738–1743. PMID: 21489717.
Article6. Chataigner H, Onimus M. Surgery in spinal metastasis without spinal cord compression : indications and strategy related to the risk of recurrence. Eur Spine J. 2000; 9:523–527. PMID: 11189921.
Article7. Chen H, Xiao J, Yang X, Zhang F, Yuan W. Preoperative scoring systems and prognostic factors for patients with spinal metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:E1339–E1346. PMID: 20938387.
Article8. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma : a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:25–34. PMID: 19095497.
Article9. Cole JS, Patchell RA. Metastatic epidural spinal cord compression. Lancet Neurol. 2008; 7:459–466. PMID: 18420159.
Article10. El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L, Reddy KR. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1752–1763. PMID: 18471552.
Article11. Fourney DR, Frangou EM, Ryken TC, Dipaola CP, Shaffrey CI, Berven SH, et al. Spinal instability neoplastic score : an analysis of reliability and validity from the spine oncology study group. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3072–3077. PMID: 21709187.
Article12. Fukutomi M, Yokota M, Chuman H, Harada H, Zaitsu Y, Funakoshi A, et al. Increased incidence of bone metastases in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 13:1083–1088. PMID: 11564960.
Article13. Gerszten PC, Burton SA, Ozhasoglu C, Welch WC. Radiosurgery for spinal metastases : clinical experience in 500 cases from a single institution. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:193–199. PMID: 17224814.14. Gerszten PC, Mendel E, Yamada Y. Radiotherapy and radiosurgery for metastatic spine disease : what are the options, indications, and outcomes? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(22 Suppl):S78–S92. PMID: 19829280.15. He J, Zeng ZC, Tang ZY, Fan J, Zhou J, Zeng MS, et al. Clinical features and prognostic factors in patients with bone metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma receiving external beam radiotherapy. Cancer. 2009; 115:2710–2720. PMID: 19382203.
Article16. Helweg-Larsen S, Sørensen PS, Kreiner S. Prognostic factors in metastatic spinal cord compression : a prospective study using multivariate analysis of variables influencing survival and gait function in 153 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 46:1163–1169. PMID: 10725627.
Article17. Horn EM, Henn JS, Lemole GM Jr, Hott JS, Dickman CA. Thoracoscopic placement of dual-rod instrumentation in thoracic spinal trauma. Neurosurgery. 2004; 54:1150–1153. discussion 1153-1154PMID: 15113470.
Article18. Itshayek E, Yamada J, Bilsky M, Schmidt M, Shaffrey C, Gerszten P, et al. Timing of surgery and radiotherapy in the management of metastatic spine disease : a systematic review. Int J Oncol. 2010; 36:533–544. PMID: 20126972.19. Kim CH, Chung CK, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Surgical outcome of spinal hepatocellular carcinoma metastases. Neurosurgery. 2011; 68:888–896. PMID: 21221023.
Article20. Kim J, Lee SH, Park SJ, Chung SS, Kim ES, Eoh W, et al. Analysis of the predictive role and new proposal for surgical strategies based on the modified Tomita and Tokuhashi scoring systems for spinal metastasis. World J Surg Oncol. 2014; 12:245. PMID: 25085251.
Article21. Klimo P Jr, Thompson CJ, Kestle JR, Schmidt MH. A meta-analysis of surgery versus conventional radiotherapy for the treatment of metastatic spinal epidural disease. Neuro Oncol. 2005; 7:64–76. PMID: 15701283.
Article22. Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Leichner PK, Magid D, Order SE, Siegelman SS. Skeletal metastases from hepatoma : frequency, distribution, and radiographic features. Radiology. 1986; 160:175–178. PMID: 3012630.
Article23. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008; 48:1312–1327. PMID: 18821591.
Article24. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–390. PMID: 18650514.
Article25. Maranzano E, Latini P. Effectiveness of radiation therapy without surgery in metastatic spinal cord compression : final results from a prospective trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995; 32:959–967. PMID: 7607970.
Article26. Okazaki N, Yoshino M, Yoshida T, Hirohashi S, Kishi K, Shimosato Y. Bone metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1985; 55:1991–1994. PMID: 2983871.
Article27. Park KW, Park JW, Choi JI, Kim TH, Kim SH, Park HS, et al. Survival analysis of 904 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a hepatitis B virus-endemic area. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:467–473. PMID: 17764529.
Article28. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Payne R, Saris S, Kryscio RJ, et al. Direct decompressive surgical resection in the treatment of spinal cord compression caused by metastatic cancer : a randomised trial. Lancet. 2005; 366:643–648. PMID: 16112300.
Article29. Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973; 60:646–649. PMID: 4541913.
Article30. Sohn S, Chung CK. The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in metastasis to the spine. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 51:1–7. PMID: 22396835.
Article31. Tokuhashi Y, Matsuzaki H, Oda H, Oshima M, Ryu J. A revised scoring system for preoperative evaluation of metastatic spine tumor prognosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:2186–2191. PMID: 16205345.
Article32. Tomita K, Kawahara N, Kobayashi T, Yoshida A, Murakami H, Akamaru T. Surgical strategy for spinal metastases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:298–306. PMID: 11224867.
Article33. Tralhão JG, Dagher I, Lino T, Roudié J, Franco D. Treatment of tumour recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Analysis of 97 consecutive patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007; 33:746–751. PMID: 17188454.
Article34. Witham TF, Khavkin YA, Gallia GL, Wolinsky JP, Gokaslan ZL. Surgery insight : current management of epidural spinal cord compression from metastatic spine disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006; 2:87–94. quiz 116PMID: 16932530.
Article35. Yamada Y, Bilsky MH, Lovelock DM, Venkatraman ES, Toner S, Johnson J, et al. High-dose, single-fraction image-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for metastatic spinal lesions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 71:484–490. PMID: 18234445.
Article36. Zhang D, Xu W, Liu T, Yin H, Yang X, Wu Z, et al. Surgery and prognostic factors of patients with epidural spinal cord compression caused by hepatocellular carcinoma metastases : retrospective study of 36 patients in a single center. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:E1090–E1095. PMID: 23632333.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long Term Survival in Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Surgical Resection of Brain Metastasis: A Case Report
- Treatment Strategy for Metastatic Spinal Tumors: A Narrative Review
- Spinal Epidural Metastasis Presenting Atypical Images in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Treatments Other than Sorafenib for Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A Case of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Metastasis to The Spinal Cord