J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Jun;53(6):371-373. 10.3340/jkns.2013.53.6.371.
Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm in a Premature Neonate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Goyang, Korea. cychoi@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2190827
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.6.371
Abstract
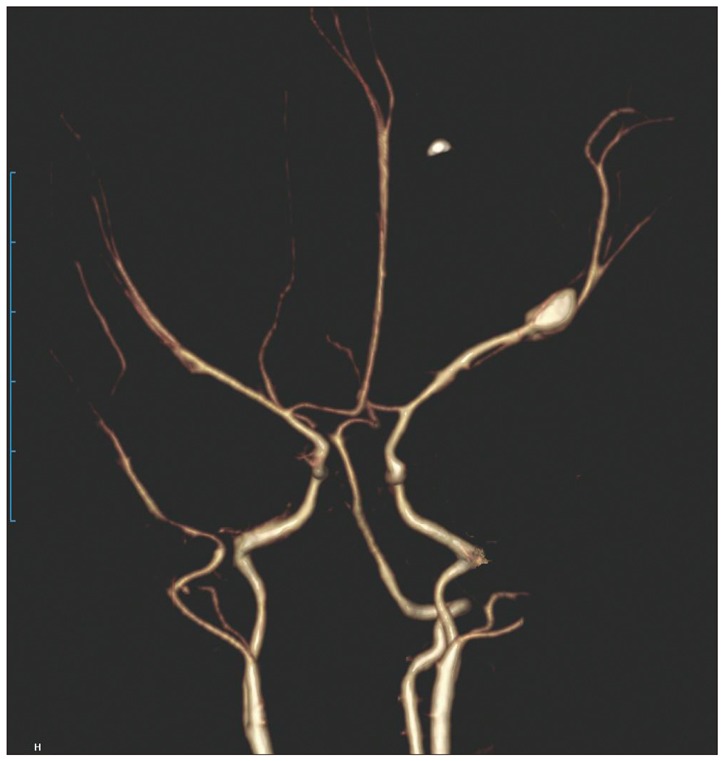
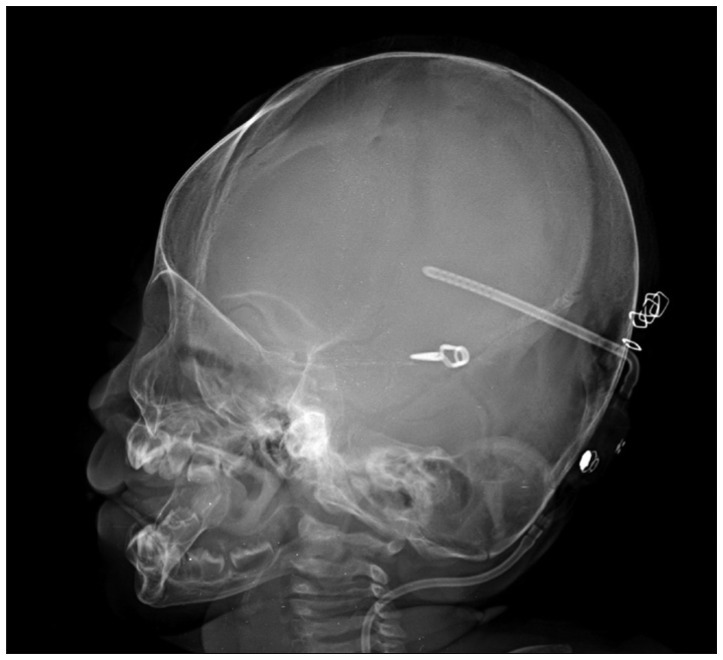
- Intracranial aneurysms in the neonate are very rare and their clinicopathological findings remain unclear. We report a 26-day-old premature neonate who underwent microsurgical clipping on the ruptured middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm successfully with a review of relevant literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Buis DR, van Ouwerkerk WJ, Takahata H, Vandertop WP. Intracranial aneurysms in children under 1 year of age : a systematic review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2006; 22:1395–1409. PMID: 16807726.
Article2. Elgamal EA, Murshid WR, Abu-Rahma HM, Samir D. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the first year of life : case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2004; 20:489–493. PMID: 15029447.3. Herman JM, Rekate HL, Spetzler RF. Pediatric intracranial aneurysms : simple and complex cases. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1991-1992; 17:66–72. discussion 73. PMID: 1815731.
Article4. Huang J, McGirt MJ, Gailloud P, Tamargo RJ. Intracranial aneurysms in the pediatric population : case series and literature review. Surg Neurol. 2005; 63:424–432. discussion 432-433. PMID: 15883063.
Article5. Koroknay-Pál P, Laakso A, Lehto H, Seppä K, Kivisaari R, Hernesniemi J, et al. Long-term excess mortality in pediatric patients with cerebral aneurysms. Stroke. 2012; 43:2091–2096. PMID: 22693125.
Article6. Meyer FB, Sundt TM Jr, Fode NC, Morgan MK, Forbes GS, Mellinger JF. Cerebral aneurysms in childhood and adolescence. J Neurosurg. 1989; 70:420–425. PMID: 2644400.
Article7. Pasqualin A, Mazza C, Cavazzani P, Scienza R, DaPian R. Intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage in children and adolescents. Childs Nerv Syst. 1986; 2:185–190. PMID: 3779680.
Article8. Proust F, Toussaint P, Garniéri J, Hannequin D, Legars D, Houtteville JP, et al. Pediatric cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2001; 94:733–739. PMID: 11354404.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Duplication of the Middle Cerebral Artery: Case Report
- Middle Cerebral Artery Variations Associated with Intracranial Aneurysmal Rupture
- Traumatic Rupture of Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm
- Cerebral Aneurysm in the Long Fenestration at the Middle Portion of M1 Segment
- Middle Cerebral Artery Fenestration Associated with an Aneurysm: Case Report