J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 Jan;51(1):1-7. 10.3340/jkns.2012.51.1.1.
The Role of Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Metastasis to the Spine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. chungc@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2190460
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.51.1.1
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The incidence and prevalence of spinal metastases are increasing, and although the role of radiation therapy in the treatment of metastatic tumors of the spine has been well established, the same cannot be said about the role of stereotactic radiosurgery. Herein, the authors present a systematic review regarding the value of spinal stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of spinal metastasis.
METHODS
A systematic literature search for stereotactic radiosurgery of spinal metastases was undertaken. Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Education (GRADE) working group criteria was used to evaluate the qualities of study datasets.
RESULTS
Thirty-one studies met the study inclusion criteria. Twenty-three studies were of low quality, and 8 were of very low quality according to the GRADE criteria. Stereotactic radiosurgery was reported to be highly effective in reducing pain, regardless of prior treatment. The overall local control rate was approximately 90%. Additional asymptomatic lesions may be treated by stereotactic radiosurgery to avoid further irradiation of neural elements and further bone-marrow suppression. Stereotactic radiosurgery may be preferred in previously irradiated patients when considering the radiation tolerance of the spinal cord. Furthermore, residual tumors after surgery can be safely treated by stereotactic radiosurgery, which decreases the likelihood of repeat surgery and accompanying surgical morbidities. Encompassing one vertebral body above and below the involved vertebrae is unnecessary. Complications associated with stereotactic radiosurgery are generally self-limited and mild.
CONCLUSION
In the management of spinal metastasis, stereotactic radiosurgery appears to provide high rates of tumor control, regardless of histologic diagnosis, and can be used in previously irradiated patients. However, the quality of literature available on the subject is not sufficient.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
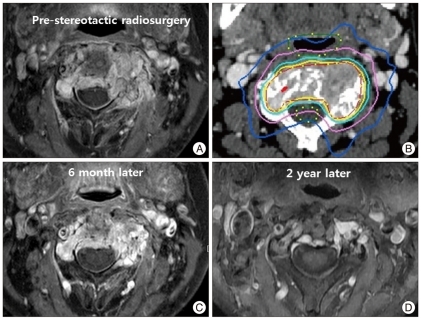
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Survival-Related Factors of Spinal Metastasis with Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Current Surgical Treatment Modalities : A Single Institute Experience
Min Ho Lee, Sun-Ho Lee, Eun-Sang Kim, Whan Eoh, Sung-Soo Chung, Chong-Suh Lee
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(5):448-453. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.5.448.Radiosurgery Compared with External Radiation Therapy as a Primary Treatment in Spine Metastasis from Hepatocellular Carcinoma : A Multicenter, Matched-Pair Study
Seil Sohn, Chun Kee Chung, Moon Jun Sohn, Sung Hwan Kim, Jinhee Kim, Eunjung Park
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016;59(1):37-43. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.1.37.
Reference
-
1. Benzil DL, Saboori M, Mogilner AY, Rocchio R, Moorthy CR. Safety and efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery for tumors of the spine. J Neurosurg. 2004; 101(Suppl 3):413–418. PMID: 15537198.
Article2. Bernstein EF, Sullivan FJ, Mitchell JB, Salomon GD, Glatstein E. Biology of chronic radiation effect on tissues and wound healing. Clin Plast Surg. 1993; 20:435–453. PMID: 8324983.
Article3. Chang EL, Shiu AS, Mendel E, Mathews LA, Mahajan A, Allen PK, et al. Phase I/II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastasis and its pattern of failure. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 7:151–160. PMID: 17688054.
Article4. Choi CY, Adler JR, Gibbs IC, Chang SD, Jackson PS, Minn AY, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of spinal metastases recurring in close proximity to previously irradiated spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 78:499–506. PMID: 20133079.
Article5. De Salles AA, Pedroso AG, Medin P, Agazaryan N, Solberg T, Cabatan-Awang C, et al. Spinal lesions treated with Novalis shaped beam intensity-modulated radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy. J Neurosurg. 2004; 101(Suppl 3):435–440. PMID: 15537201.
Article6. Degen JW, Gagnon GJ, Voyadzis JM, McRae DA, Lunsden M, Dieterich S, et al. CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of spinal tumors for pain control and quality of life. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 2:540–549. PMID: 15945428.
Article7. Faul CM, Flickinger JC. The use of radiation in the management of spinal metastases. J Neurooncol. 1995; 23:149–161. PMID: 7643149.
Article8. Gagnon GJ, Henderson FC, Gehan EA, Sanford D, Collins BT, Moulds JC, et al. Cyberknife radiosurgery for breast cancer spine metastases : a matched-pair analysis. Cancer. 2007; 110:1796–1802. PMID: 17786939.
Article9. Gagnon GJ, Nasr NM, Liao JJ, Molzahn I, Marsh D, McRae D, et al. Treatment of spinal tumors using cyberknife fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery : pain and quality-of-life assessment after treatment in 200 patients. Neurosurgery. 2009; 64:297–306. discussion 306-307. PMID: 19057426.10. Gerszten PC, Burton SA, Ozhasoglu C, Vogel WJ, Welch WC, Baar J, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for spinal metastases from renal cell carcinoma. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 3:288–295. PMID: 16266070.
Article11. Gerszten PC, Burton SA, Ozhasoglu C, Welch WC. Radiosurgery for spinal metastases : clinical experience in 500 cases from a single institution. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:193–199. PMID: 17224814.12. Gerszten PC, Mendel E, Yamada Y. Radiotherapy and radiosurgery for metastatic spine disease : what are the options, indications, and outcomes? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:S78–S92. PMID: 19829280.13. Gerszten PC, Monaco EA 3rd. Complete percutaneous treatment of vertebral body tumors causing spinal canal compromise using a transpedicular cavitation, cement augmentation, and radiosurgical technique. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 27:E9. PMID: 19951062.
Article14. Gerszten PC, Novotny J Jr, Quader M, Dewald VC, Flickinger JC. Prospective evaluation of a dedicated spine radiosurgery program using the Elekta Synergy S system. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113(Suppl):236–241. PMID: 21121807.
Article15. Gibbs IC. Frameless image-guided intracranial and extracranial radiosurgery using the Cyberknife robotic system. Cancer Radiother. 2006; 10:283–287. PMID: 16859948.
Article16. Gibbs IC, Kamnerdsupaphon P, Ryu MR, Dodd R, Kiernan M, Chang SD, et al. Image-guided robotic radiosurgery for spinal metastases. Radiother Oncol. 2007; 82:185–190. PMID: 17257702.
Article17. Gibbs IC, Patil C, Gerszten PC, Adler JR Jr, Burton SA. Delayed radiation-induced myelopathy after spinal radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2009; 64:A67–A72. PMID: 19165076.
Article18. Haley ML, Gerszten PC, Heron DE, Chang YF, Atteberry DS, Burton SA. Efficacy and cost-effectiveness analysis of external beam and stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of spine metastases : a matched-pair analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14:537–542. PMID: 21314284.
Article19. Hamilton AJ, Lulu BA, Fosmire H, Stea B, Cassady JR. Preliminary clinical experience with linear accelerator-based spinal stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:311–319. PMID: 7731511.
Article20. Harel R, Angelov L. Spine metastases : current treatments and future directions. Eur J Cancer. 2010; 46:2696–2707. PMID: 20627705.21. Hayat MJ, Howlader N, Reichman ME, Edwards BK. Cancer statistics, trends, and multiple primary cancer analyses from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Oncologist. 2007; 12:20–37. PMID: 17227898.
Article22. Heidecke V, Rainov NG, Burkert W. Results and outcome of neurosurgical treatment for extradural metastases in the cervical spine. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003; 145:873–880. discussion 880-881. PMID: 14577009.
Article23. Kim YH, Fayos JV. Radiation tolerance of the cervical spinal cord. Radiology. 1981; 139:473–478. PMID: 7220892.
Article24. Levine AM, Coleman C, Horasek S. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of primary sarcomas and sarcoma metastases of the spine. Neurosurgery. 2009; 64:A54–A59. PMID: 19165074.
Article25. McPhee IB, Williams RP, Swanson CE. Factors influencing wound healing after surgery for metastatic disease of the spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23:726–732. discussion 732-733. PMID: 9549795.
Article26. Nelson JW, Yoo DS, Sampson JH, Isaacs RE, Larrier NA, Marks LB, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for lesions of the spine and paraspinal regions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 73:1369–1375. PMID: 19004569.
Article27. Ortiz Gómez JA. The incidence of vertebral body metastases. Int Orthop. 1995; 19:309–311. PMID: 8567140.28. Rock JP, Ryu S, Shukairy MS, Yin FF, Sharif A, Schreiber F, et al. Postoperative radiosurgery for malignant spinal tumors. Neurosurgery. 2006; 58:891–898. discussion 891-898. PMID: 16639323.
Article29. Ryu S, Fang Yin F, Rock J, Zhu J, Chu A, Kagan E, et al. Image-guided and intensity-modulated radiosurgery for patients with spinal metastasis. Cancer. 2003; 97:2013–2018. PMID: 12673732.
Article30. Ryu S, Jin JY, Jin R, Rock J, Ajlouni M, Movsas B, et al. Partial volume tolerance of the spinal cord and complications of single-dose radiosurgery. Cancer. 2007; 109:628–636. PMID: 17167762.
Article31. Ryu S, Jin R, Jin JY, Chen Q, Rock J, Anderson J, et al. Pain control by image-guided radiosurgery for solitary spinal metastasis. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2008; 35:292–298. PMID: 18215498.
Article32. Ryu S, Rock J, Jain R, Lu M, Anderson J, Jin JY, et al. Radiosurgical decompression of metastatic epidural compression. Cancer. 2010; 116:2250–2257. PMID: 20209611.
Article33. Ryu S, Rock J, Rosenblum M, Kim JH. Patterns of failure after single-dose radiosurgery for spinal metastasis. J Neurosurg. 2004; 101(Suppl 3):402–405. PMID: 15537196.
Article34. Sahgal A, Ames C, Chou D, Ma L, Huang K, Xu W, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy is effective salvage therapy for patients with prior radiation of spinal metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 74:723–731. PMID: 19095374.
Article35. Schünemann HJ, Jaeschke R, Cook DJ, Bria WF, El-Solh AA, Ernst A, et al. An official ATS statement : grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in ATS guidelines and recommendations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006; 174:605–614. PMID: 16931644.
Article36. Sheehan JP, Shaffrey CI, Schlesinger D, Williams BJ, Arlet V, Larner J. Radiosurgery in the treatment of spinal metastases : tumor control, survival, and quality of life after helical tomotherapy. Neurosurgery. 2009; 65:1052–1061. discussion 1061-1062. PMID: 19934964.37. Sundaresan N, Digiacinto GV, Hughes JE, Cafferty M, Vallejo A. Treatment of neoplastic spinal cord compression : results of a prospective study. Neurosurgery. 1991; 29:645–650. PMID: 1961391.
Article38. Teh BS, Paulino AC, Lu HH, Chiu JK, Richardson S, Chiang S, et al. Versatility of the Novalis system to deliver image-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for various anatomical sites. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2007; 6:347–354. PMID: 17668943.
Article39. Tibbs MK. Wound healing following radiation therapy : a review. Radiother Oncol. 1997; 42:99–106. PMID: 9106919.40. Tsai JT, Lin JW, Chiu WT, Chu WC. Assessment of image-guided CyberKnife radiosurgery for metastatic spine tumors. J Neurooncol. 2009; 94:119–127. PMID: 19255725.
Article41. Wong DA, Fornasier VL, MacNab I. Spinal metastases : the obvious, the occult, and the impostors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990; 15:1–4. PMID: 2326692.42. Wowra B, Zausinger S, Drexler C, Kufeld M, Muacevic A, Staehler M, et al. CyberKnife radiosurgery for malignant spinal tumors : characterization of well-suited patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:2929–2934. PMID: 19092627.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Contemporary treatment with radiosurgery for spine metastasis and spinal cord compression in 2015
- Stereotactic body radiotherapy for solitary spine metastasis
- Review of Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Intramedullary Spinal Lesions
- The mixed era of stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy
- Characteristics and Treatments of Large Cystic Brain Metastasis: Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Aspiration