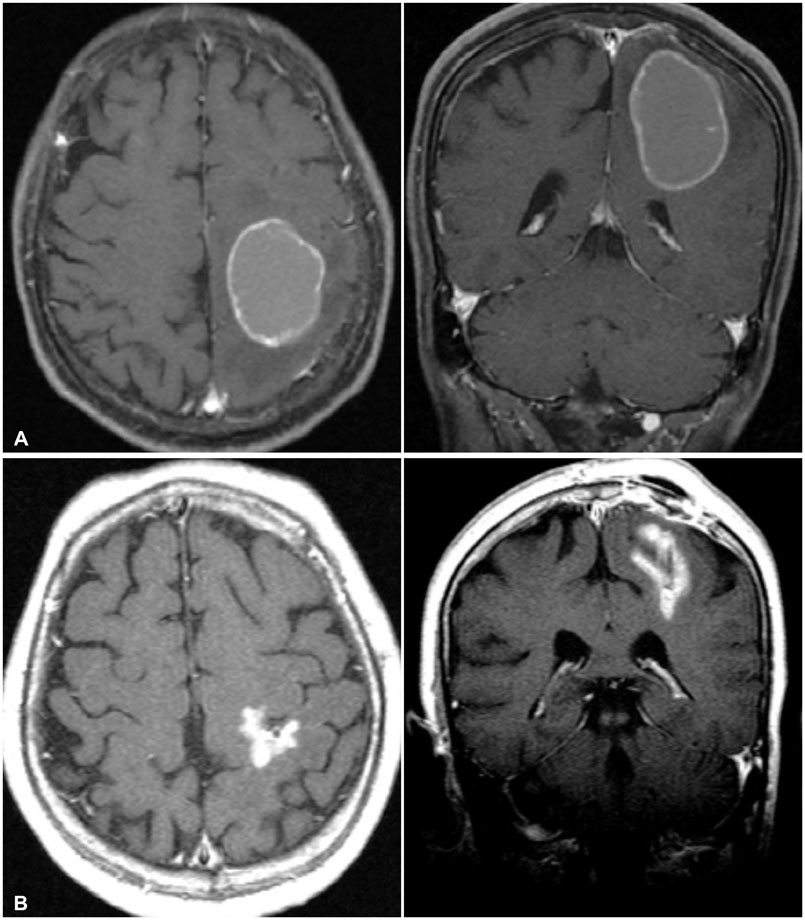
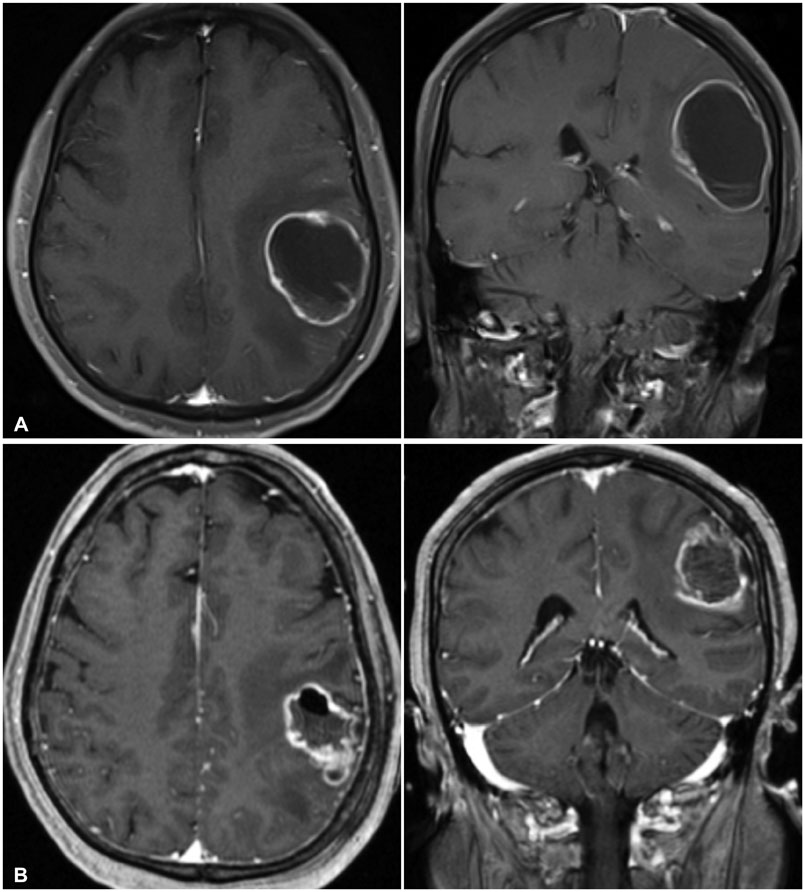
Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2015 Apr;3(1):1-7. 10.14791/btrt.2015.3.1.1.
Characteristics and Treatments of Large Cystic Brain Metastasis: Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Aspiration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA. iyang@mednet.ucla.edu
- 3Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
- 4Department of Radiation Oncology, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
- KMID: 1882004
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2015.3.1.1
Abstract
- Brain metastasis represents one of the most common causes of intracranial tumors in adults, and the incidence of brain metastasis continues to rise due to the increasing survival of cancer patients. Yet, the development of cystic brain metastasis remains a relatively rare occurrence. In this review, we describe the characteristics of cystic brain metastasis and evaluate the combined use of stereotactic aspiration and radiosurgery in treating large cystic brain metastasis. The results of several studies show that stereotactic radiosurgery produces comparable local tumor control and survival rates as other surgery protocols. When the size of the tumor interferes with radiosurgery, stereotactic aspiration of the metastasis should be considered to reduce the target volume as well as decreasing the chance of radiation induced necrosis and providing symptomatic relief from mass effect. The combined use of stereotactic aspiration and radiosurgery has strong implications in improving patient outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Patchell RA. The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev. 2003; 29:533–540.
Article2. Patchell RA, Regine WF. The rationale for adjuvant whole brain radiation therapy with radiosurgery in the treatment of single brain metastases. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2003; 2:111–115.
Article3. Wen PY, Loeffler LS. Management of brain metastases. Oncology. 1999; 13:941–954.4. Hazuka MB, Burleson WD, Stroud DN, Leonard CE, Lillehei KO, Kinzie JJ. Multiple brain metastases are associated with poor survival in patients treated with surgery and radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1993; 11:369–373.
Article5. Lagerwaard FJ, Levendag PC, Nowak PJ, Eijkenboom WM, Hanssens PE, Schmitz PI. Identification of prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases: a review of 1292 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:795–803.
Article6. Markesbery WR, Brooks WH, Gupta GD, Young AB. Treatment for patients with cerebral metastases. Arch Neurol. 1978; 35:754–756.
Article7. Andrews RJ, Gluck DS, Konchingeri RH. Surgical resection of brain metastases from lung cancer. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996; 138:382–389.
Article8. Hossmann KA. Development and resolution of ischemic brain swelling. Wien, New York: Springer-Verlag;1976. p. 249–258.9. Cumings JN. The chemistry of cerebral cysts. Brain. 1950; 73:244–250.
Article10. Gardner WJ, Collis JS Jr, Lewis LA. Cystic brain tumors and the blood-brain barrier. Comparison of protein fractions in cyst fluids and sera. Arch Neurol. 1963; 8:291–298.11. Alexander E 3rd, Moriarty TM, Davis RB, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the definitive, noninvasive treatment of brain metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995; 87:34–40.
Article12. Boyd TS, Mehta MP. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Oncology (Williston Park). 1999; 13:1397–1409.13. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, et al. A multi-institutional experience with stereotactic radiosurgery for solitary brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994; 28:797–802.
Article14. Gerosa M, Nicolato A, Foroni R, et al. Gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases: a primary therapeutic option. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:5 Suppl. 515–524.
Article15. Loeffler JS, Barker FG, Chapman PH. Role of radiosurgery in the management of central nervous system metastases. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999; 43:S11–S14.
Article16. Mehta M, Noyes W, Craig B, et al. A cost-effectiveness and cost-utility analysis of radiosurgery vs. resection for single-brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997; 39:445–454.
Article17. Nakagawa K, Tago M, Terahara A, et al. A single institutional outcome analysis of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for single or multiple brain metastases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2000; 102:227–232.
Article18. O'Neill BP, Iturria NJ, Link MJ, Pollock BE, Ballman KV, O'Fallon JR. A comparison of surgical resection and stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of solitary brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 55:1169–1176.19. Franzin A, Vimercati A, Picozzi P, et al. Stereotactic drainage and Gamma Knife radiosurgery of cystic brain metastasis. J Neurosurg. 2008; 109:259–267.
Article20. Reda WA, Hay AA, Ganz JC. A planned combined stereotactic approach for cystic intracranial tumors. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:5 Suppl. 610–612.
Article21. Liu X, Yu Q, Zhang Z, et al. Same-day stereotactic aspiration and Gamma Knife surgery for cystic intracranial tumors. J Neurosurg. 2012; 117:Suppl. 45–48.
Article22. Flickinger JC. Radiotherapy and radiosurgical management of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep. 2001; 3:484–489.
Article23. Kim MS, Lee SI, Sim SH. Brain tumors with cysts treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery: is microsurgery indicated. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1999; 72:Suppl 1. 38–44.
Article24. Niranjan A, Witham T, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. The role of stereotactic cyst aspiration for glial and metastatic brain tumors. Can J Neurol Sci. 2000; 27:229–235.
Article25. Uchino M, Nagao T, Seiki Y, Shibata I, Terao H, Kaneko I. [Radiosurgery for cystic metastatic brain tumor]. No Shinkei Geka. 2000; 28:417–421.26. Ebinu JO, Lwu S, Monsalves E, et al. Gamma knife radiosurgery for the treatment of cystic cerebral metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013; 85:667–671.
Article27. Park WH, Jang IS, Kim CJ, Kwon do H. Gamma knife radiosurgery after stereotactic aspiration for large cystic brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:360–364.
Article28. Higuchi F, Kawamoto S, Abe Y, Kim P, Ueki K. Effectiveness of a 1-day aspiration plus Gamma Knife surgery procedure for metastatic brain tumor with a cystic component. J Neurosurg. 2012; 117:17–22.
Article29. Willis RA. Secondary tumors. In : Minckler J, editor. Pathology of the Nervous System. New York: McGraw-Hill;1971. p. 2178–2196.30. Yamanaka Y, Shuto T, Kato Y, et al. Ommaya reservoir placement followed by Gamma Knife surgery for large cystic metastatic brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:79–81.
Article31. Schoeggl A, Kitz K, Ertl A, Reddy M, Bavinzski G, Schneider B. Prognostic factor analysis for multiple brain metastases after gamma knife radiosurgery: results in 97 patients. J Neurooncol. 1999; 42:169–175.32. Sneed PK, Lamborn KR, Forstner JM, et al. Radiosurgery for brain metastases: is whole brain radiotherapy necessary. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:549–558.
Article33. Petrovich Z, Yu C, Giannotta SL, O'Day S, Apuzzo ML. Survival and pattern of failure in brain metastasis treated with stereotactic gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:5 Suppl. 499–506.
Article34. Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, et al. Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 47:291–298.
Article35. Lunsford LD, Martinez AJ. Stereotactic exploration of the brain in the era of computed tomography. Surg Neurol. 1984; 22:222–230.
Article36. Bernstein M, Parrent AG. Complications of CT-guided stereotactic biopsy of intra-axial brain lesions. J Neurosurg. 1994; 81:165–168.
Article37. Werner-Wasik M, Rudoler S, Preston PE, et al. Immediate side effects of stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:299–304.
Article38. Kondziolka D, Firlik AD, Lunsford LD. Complications of stereotactic brain surgery. Neurol Clin. 1998; 16:35–54.
Article39. Minniti G, Clarke E, Lanzetta G, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat Oncol. 2011; 6:48.
Article40. Barloon TJ, Yuh WT, Sato Y, Sickels WJ. Frontal lobe implantation of craniopharyngioma by repeated needle aspirations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988; 9:406–407.41. Karlsson B, Ericson K, Kihlström L, Grane P. Tumor seeding following stereotactic biopsy of brain metastases. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1997; 87:327–330.42. Perrin RG, Bernstein M. Iatrogenic seeding of anaplastic astrocytoma following stereotactic biopsy. J Neurooncol. 1998; 36:243–246.43. Rosenfeld JV, Murphy MA, Chow CW. Implantation metastasis of pineoblastoma after stereotactic biopsy. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1990; 73:287–290.44. Tendulkar RD, Liu SW, Barnett GH, et al. RPA classification has prognostic significance for surgically resected single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 66:810–817.
Article45. Lutterbach J, Cyron D, Henne K, Ostertag CB. Radiosurgery followed by planned observation in patients with one to three brain metastases. Neurosurgery. 2003; 52:1066–1073.
Article46. Sneed PK, Suh JH, Goetsch SJ, et al. A multi-institutional review of radiosurgery alone vs. radiosurgery with whole brain radiotherapy as the initial management of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 53:519–526.
Article47. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:494–500.
Article48. Mandell L, Hilaris B, Sullivan M, et al. The treatment of single brain metastasis from non-oat cell lung carcinoma. Surgery and radiation versus radiation therapy alone. Cancer. 1986; 58:641–649.
Article49. Muacevic A, Kreth FW, Horstmann GA, et al. Surgery and radiotherapy compared with gamma knife radiosurgery in the treatment of solitary cerebral metastases of small diameter. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91:35–43.
Article50. Lohr F, Pirzkall A, Hof H, Fleckenstein K, Debus J. Adjuvant treatment of brain metastases. Semin Surg Oncol. 2001; 20:50–56.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery after Stereotactic Aspiration for Large Cystic Brain Metastases
- The mixed era of stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumor
- Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases Using the Novalis Tx® System
- The Role of Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Metastasis to the Spine