J Korean Med Assoc.
2007 Jul;50(7):573-581. 10.5124/jkma.2007.50.7.573.
Trends of Recent Food-Borne Disease Outbreaks in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Communicable Disease Control Team, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Korea. kjw9925@mohw.go.kr, cheolheon@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2184867
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2007.50.7.573
Abstract
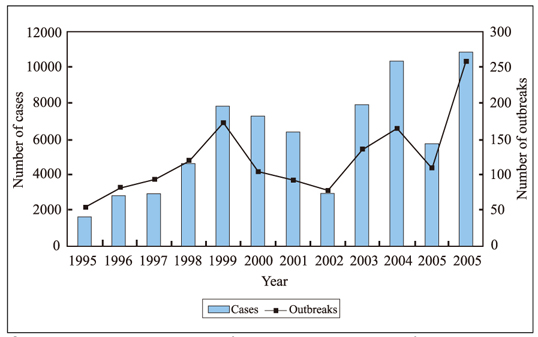
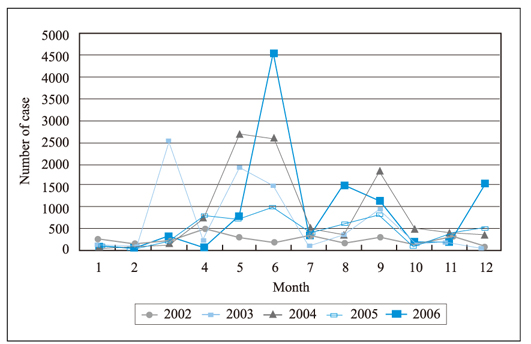
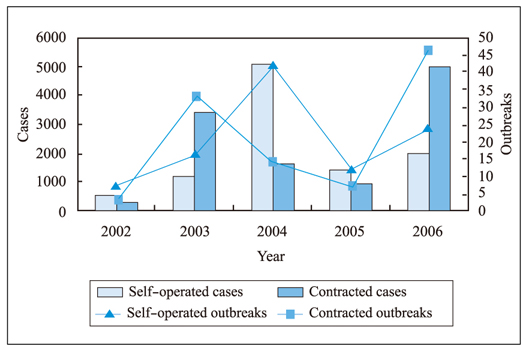
- This report summarizes recent food-borne disease outbreaks in Korea by month, pathogen, dining place, and scale. In particular, imported cases are described separately. Sources of information include surveillance and statistic data and reports of KCDC/MOHW and KFDA, and scientific journals from home and abroad. Investigation results indicate that reports of food-borne disease cases and imported cases are increasing continuously in Korea. Many cases still occur in May and June, and new cases increasingly occur in December. Other new characteristic of the recent outbreaks is that they are increasingly attributable to pathogens such as Norovirus and EHEC. Outbreaks at mass meal preparation facilities represent a large proportion of cases, mainly due to the increase in the possibilities for common exposure, pathogen mobility, meat consumption, and the detection itself. To address this health problem, water and sewer service must be widely provided, food materials must be handled thoroughly, and good personal hygiene including proper hand washing must be further underscored. As a responsible agency, KCDC will also need to conduct thorough epidemiological investigations, establish an efficient surveillance system, work in a prompt manner, and enhance partnerships with various agencies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Trends in Childhood Bacterial Infectious Diseases in the Republic of Korea
Young June Choe, Hoan Jong Lee
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(6):468-473. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.6.468.Characteristics and Clinical Correlations of
Staphylococcus aureus Discovered in Stools from Children Hospitalized at a Secondary Hospital
Eun Hye Shin, Byung Wook Eun, Young Min An, Mi Ok Song
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2018;25(2):61-71. doi: 10.14776/piv.2018.25.e1.
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Basic food safety for health workers. 1999. Geneva: World Health Organization;10–12. (WHO document WHO/SDE/PHE/FOS/99.1).2. Hall GV, D'Souza RM, Kirk MD. Foodborne disease in the new millennium: out of the frying pan and into the fire? Med J Aust. 2002. 12. 02-16. 177:614–618.
Article5. Lee JK. Food poisoning and contamination related to institutional foodservices. Korean J Community Nutr. 1999. 4:632–639.6. Jee YM. Norovirus food poisoning and laboratory surveillance for viral gastroenteritis in korea. Health and Welfare Policy Forum. 2006. 118:26–34.7. Kwak RS. Recommendations for the improvement of national food poisoning control system. Health and Welfare Policy Forum. 2002. 68:49–58.8. Jeong JS, Choi JK, Jeong IS, Paek KR, In HK, Park KD. A nationwide survey on the hand washing behavior and awareness. J Prev Med Public Health. 2007. 40:197–204.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Emerging Pathogens and Vehicles of Food- and Water-borne Disease Outbreaks in Korea, 2007–2012
- Characteristics and related factors of waterborne and foodborne infectious disease outbreaks before and after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic (2017–2021) in the Republic of Korea: a descriptive study
- Trends in recent waterborne and foodborne disease outbreaks in South Korea, 2015–2019
- Enteropathogenic
Escherichia coli Outbreak and its Incubation Period: Is it Short or Long? - Trends in Water- and Foodborne Disease Outbreaks in Korea, 2007–2009