Blood Res.
2014 Mar;49(1):36-41. 10.5045/br.2014.49.1.36.
Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: a single-center experience in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. csuh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Gangneung Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2172821
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2014.49.1.36
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBL) is a distinct subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which has no consensus for its ideal treatment or prognosis.
METHODS
We reviewed the clinicopathologic features and clinical outcomes of 25 PMBL cases diagnosed at a single institution between 1993 and 2009 and compared them with 588 cases of non-mediastinal, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL, control group) diagnosed during the same period.
RESULTS
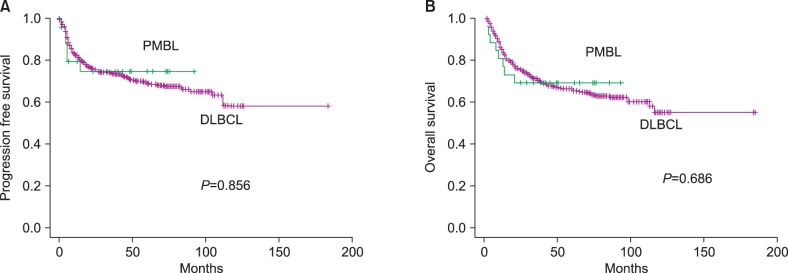
Thirteen (52.0%) PMBL patients had Ann Arbor stage III or IV disease, and 10 (40.0%) had B symptoms. Thirteen (52%) PMBL patients were classified as high-intermediate/high-risk according to the International Prognostic Index. There was a significant prevalence of young (median: 31 years; range, 15-78 years; P<0.001), female (68%; P=0.014) patients in the PMBL group compared to the control group (median: 56 years; range, 15-85 years; 43.2% female). Bulky disease and elevated levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were more frequent in the PMBL group (P<0.001 and P=0.003, respectively). Nineteen (76%) PBML patients achieved complete remission, and 18 were alive at the last follow-up (median: 43 months; range, 1-92 months). There was no difference in the 3-year, overall survival rate (72%, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 54.0-83.0 versus 70.1%, 95% CI, 109.0-126.0; P=0.686) between PMBL and control patients, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Compared to patients with non-mediastinal DLBCL, Korean patients with PMBL are predominantly young women with bulky disease and high LDH levels but with no significant difference in survival.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J. Lymphoma classification-from controversy to consensus: the R.E.A.L. and WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Ann Oncol. 2000; 11(Suppl 1):3–10. PMID: 10707771.2. Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994; 84:1361–1392. PMID: 8068936.3. Lazzarino M, Orlandi E, Paulli M, et al. Treatment outcome and prognostic factors for primary mediastinal (thymic) B-cell lymphoma: a multicenter study of 106 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1997; 15:1646–1653. PMID: 9193365.
Article4. Cazals-Hatem D, Lepage E, Brice P, et al. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. A clinicopathologic study of 141 cases compared with 916 nonmediastinal large B-cell lymphomas, a GELA ("Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte") study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996; 20:877–888. PMID: 8669537.5. van Besien K, Kelta M, Bahaguna P. Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma: a review of pathology and management. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:1855–1864. PMID: 11251018.
Article6. Savage KJ, Al-Rajhi N, Voss N, et al. Favorable outcome of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma in a single institution: the British Columbia experience. Ann Oncol. 2006; 17:123–130. PMID: 16236753.
Article7. Hamlin PA, Portlock CS, Straus DJ, et al. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: optimal therapy and prognostic factor analysis in 141 consecutive patients treated at Memorial Sloan Kettering from 1980 to 1999. Br J Haematol. 2005; 130:691–699. PMID: 16115124.
Article8. Todeschini G, Secchi S, Morra E, et al. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMLBCL): long-term results from a retrospective multicentre Italian experience in 138 patients treated with CHOP or MACOP-B/VACOP-B. Br J Cancer. 2004; 90:372–376. PMID: 14735179.
Article9. Lazzarino M, Orlandi E, Paulli M, et al. Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma with sclerosis: an aggressive tumor with distinctive clinical and pathologic features. J Clin Oncol. 1993; 11:2306–2313. PMID: 8246020.
Article10. Lichtenstein AK, Levine A, Taylor CR, et al. Primary mediastinal lymphoma in adults. Am J Med. 1980; 68:509–514. PMID: 6892753.
Article11. Trump DL, Mann RB. Diffuse large cell and undifferentiated lymphomas with prominent mediastinal involvement. Cancer. 1982; 50:277–282. PMID: 7044520.12. Todeschini G, Ambrosetti A, Meneghini V, et al. Mediastinal large-B-cell lymphoma with sclerosis: a clinical study of 21 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1990; 8:804–808. PMID: 1692089.
Article13. Haioun C, Gaulard P, Roudot-Thoraval F, et al. Mediastinal diffuse large-cell lymphoma with sclerosis: a condition with a poor prognosis. Am J Clin Oncol. 1989; 12:425–429. PMID: 2801603.14. Kirn D, Mauch P, Shaffer K, et al. Large-cell and immunoblastic lymphoma of the mediastinum: prognostic features and treatment outcome in 57 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1993; 11:1336–1343. PMID: 8315431.
Article15. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC;2008. p. 250–251.16. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:987–994. PMID: 8141877.17. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:579–586. PMID: 17242396.18. Sekiguchi N, Nishimoto J, Tanimoto K, et al. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: a single-institution clinical study in Japan. Int J Hematol. 2004; 79:465–471. PMID: 15239397.
Article19. Anderson JR, Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. Epidemiology of the non-Hodgkins lymphomas: distributions of the major subtypes differ by geographic locations. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. Ann Oncol. 1998; 9:717–720. PMID: 9739436.20. Zinzani PL, Martelli M, Bertini M, et al. Induction chemotherapy strategies for primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma with sclerosis: a retrospective multinational study on 426 previously untreated patients. Haematologica. 2002; 87:1258–1264. PMID: 12495899.21. Rodriguez J, Conde E, Gutierrez A, et al. Primary mediastinal large cell lymphoma (PMBL): frontline treatment with autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). The GEL-TAMO experience. Hematol Oncol. 2008; 26:171–178. PMID: 18432630.22. Abou-Elella AA, Weisenburger DD, Vose JM, et al. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of 43 patients from the Nebraska Lymphoma Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:784–790. PMID: 10071267.
Article23. Dunleavy K, Pittaluga S, Shovlin M, et al. Untreated primary mediastinal B-cell (PMBL) and mediastinal grey zone (MGZL) lymphomas: comparison of biological features and clinical outcome following DA-EPOCH-R without radiation. Ann Oncol. 2011; 22(Suppl 4):134(abst 150).24. Ahn HK, Kim SJ, Yun J, et al. Improved treatment outcome of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma after introduction of rituximab in Korean patients. Int J Hematol. 2010; 91:456–463. PMID: 20198460.
Article25. Tai WM, Quah D, Yap SP, et al. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: optimal therapy and prognostic factors in 41 consecutive Asian patients. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011; 52:604–612. PMID: 21261504.
Article26. Savage KJ, Yenson PR, Shenkier T, et al. The outcome of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) in the R-CHOP treatment era. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 2012; 120(Suppl):abst 303.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rare Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Childhood; A Single Center Experience
- Dermatofibroma in Patient with Relapsing Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma on the Dorsum of the Hand
- A Case of Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- Primary Cutaneous T-cell/histiocyte-rich B-cell Lymphoma