Ann Dermatol.
2010 Feb;22(1):102-105. 10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.102.
A Case of Hydroxychloroquine Induced Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Confirmed by Accidental Oral Provocation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. schul@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2172052
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.102
Abstract
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a clinical reaction pattern that is principally drug induced and this is characterized by acute, nonfollicular sterile pustules on a background of edematous erythema. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) has been widely used to treat rheumatic and dermatologic diseases and HCQ has been reported to be an uncommon cause of AGEP. A 38-year-old woman with a 1-year history of dermatomyositis and polyarthralgia was treated with HCQ due to a lack of response to a previous medication. Three weeks after starting HCQ therapy, the pustular skin lesion developed and then this resolved after the HCQ was withdrawn and steroid treatment was started. A similar pustular eruption developed after HCQ was accidentally readministered.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
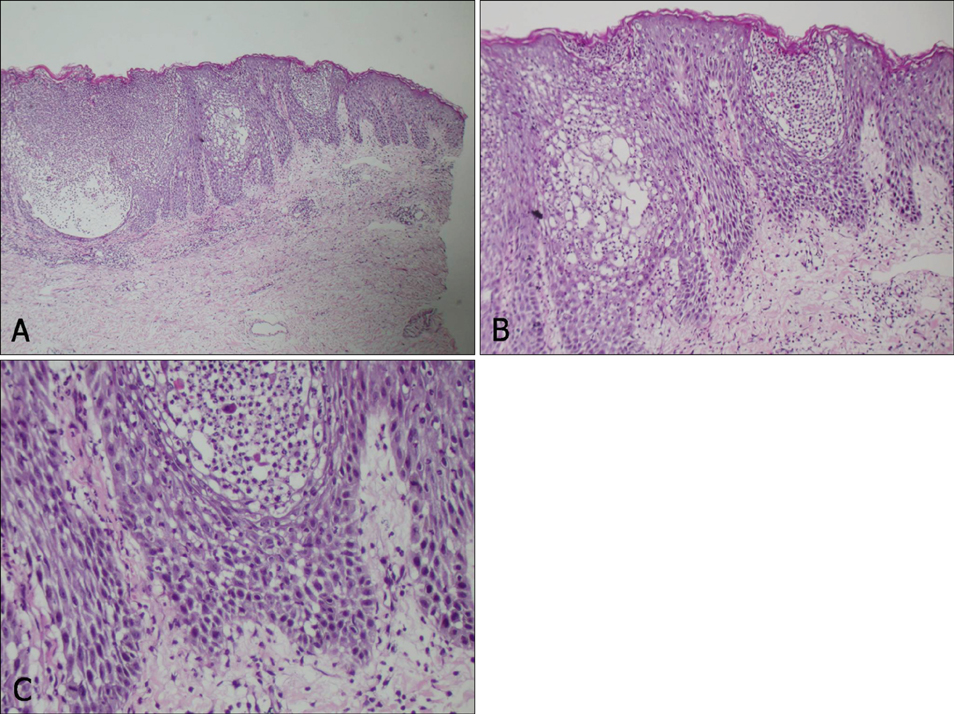
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Successful Treatment of Hydroxychloroquine-Induced Recalcitrant Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Cyclosporine: Case Report and Literature Review
Başak Yalçın, Seray Çakmak, Betül Yıldırım
Ann Dermatol. 2015;27(4):431-434. doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.4.431.Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to hydroxychloroquine in a rheumatoid arthritis patient
Hye Jin Lim, Ji Hye Jung, Min Jeoung Kim, Jeoung Min Kim, Hye Ran Kang, Yoon Kyung Song, Jin Wuk Hur, Sang-Hoon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(2):176-178. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.2.176.
Reference
-
1. Arroyo MP, Heller P, Pomeranz MK. Generalized pustules in a healthy woman. J Drugs Dermatol. 2002. 1:63–65.2. Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)--a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001. 28:113–119.
Article3. Paradisi A, Bugatti L, Sisto T, Filosa G, Amerio PL, Capizzi R. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine: three cases and a review of the literature. Clin Ther. 2008. 30:930–940.
Article4. Mackenzie AH. Pharmacologic actions of 4-aminoquinoline compounds. Am J Med. 1983. 75:5–10.
Article5. Choi JH, Sim HS, Jung Y, Lee SK. A case of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine. Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:138–140.6. Baker H, Ryan TJ. Generalized pustular psoriasis. A clinical and epidemiological study of 104 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1968. 80:771–793.7. Beylot C, Bioulac P, Doutre MS. Acute generalized exanthematic pustuloses (four cases). Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1980. 107:37–48.8. Gebhardt M, Lustig A, Bocker T, Wollina U. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): manifestation of drug allergy to propicillin. Contact Dermatitis. 1995. 33:204–205.
Article9. Braun-Falco O, Luderschmidt C, Maciejewski W, Scherer R. Generalized acute pustulosis. An unusual presentation of leukocytoclastic vasculitis. Hautarzt. 1978. 29:371–377.10. Burrows NP, Russell Jones RR. Pustular drug eruptions: a histopathological spectrum. Histopathology. 1993. 22:569–573.
Article11. Plaquenil (hydroxychloroquine sulfate) tablets. Adverse reactions [Internet]. 2006 Oct 5. Bridgewater (NJ): Sanofi;Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/009768s041lbl.pdf.12. Das J, Mandal AC. A study of drug eruptions by provocative tests. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2001. 67:238–239.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Treatment of Hydroxychloroquine-Induced Recalcitrant Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Cyclosporine: Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Induced by Hydroxychloroquine
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Hemodynamic Instability Induced by Ingestion of Lacquer Chicken
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Possibly Induced by Ritodrine
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by terbinafine