Ann Dermatol.
2015 Aug;27(4):431-434. 10.5021/ad.2015.27.4.431.
Successful Treatment of Hydroxychloroquine-Induced Recalcitrant Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Cyclosporine: Case Report and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Yildirim Beyazit University, Ankara, Turkey. yalcinbasak@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Dermatology, Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey.
- KMID: 2171501
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.4.431
Abstract
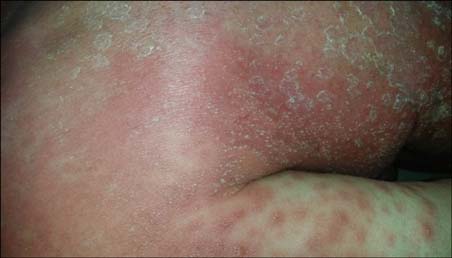
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a cutaneous reaction principally induced by drugs. Spontaneous resolution is observed in most patients. However, severe cases required systemic corticosteroid administration. Hydroxychloroquine, which is used to treat some dermatologic and rheumatologic diseases because of its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, is an uncommon cause of AGEP. A 67-year-old female patient presented with severe AGEP due to hydroxychloroquine treatment. She was recalcitrant to supportive care and systemic corticosteroid treatment butwas successfully treated with cyclosporine. Hydroxychloroquine-induced AGEP occurs in women with underlying rheumatologic diseases, has a longer latent period, and has a severe course usually requiring systemic treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fernando SL. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012; 53:87–92.
Article2. Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)--a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001; 28:113–119.
Article3. Paradisi A, Bugatti L, Sisto T, Filosa G, Amerio PL, Capizzi R. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine: three cases and a review of the literature. Clin Ther. 2008; 30:930–940.
Article4. Assier-Bonnet H, Saada V, Bernier M, Clerici T, Saïag P. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine. Dermatology. 1996; 193:70–71.
Article5. Evans CC, Bergstresser PR. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis precipitated by hydroxychloroquine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004; 50:650–651.
Article6. Martins A, Lopes LC, Paiva Lopes MJ, Rodrigues JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine. Eur J Dermatol. 2006; 16:317–318.7. Lateef A, Tan KB, Lau TC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by hydroxychloroquine. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28:1449–1452.
Article8. Di Lernia V, Grenzi L, Guareschi E, Ricci C. Rapid clearing of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis after administration of ciclosporin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009; 34:e757–e759.
Article9. Park JJ, Yun SJ, Lee JB, Kim SJ, Won YH, Lee SC. A case of hydroxychloroquine induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis confirmed by accidental oral provocation. Ann Dermatol. 2010; 22:102–105.
Article10. Bailey K, McKee D, Wismer J, Shear N. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis induced by hydroxychloroquine: first case report in Canada and review of the literature. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013; 17:414–418.
Article11. Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007; 157:989–996.
Article12. Dehesa L, Abuchar A, Nuno-Gonzalez A, Vitiello M, Kerdel FA. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012; 11:979–987.13. Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Schmid S, Depta JP, Senti G, Bircher A, et al. T-cell involvement in drug-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:1433–1441.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Hydroxychloroquine Induced Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Confirmed by Accidental Oral Provocation
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Possibly Induced by Ritodrine
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Hemodynamic Instability Induced by Ingestion of Lacquer Chicken
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Induced by Hydroxychloroquine
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Diltiazem