Ann Dermatol.
2014 Apr;26(2):241-245. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.241.
Photodynamic Therapy for Bowen's Disease of the Vulva Area
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. dmjj1@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2171662
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.241
Abstract
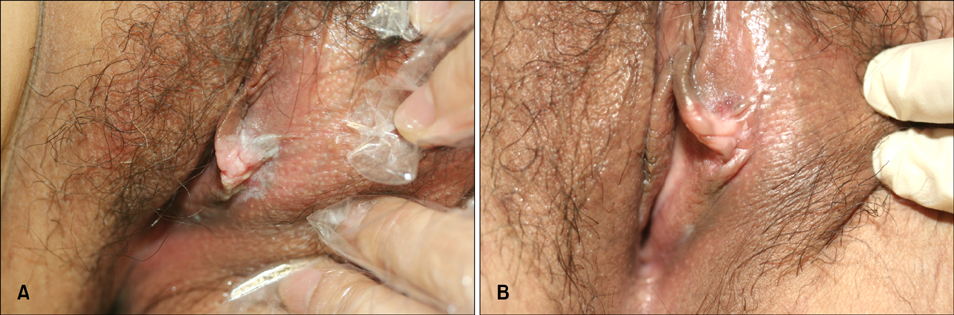
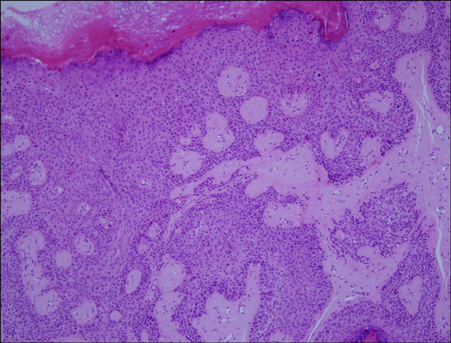
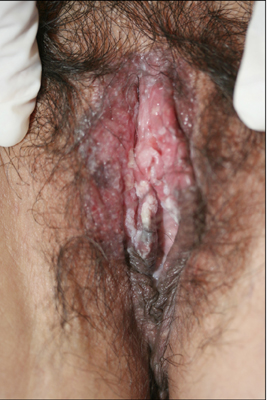
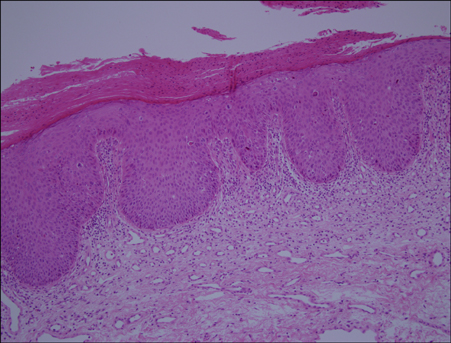
- Bowen's disease is a squamous cell carcinoma in situ and has the potential to progress to a squamous cell carcinoma. The authors treated two female patients (a 39-year-old and a 41-year-old) with Bowen's disease in the vulva area using topical photodynamic therapy (PDT), involving the use of 5-aminolaevulinic acid and a light-emitting diode device. The light was administered at an intensity of 80 mW/cm2 for a dose of 120 J/cm2 biweekly for 6 cycles. The 39-year-old patient showed excellent clinical improvement, but the other patient achieved only a partial response. Even though one patient underwent a total excision 1 year later due to recurrence, both patients were satisfied with the cosmetic outcomes of this therapy and the partial improvement over time. The common side effect of PDT was a stinging sensation. PDT provides a relatively effective and useful alternative treatment for Bowen's disease in the vulva area.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strayer DS, Santa Cruz DJ. Carcinoma in situ of the skin: a review of histopathology. J Cutan Pathol. 1980; 7:244–259.
Article2. Duncan KO, Geisse JK, Leffell DJ. Epithelial precancerous lesions. In : Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2007. p. 1021–1023.3. Svanberg K, Andersson T, Killander D, Wang I, Stenram U, Andersson-Engels S, et al. Photodynamic therapy of nonmelanoma malignant tumours of the skin using topical deltaamino levulinic acid sensitization and laser irradiation. Br J Dermatol. 1994; 130:743–751.
Article4. Fijan S, Hönigsmann H, Ortel B. Photodynamic therapy of epithelial skin tumours using delta-aminolaevulinic acid and desferrioxamine. Br J Dermatol. 1995; 133:282–288.
Article5. Morton CA, Whitehurst C, Moore JV, MacKie RM. Comparison of red and green light in the treatment of Bowen's disease by photodynamic therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 143:767–772.
Article6. Morton CA, Whitehurst C, McColl JH, Moore JV, MacKie RM. Photodynamic therapy for large or multiple patches of Bowen disease and basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 2001; 137:319–324.7. Salim A, Leman JA, McColl JH, Chapman R, Morton CA. Randomized comparison of photodynamic therapy with topical 5-fluorouracil in Bowen's disease. Br J Dermatol. 2003; 148:539–543.
Article8. Britton JE, Goulden V, Stables G, Stringer M, Sheehan-Dare R. Investigation of the use of the pulsed dye laser in the treatment of Bowen's disease using 5-aminolaevulinic acid phototherapy. Br J Dermatol. 2005; 153:780–784.
Article9. Morton C, Horn M, Leman J, Tack B, Bedane C, Tjioe M, et al. Comparison of topical methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy with cryotherapy or fluorouracil for treatment of squamous cell carcinoma in situ: results of a multicenter randomized trial. Arch Dermatol. 2006; 142:729–735.10. de Haas ER, Sterenborg HJ, Neumann HA, Robinson DJ. Response of Bowen disease to ALA-PDT using a single and a 2-fold illumination scheme. Arch Dermatol. 2007; 143:264–265.
Article11. Kim YJ, Kang HY, Lee ES, Kim YC. Photodynamic therapy for treatment of Bowen's disease. Korean J Dermatol. 2007; 45:237–241.12. de Haas ER, de Vijlder HC, Sterenborg HJ, Neumann HA, Robinson DJ. Fractionated aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy provides additional evidence for the use of PDT for non-melanoma skin cancer. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008; 22:426–430.
Article13. Calzavara-Pinton PG, Venturini M, Sala R, Capezzera R, Parrinello G, Specchia C, et al. Methylaminolaevulinatebased photodynamic therapy of Bowen's disease and squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 159:137–144.
Article14. Doffoel-Hantz V, Sparsa A, Marin B, Durox H, Bonnetblanc JM, Bédane C. The value of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of Bowen's disease. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2008; 135:822–827.15. Truchuelo M, Fernández-Guarino M, Fleta B, Alcántara J, Jaén P. Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in Bowen's disease: an observational and descriptive study in 51 lesions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012; 26:868–874.
Article16. López N, Meyer-Gonzalez T, Herrera-Acosta E, Bosch R, Castillo R, Herrera E. Photodynamic therapy in the treatment of extensive Bowen's disease. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012; 23:428–430.
Article17. Oleinick NL, Morris RL, Belichenko I. The role of apoptosis in response to photodynamic therapy: what, where, why, and how. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2002; 1:1–21.
Article18. Calin MA, Diaconeasa A, Savastru D, Tautan M. Photosensitizers and light sources for photodynamic therapy of the Bowen's disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 2011; 303:145–151.
Article19. Halldin CB, Gillstedt M, Paoli J, Wennberg AM, Gonzalez H. Predictors of pain associated with photodynamic therapy: a retrospective study of 658 treatments. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011; 91:545–551.
Article20. Lee SH, Jung BC, Woo MJ, Kim DS, Kim SW. A case of Bowen's disease partially responded to photodynamic therapy. Ann Dermatol. 2002; 14:38–38.
Article