Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Dec;87(6):340-344. 10.4174/astr.2014.87.6.340.
Pancreaticoduodenectomy performed in a patient with situs ambiguous accompanied with isolated levocardia, malrotation, and normal spleen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ushinchoi@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2167092
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.87.6.340
Abstract
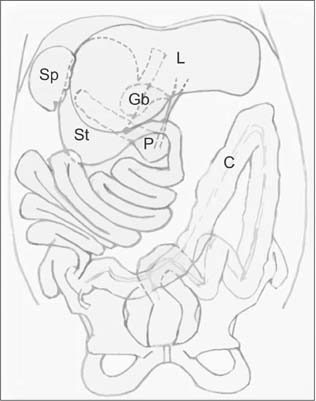
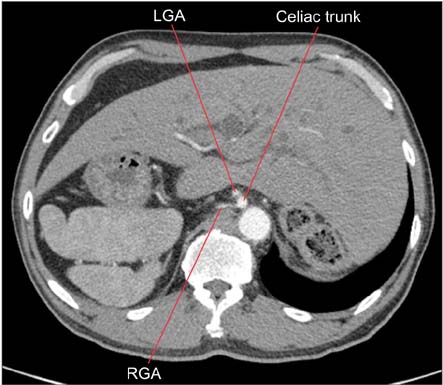
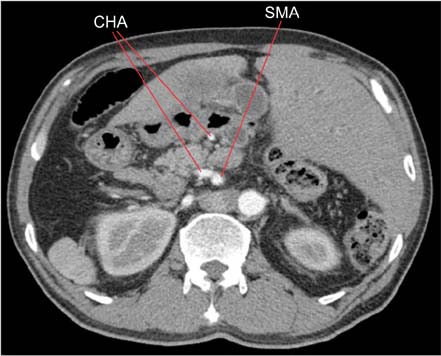
- We report a case of common bile duct (CBD) cancer, successfully managed with pancreaticoduodenectomy, in a patient with isolated levocardia, malrotation, and situs ambiguous (without splenic anomalies). A 59-year-old male patient was referred to Chung-Ang University Hospital with epigastric pain and jaundice. CT and MRI revealed distal CBD cancer without significant lymphadenopathy. Multiple abdominal anatomic anomalies were identified preoperatively, whereas no anatomic anomalies were detected within the chest. The patient had a right-sided stomach and spleen, liver at the midline, several vascular variations around the celiac axis, and intestinal malrotation, but the inferior vena cava and portal vein were normal. A pancreaticoduodenectomy was performed to treat the cancer. The postoperative course was favorable, and the patient was started on combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy 15 days after the surgery. In this case study, we report that pylorus preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy was successful for distal CBD cancer in a patient with rare situs anomalies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fulcher AS, Turner MA. Abdominal manifestations of situs anomalies in adults. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1439–1456.2. Douard R, Feldman A, Bargy F, Loric S, Delmas V. Anomalies of lateralization in man: a case of total situs inversus. Surg Radiol Anat. 2000; 22:293–297.3. Peeters H, Devriendt K. Human laterality disorders. Eur J Med Genet. 2006; 49:349–362.4. Peoples WM, Moller JH, Edwards JE. Polysplenia: a review of 146 cases. Pediatr Cardiol. 1983; 4:129–137.5. Rose V, Izukawa T, Moes CA. Syndromes of asplenia and polysplenia. A review of cardiac and non-cardiac malformations in 60 cases withspecial reference to diagnosis and prognosis. Br Heart J. 1975; 37:840–852.6. Chacko KA, Krishnaswami S, Sukumar IP, Cherian G. Isolated levocardia: two cases with abdominal situs inversus, thoracic situs solitus, and normal circulation. Am Heart J. 1983; 106(1 Pt 1):155–159.7. Beaudoin S, Seror O, Fayad F, Grapin C, Sellier N. A case of malrotation and situs ambiguus. Surg Radiol Anat. 1999; 21:143–145.8. de Reus HD, Heckman J, von der Hal I. A rare combination of congenital disorders in a 5-year-old girl. Levocardia with situs inversus abdominalis and duodenal obstruction caused by malrotation and an intraluminal diverticulum. Tijdschr Gastroenterol. 1969; 12:58–92.9. Budhiraja S, Singh G, Miglani HP, Mitra SK. Neonatal intestinal obstruction with isolated levocardia. J Pediatr Surg. 2000; 35:1115–1116.10. Carriaga MT, Henson DE. Liver, gallbladder, extrahepatic bile ducts, and pancreas. Cancer. 1995; 75:1 Suppl. 171–190.